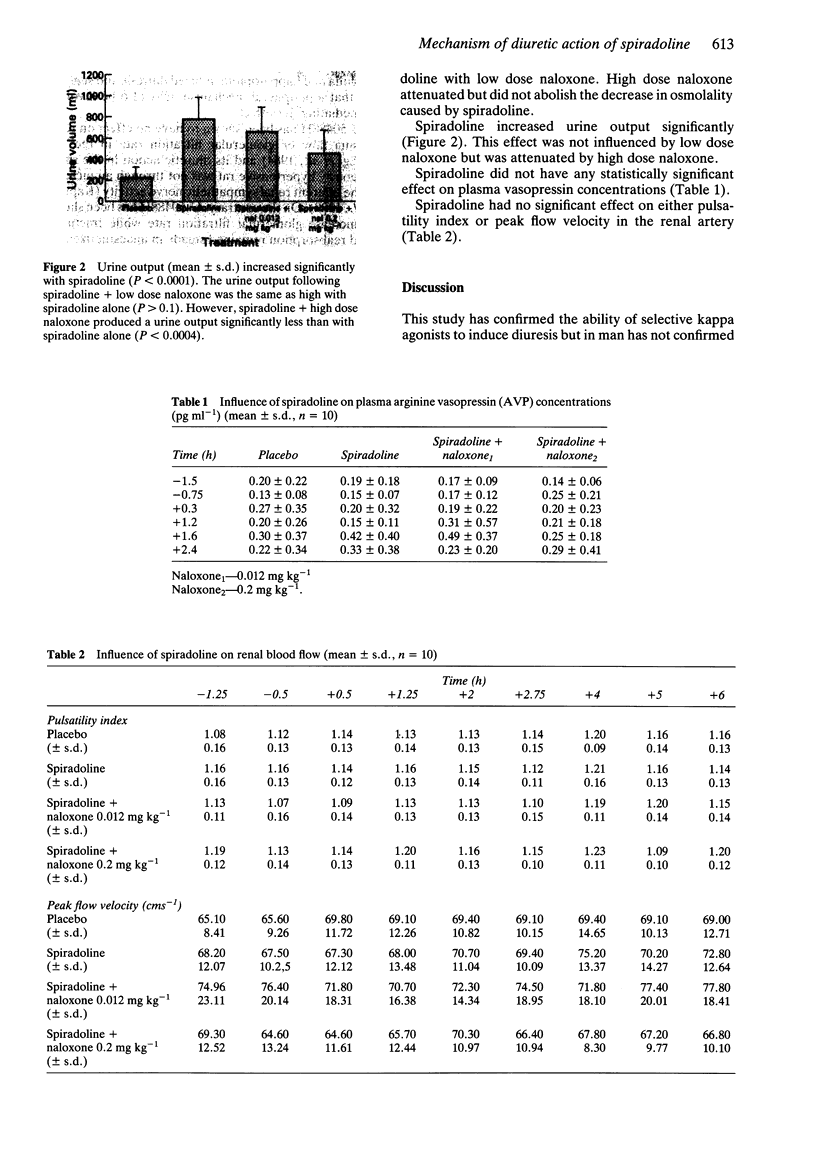
Abstract
1. The mechanism of the diuretic effect of the kappa opioid receptor agonist spiradoline was investigated in 10 healthy male subjects in a placebo-controlled, double-blind cross-over study. 2. Urine volume and osmolality, plasma vasopressin and Doppler renal blood velocity indices were recorded for 1.25 h before and 6 h following injection. 3. Spiradoline caused a significant increase in urine output which was antagonized by high but not low dose naloxone. The urine increase was accompanied by a significant decrease in osmolality which was also antagonised by high but not low dose naloxone. 4. Spiradoline had no effect on plasma vasopressin concentration or on renal blood velocity indices. 5. We conclude that kappa agonists induce diuresis in humans by a mechanism not involving suppression of vasopressin or changes in renal blood velocity indices.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton N., Balment R. J., Blackburn T. P. Kappa-opioid-induced changes in renal water and electrolyte management and endocrine secretion. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):769–776. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton N., Balment R. J., Blackburn T. P. Kappa-opioid-receptor agonists modulate the renal excretion of water and electrolytes in anaesthetized rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):181–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn T. P., Borkowski K. R., Friend J., Rance M. J. On the mechanisms of kappa-opioid-induced diuresis. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;89(3):593–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski K. R. Studies on the adrenomedullary dependence of kappa-opioid agonist-induced diuresis in conscious rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1151–1156. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns P. N. The physical principles of Doppler and spectral analysis. J Clin Ultrasound. 1987 Nov-Dec;15(9):567–590. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870150903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubbins P. A. Renal artery stenosis: duplex Doppler evaluation. Br J Radiol. 1986 Mar;59(699):225–229. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-59-699-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapusta D. R., Jones S. Y., DiBona G. F. Role of renal nerves in excretory responses to administration of kappa agonists in conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Oct;251(1):230–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti R. A., Mickelson M. M., McCall J. M., Von Voigtlander P. F. [3H]U-69593 a highly selective ligand for the opioid kappa receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D. A kappa opioid effect: increased urination in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D. Further study of kappa opioids on increased urination. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Oct;227(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D., Zerbe R. L., Hart J. C. Diuresis and suppression of vasopressin by kappa opioids: comparison with mu and delta opioids and clonidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Aug;234(2):463–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G. R., Ward N. J., Antal E. G., Lai P. Y., deMaar E. W. Diuretic actions in man of a selective kappa opioid agonist: U-62,066E. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jan;240(1):128–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Finkel M. S., Mendelsohn F. A., Zamir N. Localization of opiate binding sites in kidney and adrenal gland of the rat. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90502-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slizgi G. R., Ludens J. H. Displacement of 3H-EKC binding by opioids in rat kidney: a correlate to diuretic activity. Life Sci. 1985 Jun 10;36(23):2189–2193. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slizgi G. R., Ludens J. H. Role of ADH in ethylketocyclazocine-induced diuresis: studies in the Brattleboro rat. Life Sci. 1986 Jun 30;38(26):2437–2440. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90613-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slizgi G. R., Ludens J. H. Studies on the nature and mechanism of the diuretic activity of the opioid analgesic ethylketocyclazocine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Mar;220(3):585–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slizgi G. R., Taylor C. J., Ludens J. H. Effects of the highly selective kappa opioid, U-50, 488, on renal function in the anesthetized dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Sep;230(3):641–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson N., Ngsee J. Antidiuretic effect of acute morphine administration in the conscious rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Feb;60(2):201–204. doi: 10.1139/y82-031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Imai M., Yoshida S. Mechanism of diuretic action of U-62,066E, a kappa opioid receptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 31;160(2):229–237. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Nakano M., Yoshida S. Inhibition of elevated arginine vasopressin secretion in response to osmotic stimulation and acute haemorrhage by U-62066E, a kappa-opioid receptor agonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):384–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbe R. L., Henry D. P., Robertson G. L. A new Met-enkephalin analogue suppresses plasma vasopressin in man. Peptides. 1982 Mar-Apr;3(2):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(82)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


