Abstract
1. The possible involvement of the benzodiazepine (BZD)-GABAA-receptor complex in mediating CNS stimulatory effects of fluoroquinolones was tested in vitro, in a binding inhibition assay and in vivo, in a clinical drug interaction study using electro-encephalogram (EEG) monitoring. 2. The specific binding of [3H]-flunitrazepam to rat synaptic brain membranes was inhibited by various fluoroquinolones in a concentration-dependent manner. 3. Ofloxacin had CNS-stimulating effects as revealed by the EEG which were slightly augmented by flumazenil but reversed by coadministration of midazolam. 4. In conclusion, our findings suggest that clinically observed CNS adverse effects of fluoroquinolones could be mediated at least in part through interaction with the BZD-GABAA-receptor complex and may be controlled by BZD agonist administration.
Full text
PDF

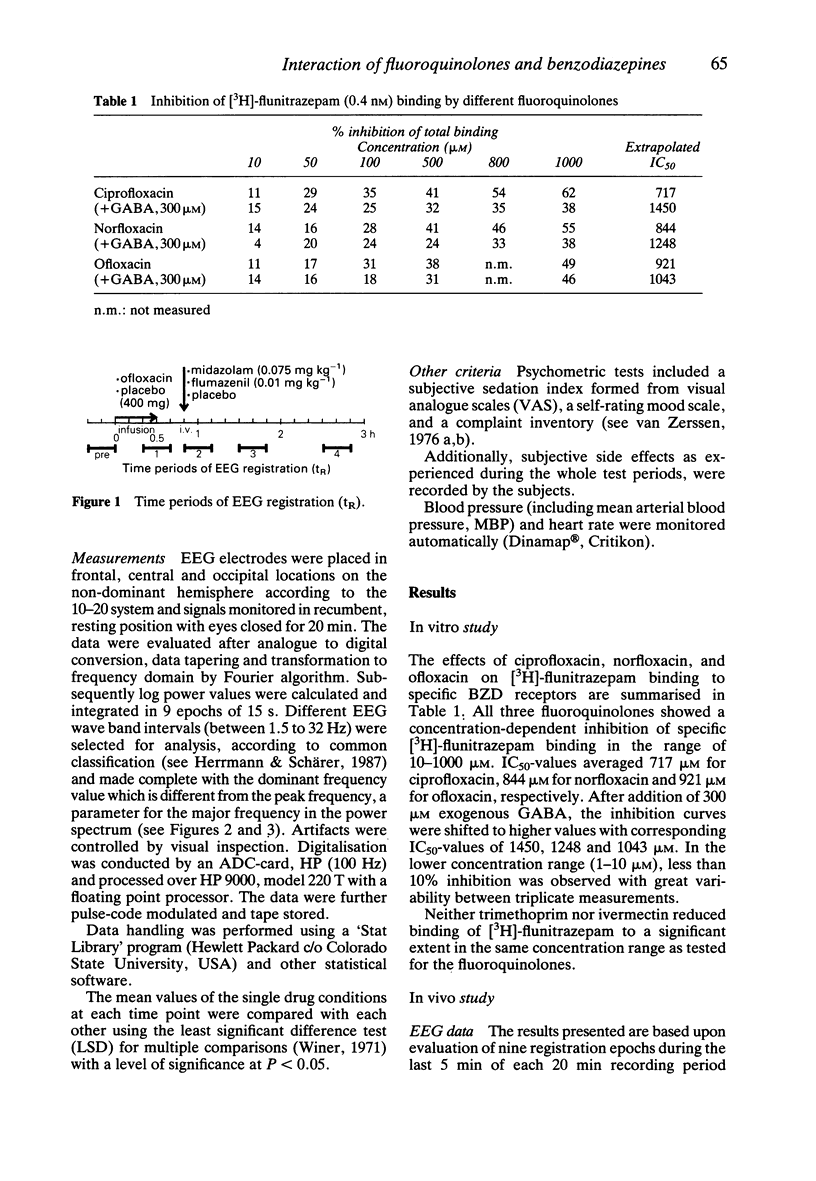
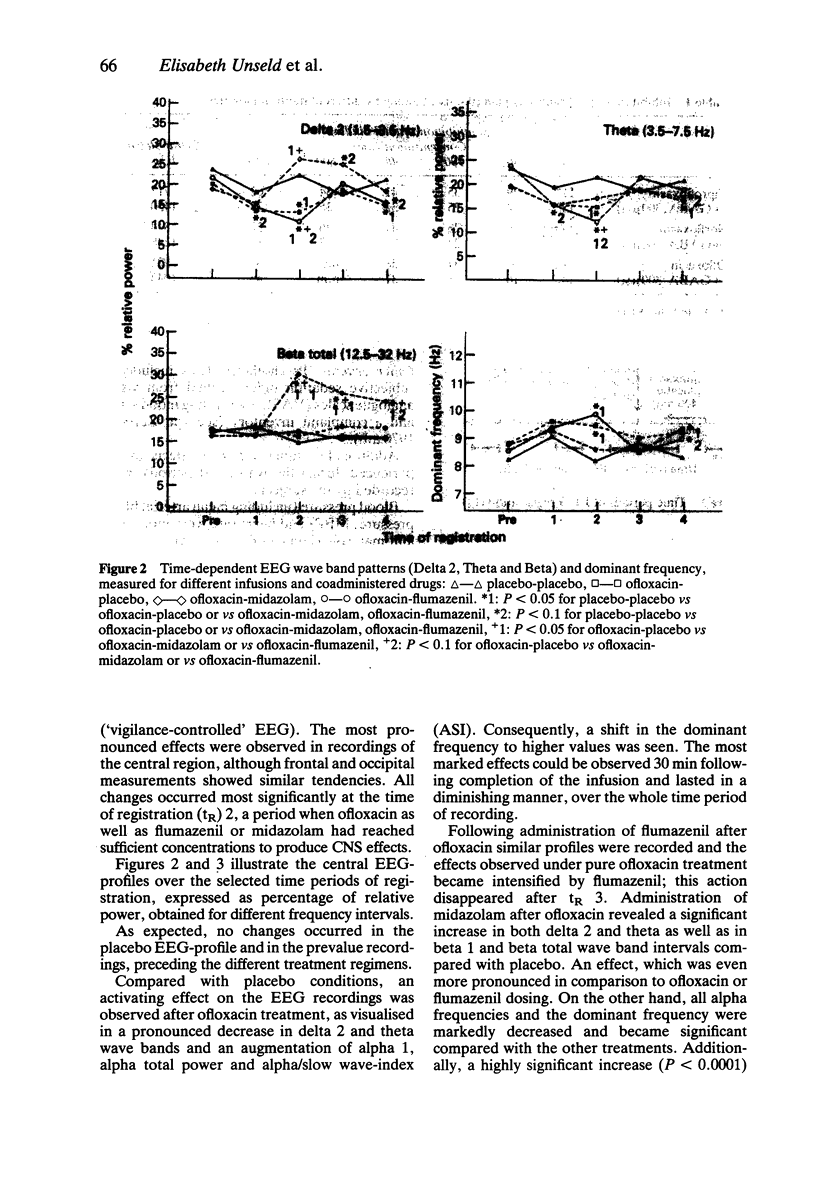
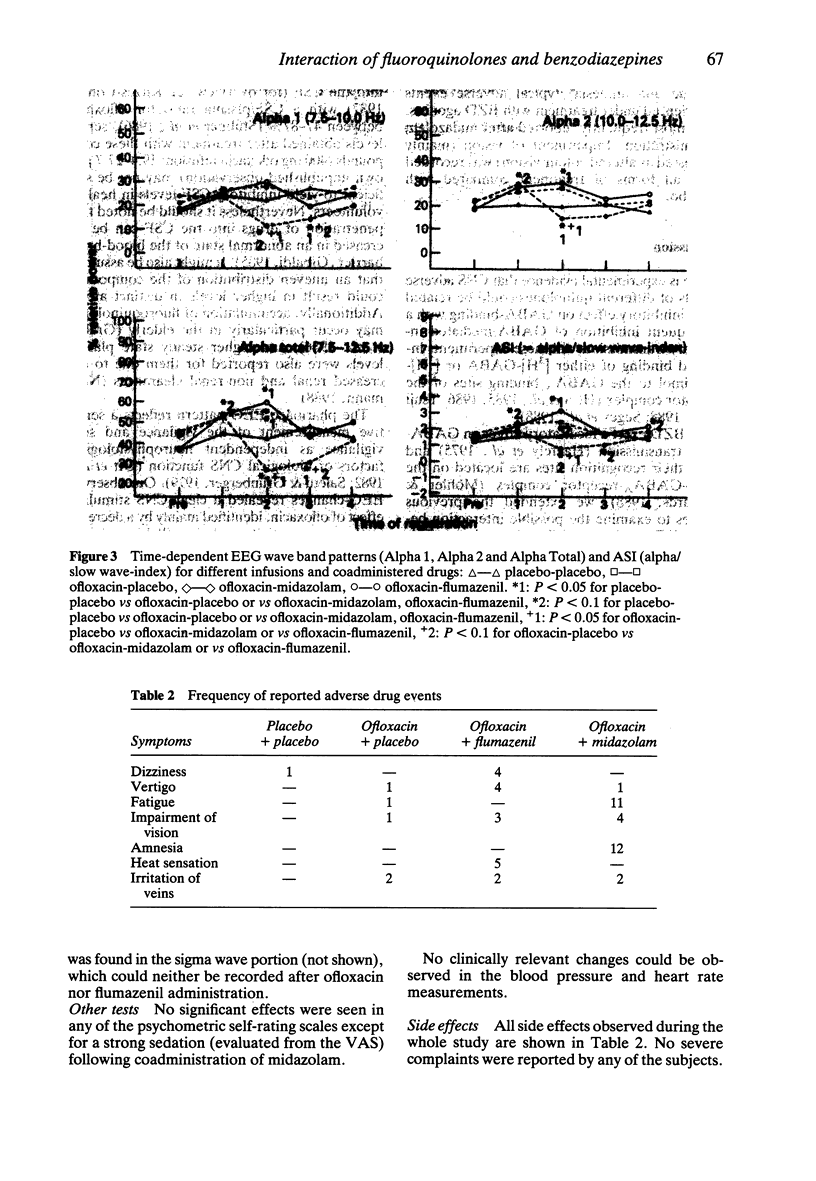



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allonen H., Ziegler G., Klotz U. Midazolam kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Nov;30(5):653–661. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altés J., Gascó J., de Antonio J., Salas A., Villalonga C. Ciprofloxacin and delirium. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Jan 15;110(2):170–171. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-2-170_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arcieri G., Griffith E., Gruenwaldt G., Heyd A., O'Brien B., Becker N., August R. Ciprofloxacin: an update on clinical experience. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):381–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf S. J., Arya S. C., Parande C. M., Sahay R., Ageel A. R. Anti-delta antibody in primary hepatocellular carcinoma patients in the Gizan area of Saudi Arabia. Infection. 1986 Sep-Oct;14(5):250–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01644273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball P. Adverse reactions and interactions of fluoroquinolones. Clin Invest Med. 1989 Feb;12(1):28–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenicke A., Suttmann H., Kapp W., Kugler J., Ebentheuer H. Zur Wirkung des Benzodiazepin-Antagonisten Ro 15-1788. Anaesthesist. 1984 Aug;33(8):343–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- File S. E., Pellow S. Intrinsic actions of the benzodiazepine receptor antagonist Ro 15-1788. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1986;88(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00310505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gath I., Weidenfeld J., Collins G. I., Hadad H. Electrophysiological aspects of benzodiazepine antagonists, Ro 15-1788 and Ro 15-3505. