Abstract
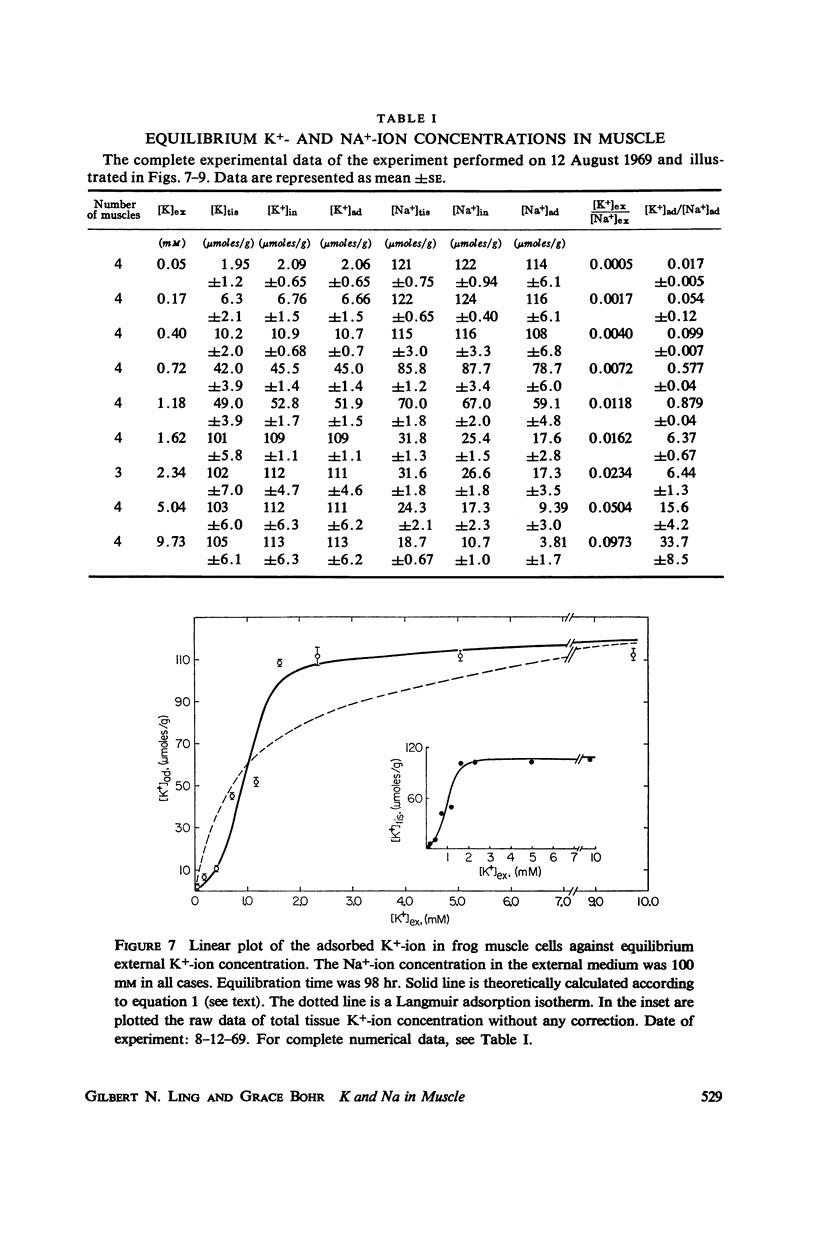
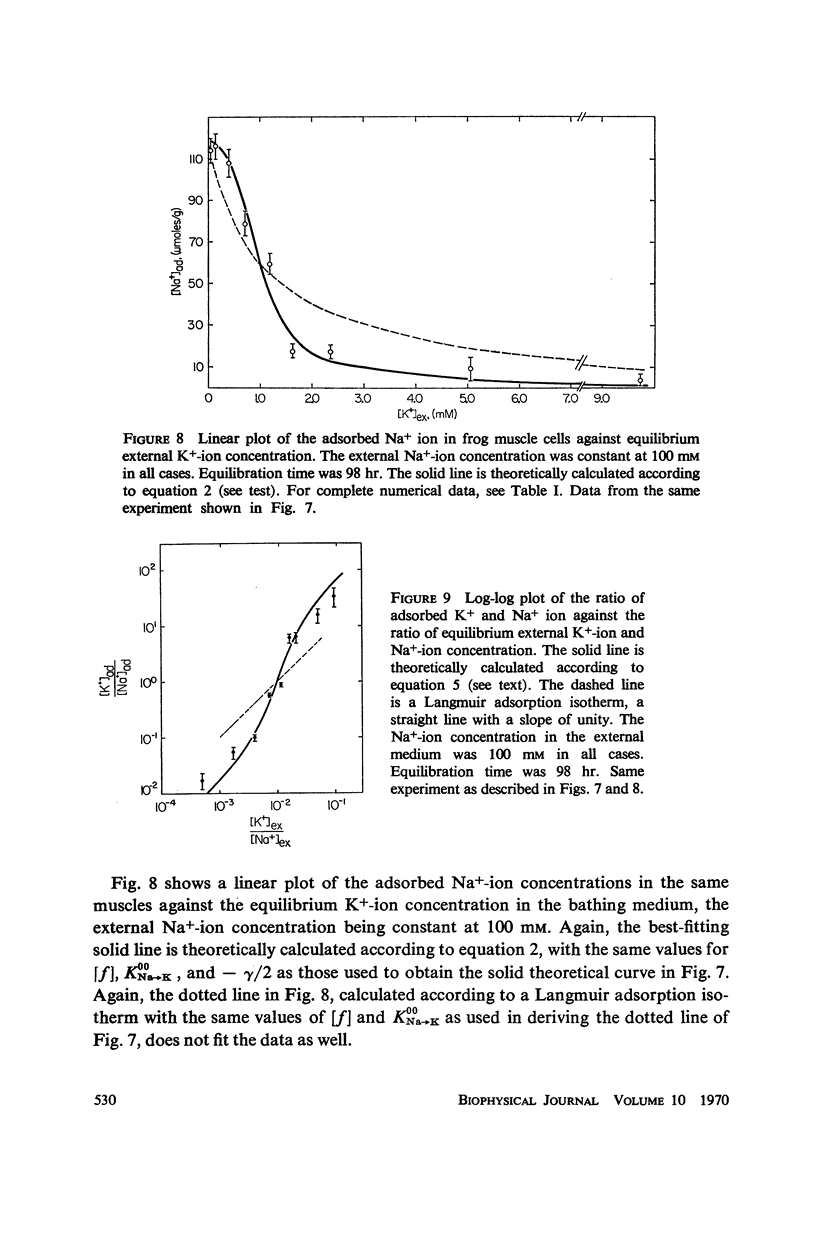
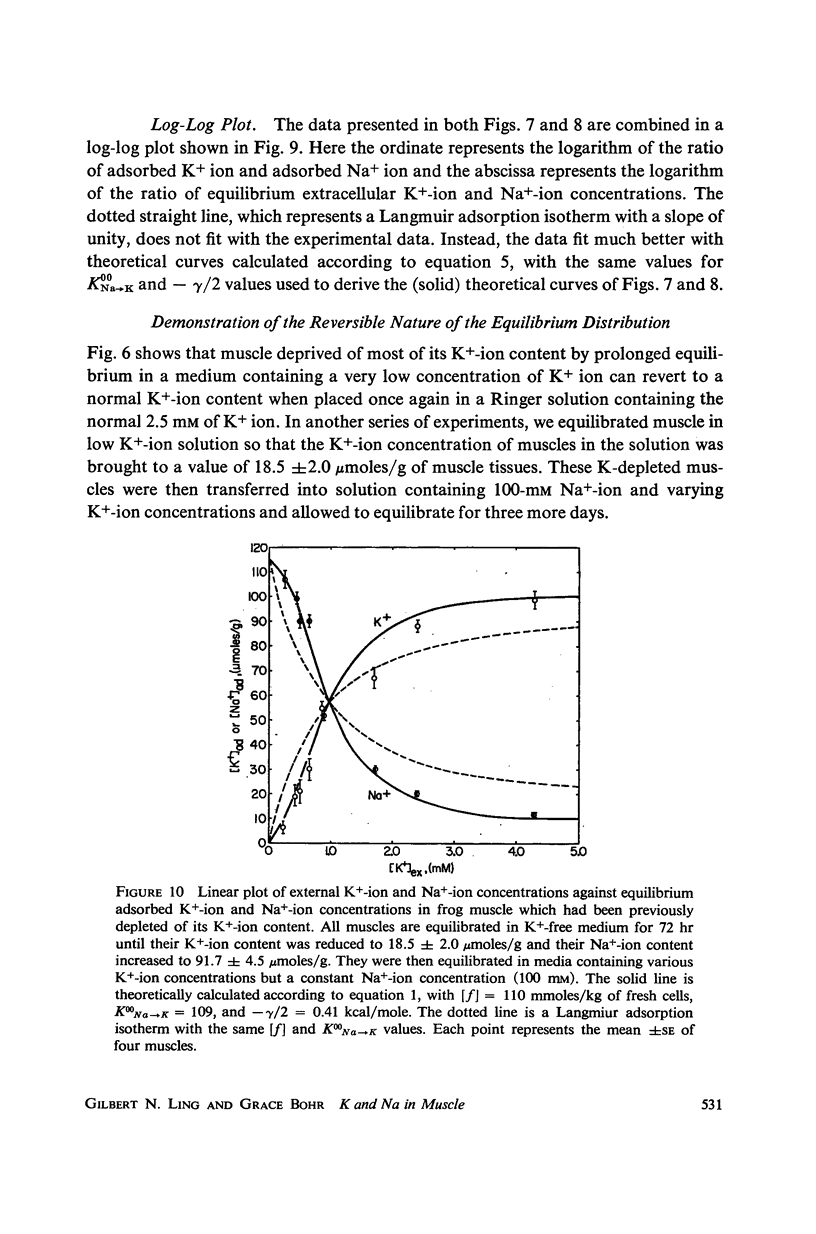
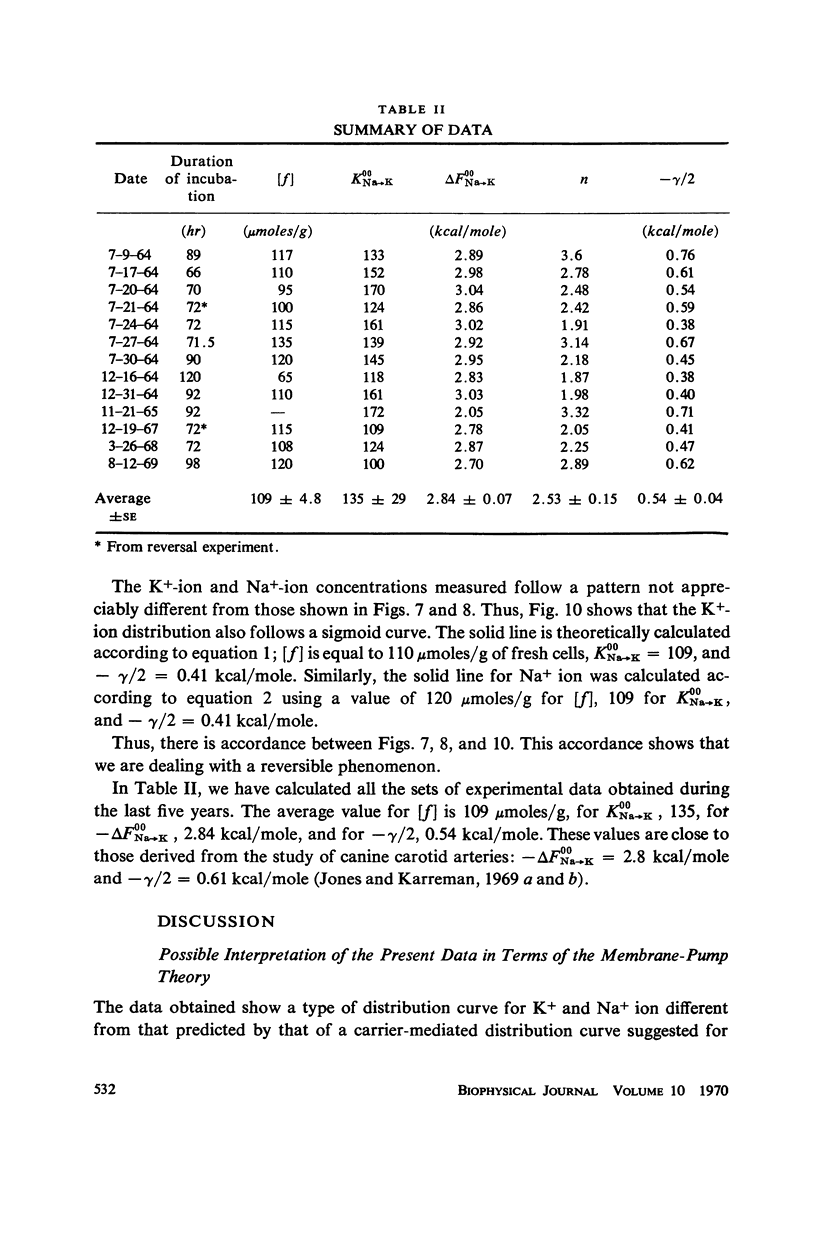
New steady levels of K+ and Na+ ion in frog sartorius muscle were reached in 72 hr at 25°C in environments containing 100-mM Na+-ion and K+-ion concentrations varying from near zero to 10 mM. These steady levels follow a pattern predicted by a cooperative adsorption isotherm presented in 1964. From a total of 13 sets of experiments carried out over a five year period, the average concentration of adsorption sites is 109 μmoles/g of fresh cells. The average intrinsic equilibrium constant for the Na → K exchange is 135, and the average free energy of nearest neighbor interaction is 0.54 kcal/mole. These values are in good agreement with those obtained by Jones and Karreman from studies on canine carotid arteries.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buck B., Goodford P. J. The distribution of ions in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):551–569. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., MONOD J. Bacterial permeases. