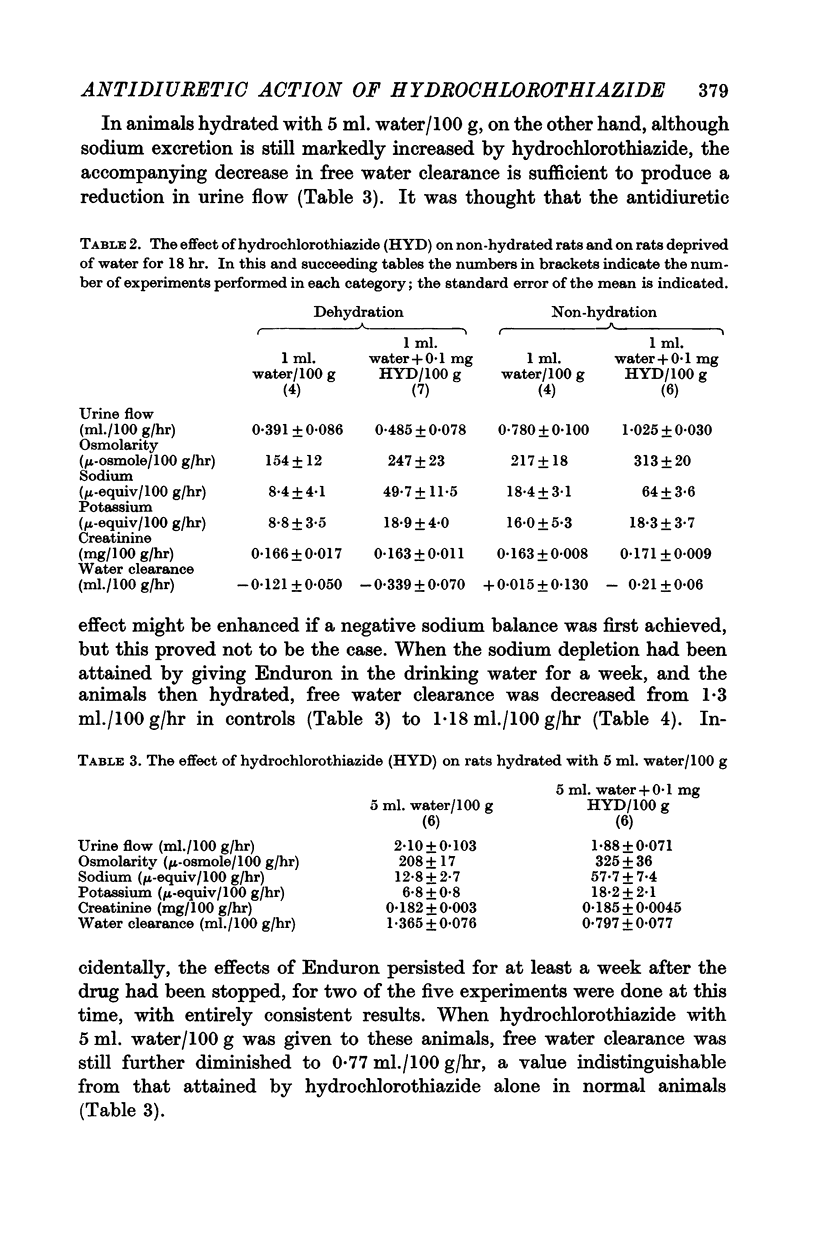
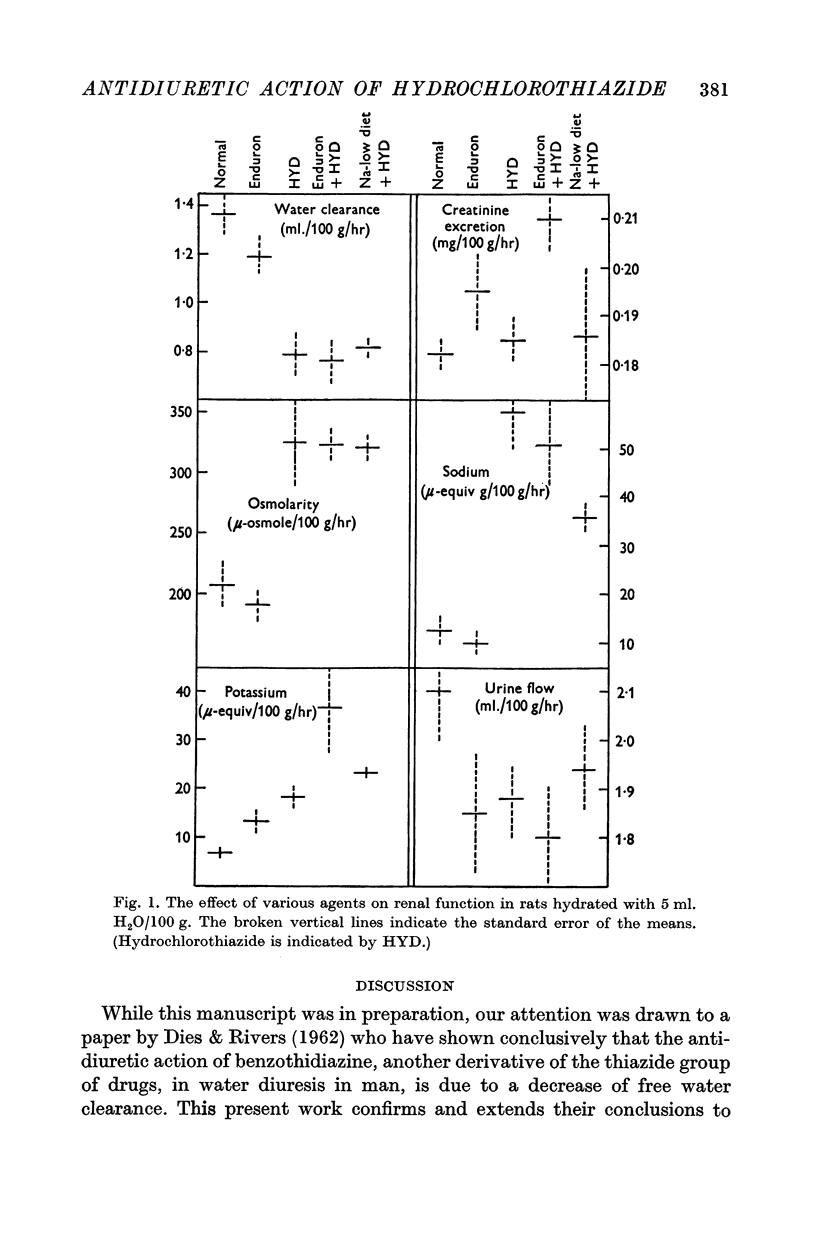
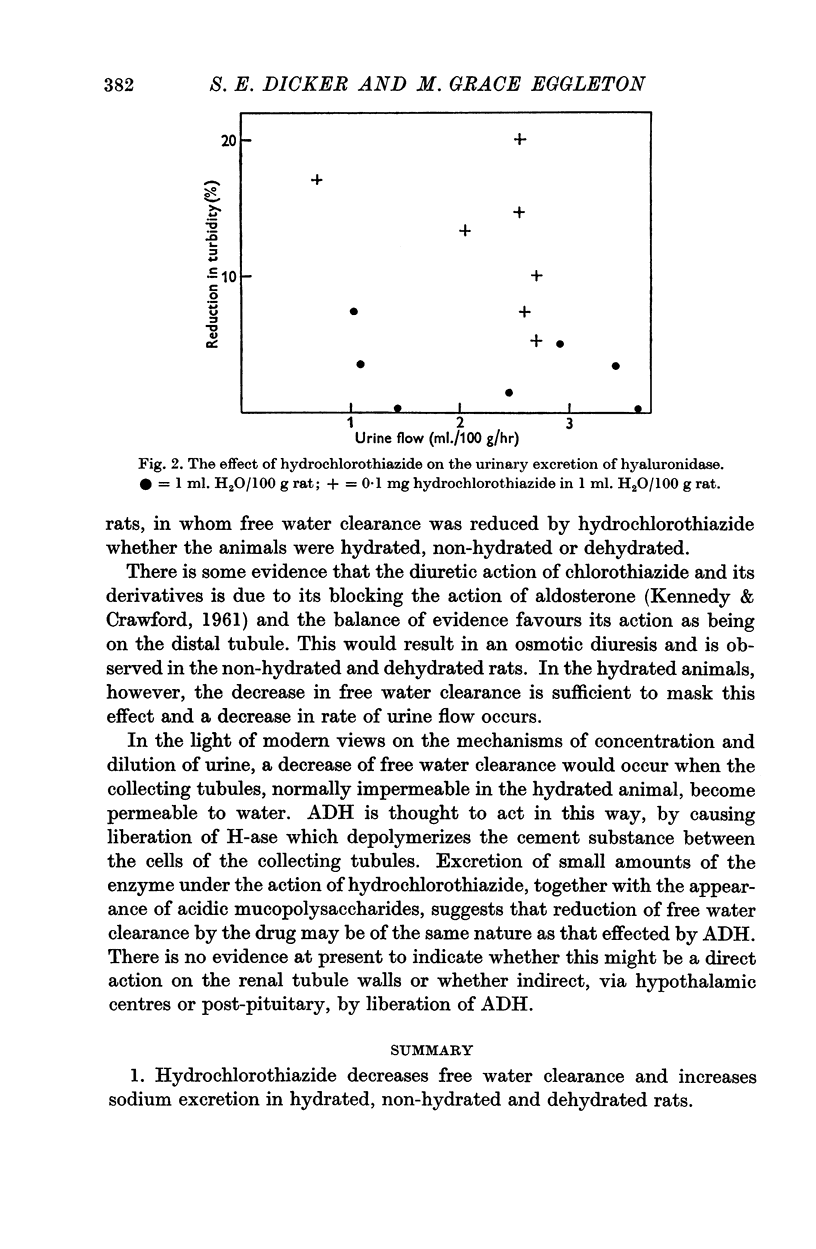
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRAWFORD J. D., FROST L., WELSH M., TERRY M. L. Relations between pharmacologic activity and molecular structure of certain saliuretic sulfonamides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Mar;135:382–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI FERRANTE N. Turbidimetric measurement of acid mucopolysaccharides and hyaluronidase activity. J Biol Chem. 1956 May;220(1):303–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIES F., RIVERA A. A possible mechanism of action of the antidiuretic effect of benzothiadiazine derivatives. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1962 Mar-Apr;3:172–179. doi: 10.1002/cpt196232172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley L. E., Orloff J. THE MECHANISM OF ANTIDIURESIS ASSOCIATED WITH THE ADMINISTRATION OF HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE TO PATIENTS WITH VASOPRESSIN-RESISTANT DIABETES INSIPIDUS. J Clin Invest. 1962 Nov;41(11):1988–1997. doi: 10.1172/JCI104657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY G. C., CRAWFORD J. D. A comparison of the effects of adrenalectomy and of chlorothiazide in experimental diabetes insipidus. J Endocrinol. 1961 Mar;22:77–86. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0220077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


