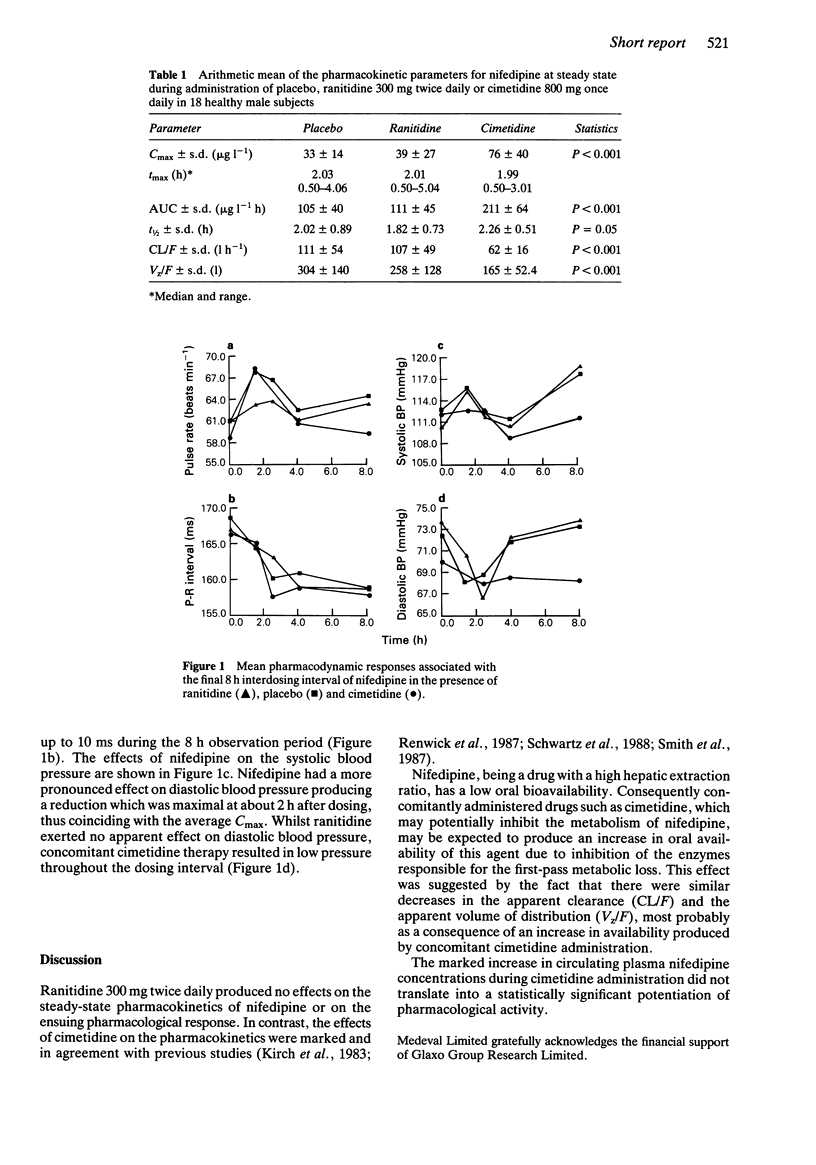
Abstract
Ranitidine may be used at doses of up to 300 mg twice daily in the healing of duodenal ulcers, and this study investigated the potential for a pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic interaction between nifedipine 10 mg three times daily and ranitidine 300 mg twice daily compared with cimetidine 800 mg daily and placebo in a randomised crossover study in 18 healthy male subjects. Twelve blood samples were taken on the fifth day in each treatment period and assayed for nifedipine by h.p.l.c. Pulse, blood pressure and ECG recordings were also taken. Cimetidine, but not ranitidine, produced significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine at steady state. Mean +/- s.d. values of AUC were 105 +/- 40 micrograms l-1 for placebo treatment, 111 +/- 45 micrograms l-1 h for ranitidine and 211 +/- 64 micrograms l-1 h for cimetidine (P less than 0.001), and Cmax values were 33 +/- 14, 39 +/- 27 and 76 +/- 40 micrograms l-1 (P less than 0.001), respectively. Neither ranitidine nor cimetidine produced statistically significant changes in the pharmacological response to nifedipine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kirch W., Hoensch H., Ohnhaus E. E., Janisch H. D. Ranitidin-Nifedipin-Interaktion. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1984 Aug 3;109(31-32):1223–1223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirch W., Janisch H. D., Heidemann H., Rämsch K., Ohnhaus E. E. Einfluss von Cimetidin und Ranitidin auf Pharmakokinetik und antihypertensiven Effekt von Nifedipin. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1983 Nov 18;108(46):1757–1761. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1069821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinbloesem C. H., Van Harten J., Van Brummelen P., Breimer D. D. Liquid chromatographic determination of nifedipine in plasma and of its main metabolite in urine. J Chromatogr. 1984 Jun 8;308:209–216. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)87547-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst G., Jaeger H. Review of methods and criteria for the evaluation of bioequivalence studies. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;38(1):5–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00314794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renwick A. G., Le Vie J., Challenor V. F., Waller D. G., Gruchy B., George C. F. Factors affecting the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;32(4):351–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00543968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. B., Upton R. A., Lin E. T., Williams R. L., Benet L. Z. Effect of cimetidine or ranitidine administration on nifedipine pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Jun;43(6):673–680. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1988.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. R., Kendall M. J., Lobo J., Beerahee A., Jack D. B., Wilkins M. R. Ranitidine and cimetidine; drug interactions with single dose and steady-state nifedipine administration. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;23(3):311–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


