Abstract
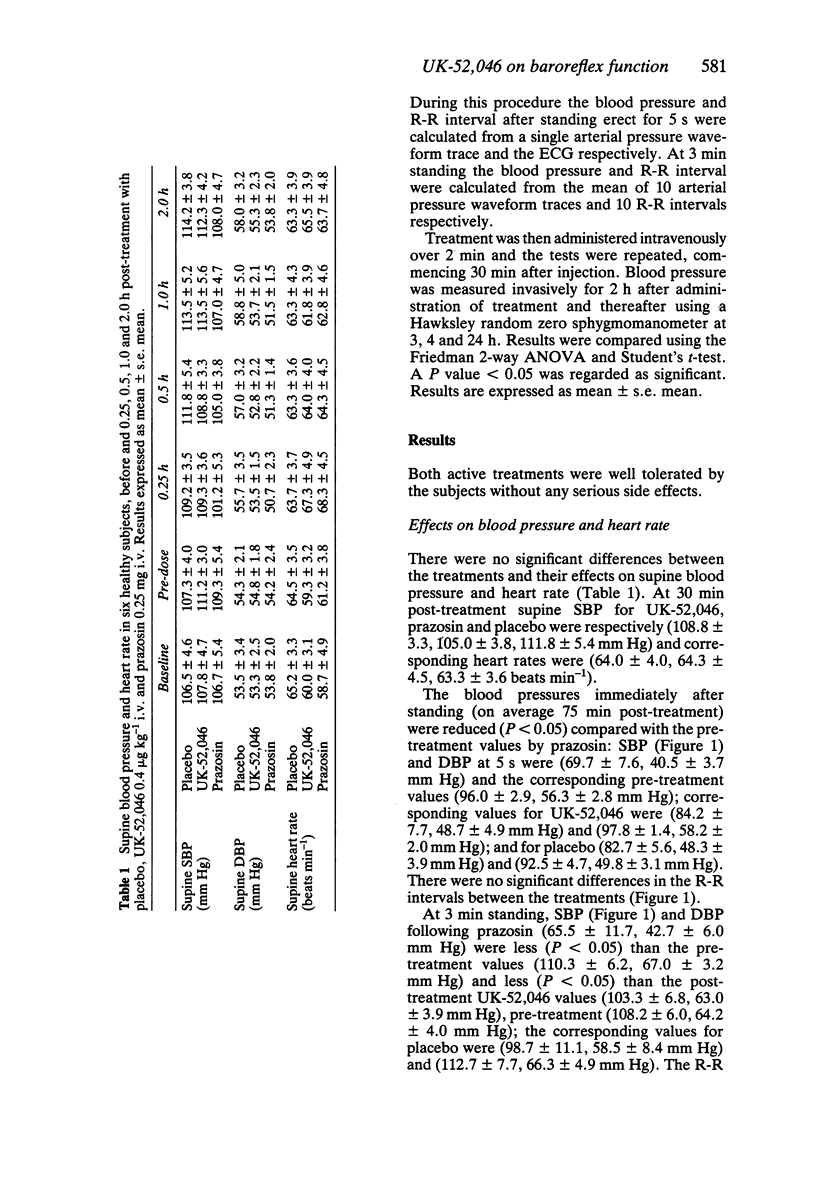
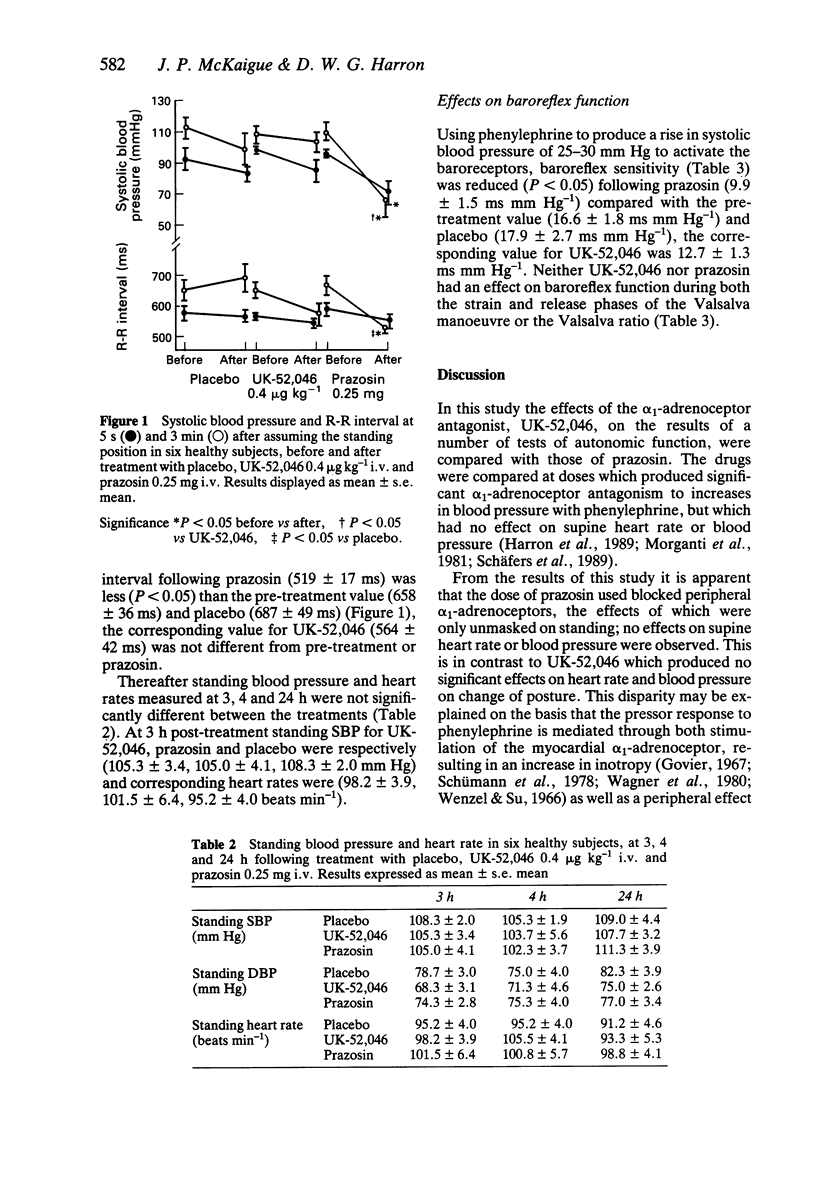
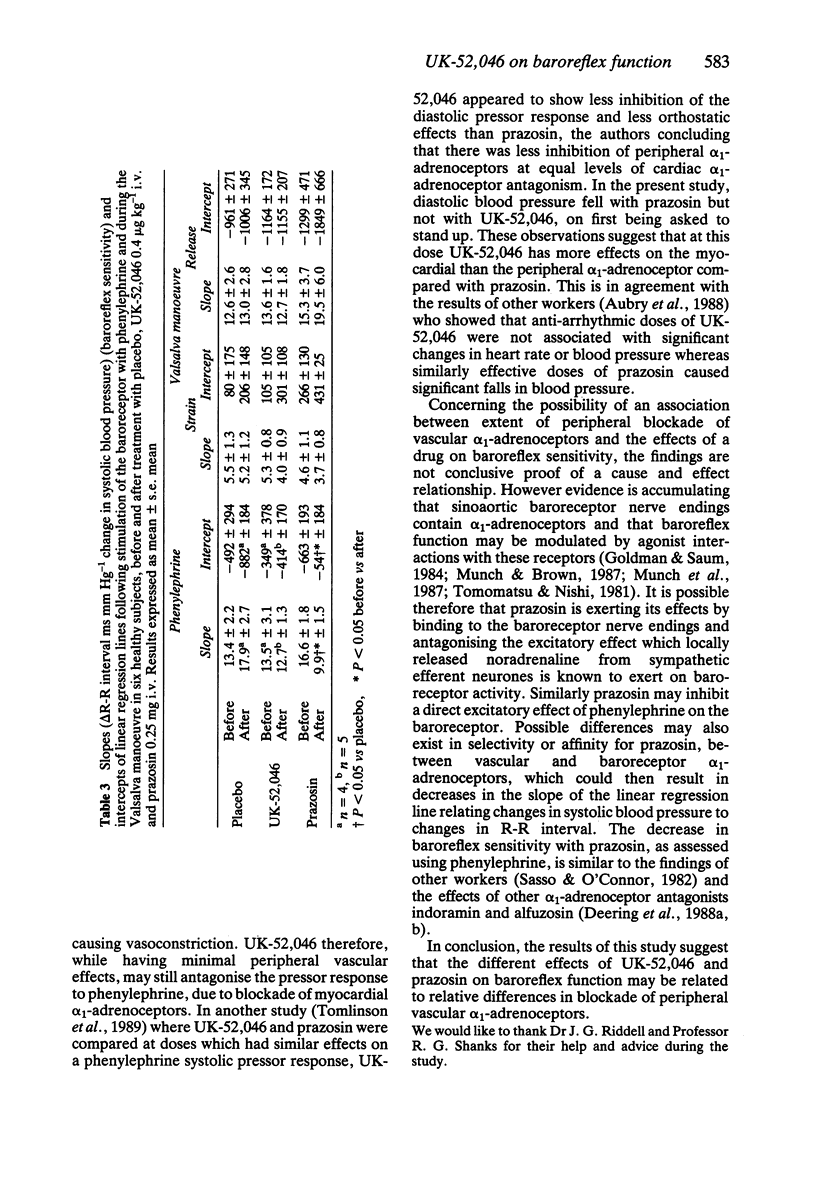
1. In a placebo controlled study (six healthy male subjects), the effects of UK-52,046 (0.4 microgram kg-1 i.v.) and prazosin (0.25 mg i.v.) on baroreflex function were compared, at doses which produced antagonism to phenylephrine, but which had no effect on supine blood pressure. 2. Baroreflex function [delta R-R interval ms mm Hg-1 change in SBP] was assessed following increases in systolic blood pressure (SBP) with phenylephrine and during the Valsalva manoeuvre. 3. At these doses neither UK-52,046 nor prazosin had an effect on supine SBP or heart rate; however following prazosin, standing SBPs at 5 s (69.7 +/- 7.6 mm Hg) and at 3 min (65.5 +/- 11.7 mm Hg) were less than the respective pre-treatment (P less than 0.05) values (96.0 +/- 2.9, 110.3 +/- 6.2 mm Hg) and placebo (82.7 +/- 5.6, 98.7 +/- 11.1 mm Hg). UK-52,046 had no significant effects on standing SBP at 5 s or 3 min. At 5 s, pre- and post-treatment R-R intervals (584 +/- 26, 541 +/- 27 ms respectively) were not significantly different with prazosin, but at 3 min the post-treatment R-R interval following prazosin (519 +/- 17 ms) was less (P less than 0.05) than the pre-treatment value (658 +/- 36 ms). 4. UK-52,046 had no effect on baroreflex sensitivity (12.7 +/- 1.3 ms mm Hg-1) compared with placebo (17.9 +/- 2.7 ms mm Hg-1).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deering A. H., Riddell J. G., Harron D. W., Shanks R. G. Effect of acute and chronic indoramin administration on baroreflex function and tremor in humans. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;11(3):284–290. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198803000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deering A. H., Riddell J. G., Harron D. W., Shanks R. G. Effect of acute and chronic oral administration of alfuzosin on baroreflex function and tremor in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;25(4):417–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman W. F., Saum W. R. A direct excitatory action of catecholamines on rat aortic baroreceptors in vitro. Circ Res. 1984 Jul;55(1):18–30. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.1.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govier W. C. A positive inotropic effect of phenylephrine mediated through alpha adrenergic receptors. Life Sci. 1967 Jul 1;6(13):1361–1365. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAloney R., Mitchell H., Deering A. H., Shanks R. G., Harron D. W. Computerized evaluation of Valsalva's Maneuver before and during alpha-adrenoceptor blockade with alfuzosin. J Pharmacol Methods. 1987 Sep;18(2):163–177. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(87)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morganti A., Sala C., Palermo A., Turolo L., Zanchetti A. Alpha 1-Adrenoceptor blockade: dissociation of its effects on renin release and arterial blood pressure in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Dec;61 (Suppl 7):307s–309s. doi: 10.1042/cs061307s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munch P. A., Brown A. M. Sympathetic modulation of rabbit aortic baroreceptors in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):H1106–H1111. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.5.H1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munch P. A., Thoren P. N., Brown A. M. Dual effects of norepinephrine and mechanisms of baroreceptor stimulation. Circ Res. 1987 Sep;61(3):409–419. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.3.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasso E. H., O'Connor D. T. Prazosin depression of baroreflex function in hypertensive man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1982;22(1):7–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00606418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümann H. J., Wagner J., Knorr A., Reidemeister J. C., Sadony V., Schramm G. Demonstration in human atrial preparations of alpha-adrenoceptors mediating positive inotropic effects. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 May;302(3):333–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00508304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomomatsu E., Nishi K. Increased activity of carotid sinus baroreceptors by sympathetic stimulation and norepinephrine. Am J Physiol. 1981 Apr;240(4):H650–H658. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.240.4.H650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uprichard A. G., Harron D. W., Wilson R., Shanks R. G. Effects of the myocardial-selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist UK-52046 and atenolol, alone and in combination, on experimental cardiac arrhythmias in dogs. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1241–1254. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J., Schümann H. J., Knorr A., Rohm N., Reidemeister J. C. Stimulation by adrenaline and dopamine but not by noradrenaline of myocardial alpha-adrenoceptors mediating positive inotropic effects in human atrial preparations. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 May;312(1):99–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00502581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel D. G., Su J. L. Interactions between sympathomimetic amines and blocking agents on the rat ventricle strip. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1966 Apr;160(2):379–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