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Sep;21(3):169–194. doi: 10.1128/br.21.3.169-194.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman G., McLauchlan K. A. Oriented water in the sciatic nerve of rabbit. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):391–392. doi: 10.1038/215391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essig A. The "pump-leak" model and exchange diffusion. Biophys J. 1968 Jan;8(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86474-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn W. O., Cobb D. M. THE POTASSIUM EQUILIBRIUM IN MUSCLE. J Gen Physiol. 1934 May 20;17(5):629–656. doi: 10.1085/jgp.17.5.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz O. G., Jr, Swift T. J. The state of water in polarized and depolarized frog nerves a proton magnetic resonance study. Biophys J. 2008 Dec 31;7(6):675–687. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86616-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Nichols B. L., Chamberlain N. F. Evidence for the existence of a minimum of two phases of ordered water in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1969 May 24;222(5195):747–750. doi: 10.1038/222747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. F., Kregenow F. M. The characterization of new energy dependent cation transport processes in red blood cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):566–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. W., Karreman G. Potassium accumulation and permeation in the canine carotid artery. Biophys J. 1969 Jul;9(7):910–924. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86426-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The effect of external sodium concentration on the sodium fluxes in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:591–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Némethy G., Filmer D. Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):365–385. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING G. N. THE ASSOCIATION-INDUCTION HYPOTHESIS. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1964;22:244–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. N. All-or-none adsorption by living cells and model protein-water systems: discussion of the problem of "permease-induction" and determination of secondary and tertiary structures of proteins. Fed Proc. 1966 May-Jun;25(3):958–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. N., Cope F. W. Potassium ion: is the bulk of intracellular K+ adsorbed? Science. 1969 Mar 21;163(3873):1335–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3873.1335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. N., Kromash M. H. The extracellular space of voluntary muscle tissues. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jan;50(3):677–694. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. N., Ochsenfeld M. M. Studies on ion accumulation in muscle cells. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):819–843. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. N. The physical state of water in living cell and model systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Oct 13;125(2):401–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb45406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYMAN J., Jr Heme proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1948;4:407–531. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


