Abstract
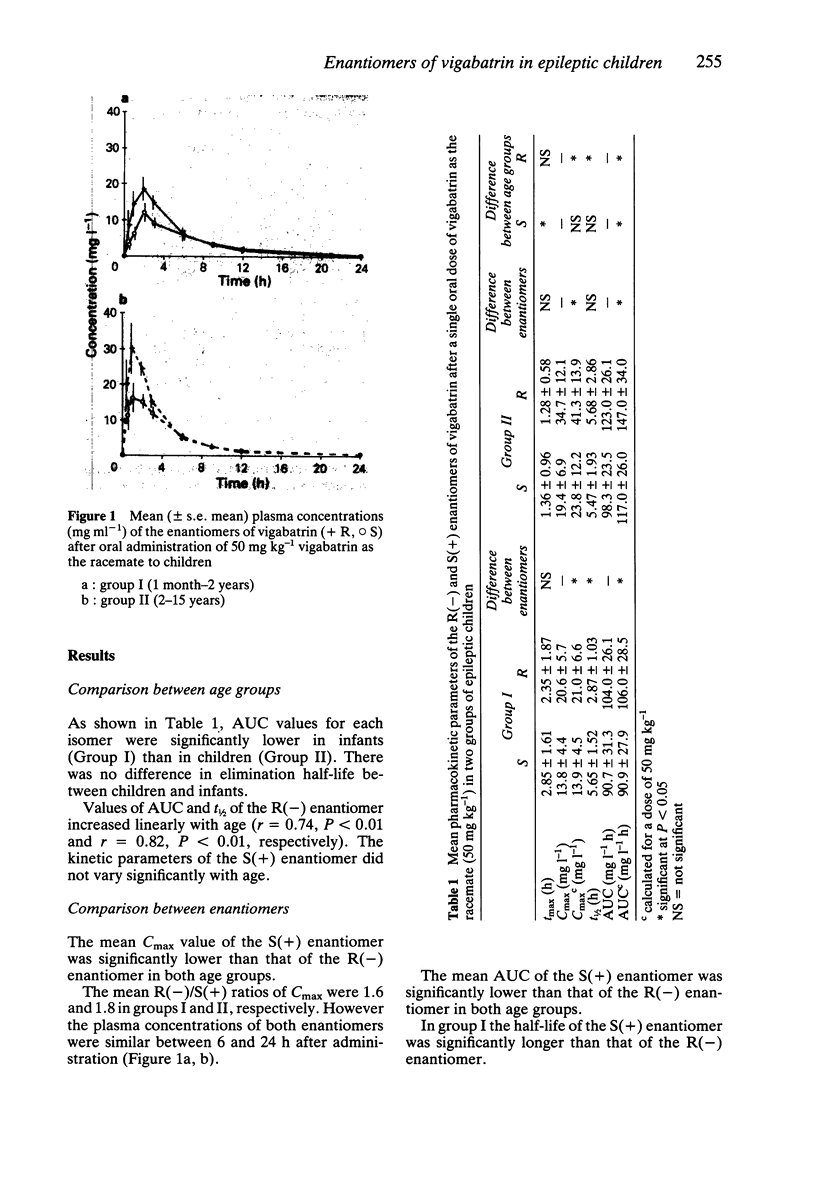
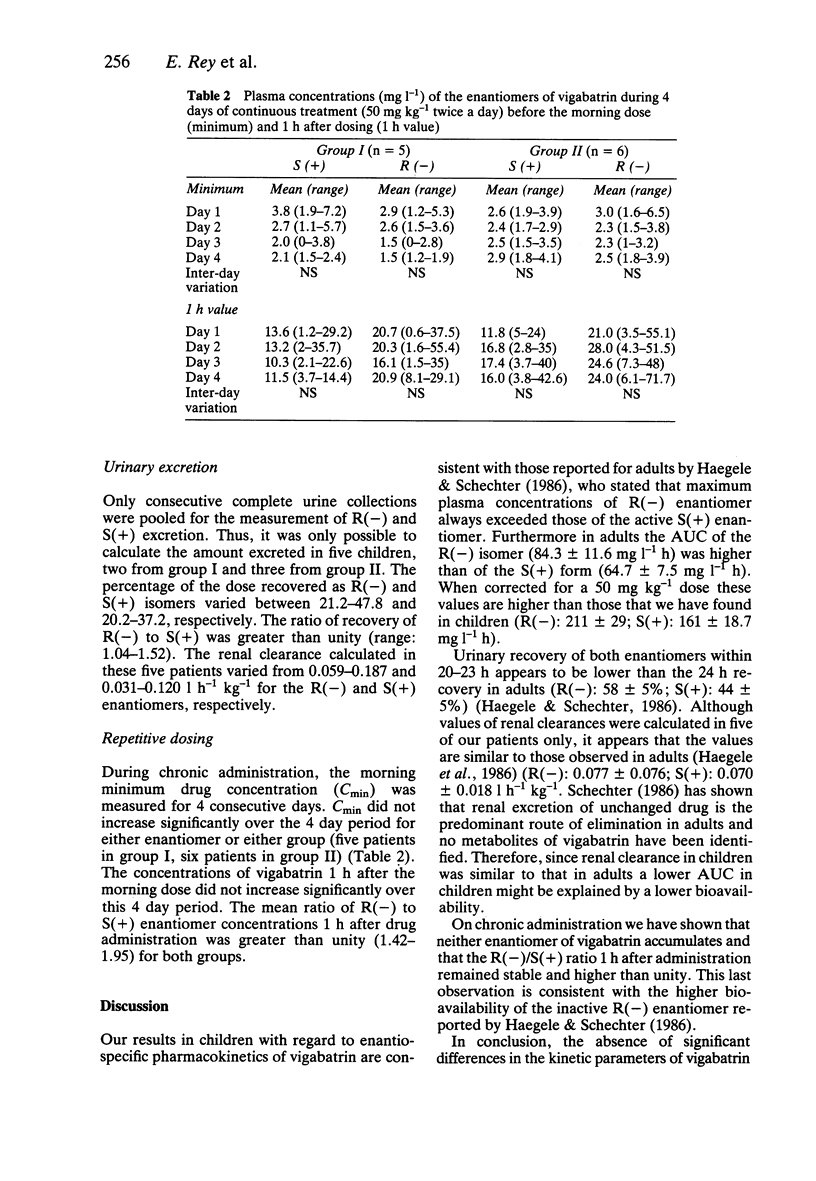
1. The pharmacokinetics of the enantiomers of vigabatrin were investigated after oral administration of a single 50 mg kg-1 dose of the racemate to two groups of six epileptic children (I: 5 months-2 years, II: 4-14 years). 2. The mean (+/- s.d.) values of maximum plasma concentration and area under the plasma concentration-time curve of the R(-) enantiomer were significantly higher than those of S(+) vigabatrin in both groups: R(-) Cmax: 21 +/- 6.6 (I)-41.3 +/- 13.9 (II) vs S(+) Cmax: 13.9 +/- 4.5 (I)-23.8 +/- 12.2 (II) mg l-1; R(-) AUC: 106 +/- 28.5 (I)-147 +/- 34 (II) vs S(+) AUC: 90.9 +/- 27.9 (I)-117 +/- 26 (II) mg l-1 h. In group I, the half-life of the R(-) isomer was significantly shorter than that of the S(+) isomer; in group II, the half-lives were comparable. 3. For the R(-) enantiomer the area under the curve, and the elimination half-life increased linearly with age. 4. During chronic administration (50 mg kg-1 vigabatrin racemate twice a day for 4 days), the morning trough plasma drug concentrations did not increase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Browne T. R., Mattson R. H., Penry J. K., Smith D. B., Treiman D. M., Wilder B. J., Ben-Menachem E., Napoliello M. J., Sherry K. M., Szabo G. K. Vigabatrin for refractory complex partial seizures: multicenter single-blind study with long-term follow-up. Neurology. 1987 Feb;37(2):184–189. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J., Schechter P. J., Tell G., Koch-Weser J., Sjoerdsma A., Warter J. M., Marescaux C., Rumbach L. Increased gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), homocarnosine and beta-alanine in cerebrospinal fluid of patients treated with gamma-vinyl GABA (4-amino-hex-5-enoic acid). Life Sci. 1981 May 21;28(21):2431–2439. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90511-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J., Tell G., Schechter P. J., Koch-Weser J., Warter J. M., Marescaux C., Rumbach L. Increased CSF gamma-aminobutyric acid after treatment with gamma-vinyl GABA. Lancet. 1980 Sep 20;2(8195 Pt 1):647–647. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegele K. D., Schechter P. J. Kinetics of the enantiomers of vigabatrin after an oral dose of the racemate or the active S-enantiomer. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 Nov;40(5):581–586. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegele K. D., Schoun J., Alken R. G., Huebert N. D. Determination of the R(-)- and S(+)-enantiomers of gamma-vinyl-gamma-aminobutyric acid in human body fluids by gas chromatography--mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr. 1983 May 13;274:103–110. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84413-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loiseau P., Hardenberg J. P., Pestre M., Guyot M., Schechter P. J., Tell G. P. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of vigabatrin (gamma-vinyl GABA) in drug-resistant epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1986 Mar-Apr;27(2):115–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb03512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. S., Murugaiah K. Anticonvulsant action in mice with sound-induced seizures of the optical isomers of gamma-vinyl GABA. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Apr 22;89(1-2):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90620-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf B. W. Inhibitors of GABA metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jun 1;28(11):1705–1712. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90529-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimmer E. M., Richens A. Double-blind study of gamma-vinyl GABA in patients with refractory epilepsy. Lancet. 1984 Jan 28;1(8370):189–190. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