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;18(4):541–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez J. P., Henwood J. M. Pefloxacin. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1989 May;37(5):628–668. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198937050-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haefely W., Kulcsár A., Möhler H., Pieri L., Polc P., Schaffner R. Possible involvement of GABA in the central actions of benzodiazepines. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1975;(14):131–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handel J., Ziegler G., Gemeinhardt A., Stuber H., Fischer C., Klotz U. Lack of effect of nitrendipine on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam during steady state. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;25(2):243–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Brogden R. N., Richards D. M. Norfloxacin. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1985 Dec;30(6):482–513. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198530060-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf G., Böcker R., Estler C. J., Radtke H. J., Floh W. Concentration of ciprofloxacin in human serum, lung and pleural tissues and fluids during and after lung surgery. Infection. 1988;16(1):29–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01646928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jüngst G., Mohr R. Side effects of ofloxacin in clinical trials and in postmarketing surveillance. Drugs. 1987;34 (Suppl 1):144–149. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198700341-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz U., Kanto J. Pharmacokinetics and clinical use of flumazenil (Ro 15-1788). Clin Pharmacokinet. 1988 Jan;14(1):1–12. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198814010-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz U., Ziegler G., Ludwig L., Reimann I. W. Pharmacodynamic interaction between midazolam and a specific benzodiazepine antagonist in humans. J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;25(6):400–406. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1985.tb02866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Richards J. G. The benzodiazepine receptor: a pharmacological control element of brain function. Eur J Anaesthesiol Suppl. 1988;2:15–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noderer J., Duka T., Dorow R. Benzodiazepin-Antagonisierung mit Ro 15-1788: psychometrische, hormonelle und biophysikalische Parameter. Anaesthesist. 1988 Aug;37(8):535–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saletu B., Grünberger J. Evaluation of pharmacodynamic properties of psychotropic drugs: quanitative EEG, psychometric and blood level investigations in normals and patients. Pharmakopsychiatr Neuropsychopharmakol. 1979 Jan;12(1):45–58. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöpf J., Laurian S., Le P. K., Gaillard J. M. Intrinsic activity of the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788 in man: an electrophysiological investigation. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1984 May;17(3):79–83. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1017413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev S., Rehavi M., Rubinstein E. Quinolones, theophylline, and diclofenac interactions with the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1624–1626. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W., Eichinger A., Riederer P., Jellinger K. Comparison of benzodiazepine receptor binding in membranes from human or rat brain. Neuropharmacology. 1985 Aug;24(8):751–759. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(85)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiébot M. H., Kloczko J., Chermat R., Simon P., Soubrié P. Oxolinic acid and diazepam: their reciprocal antagonism in rodents. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1980 Jan;67(1):91–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00427601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Sato H., Kume Y., Tamai I., Okezaki E., Nagata O., Kato H. Inhibitory effects of quinolone antibacterial agents on gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in rat brain membranes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):190–194. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Sato H., Okezaki E., Nagata O., Kato H. Effect of the anti-inflammatory agent fenbufen on the quinolone-induced inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to rat brain membranes in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Nov 15;37(22):4408–4411. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90625-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaudig M., von Bose M., Weber M. M., Bremer D., Zieglgänsberger W. Psychotoxic effects of ofloxacin. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1989 Jan;22(1):11–15. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1014570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler G., Ludwig L., Fritz G. Reversal of slow-wave sleep by benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788. Lancet. 1985 Aug 31;2(8453):510–510. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


