Full text
PDF



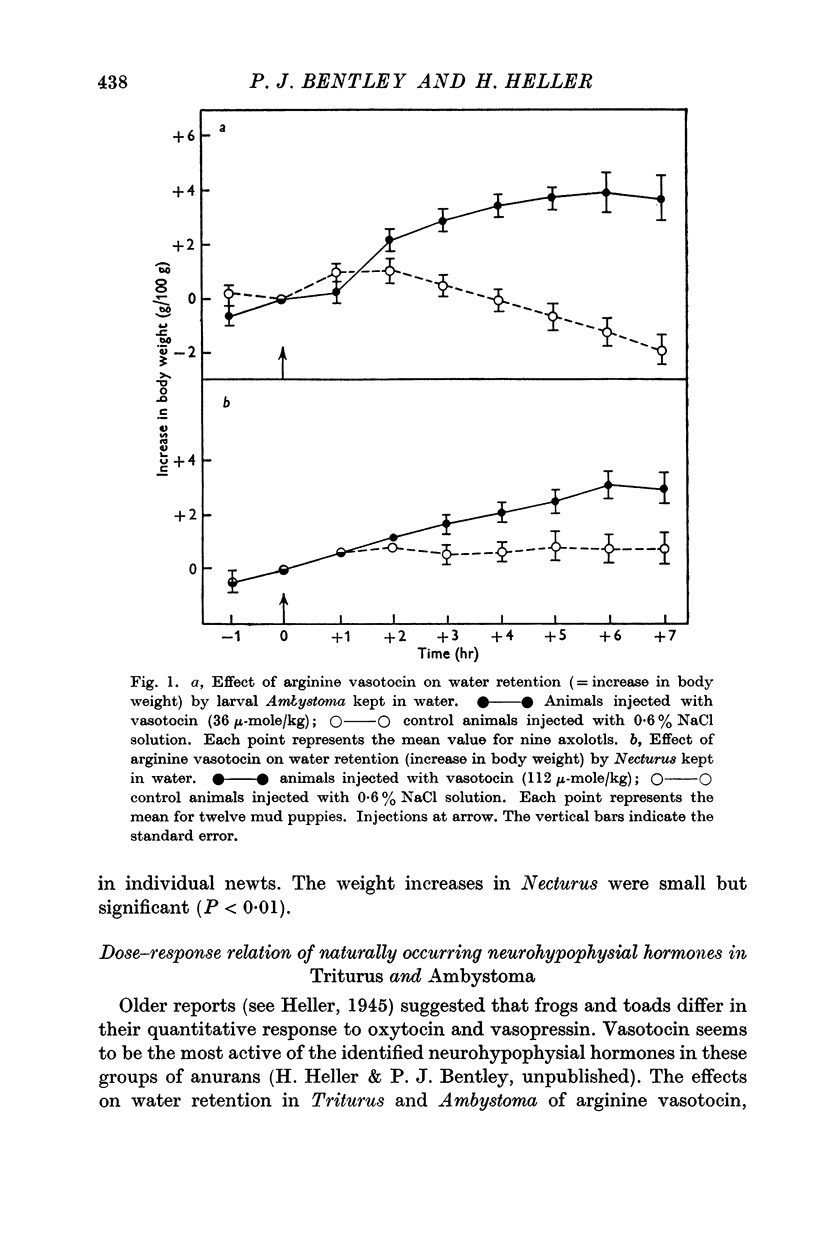
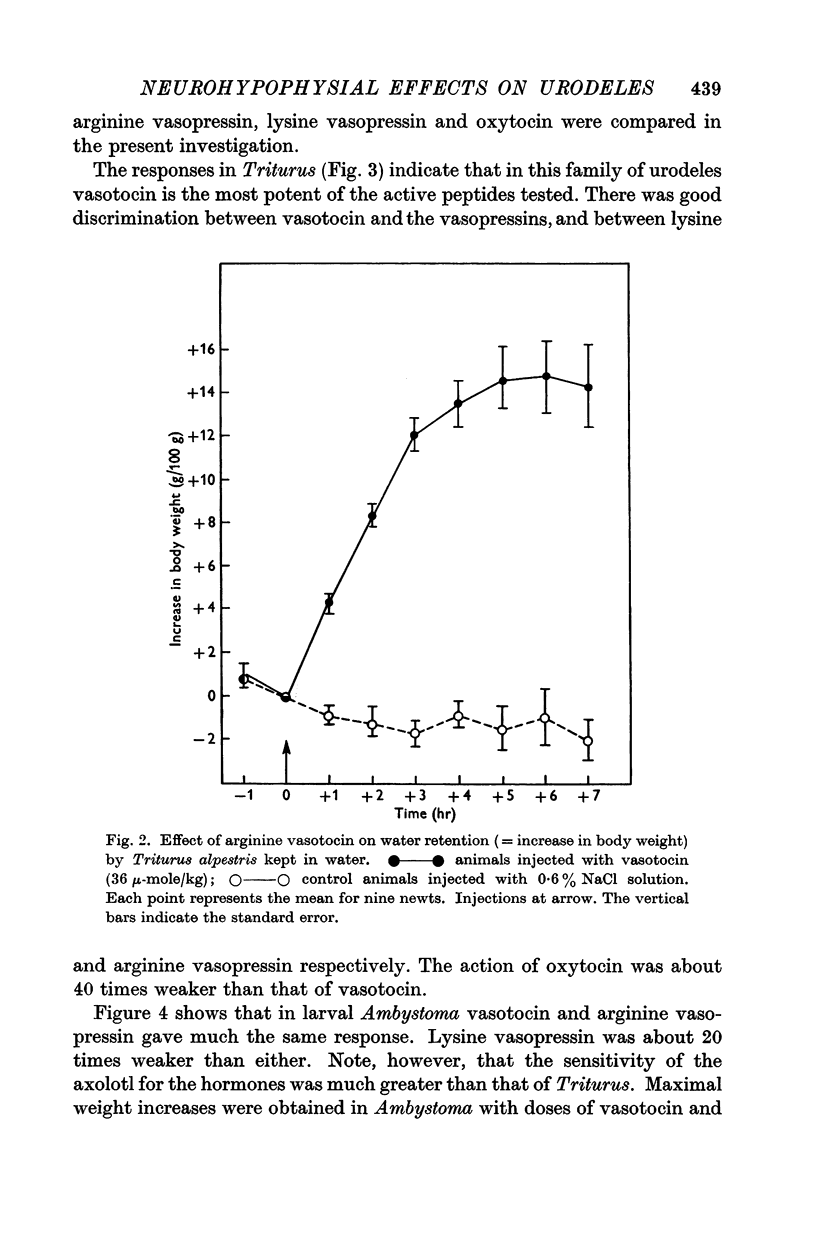
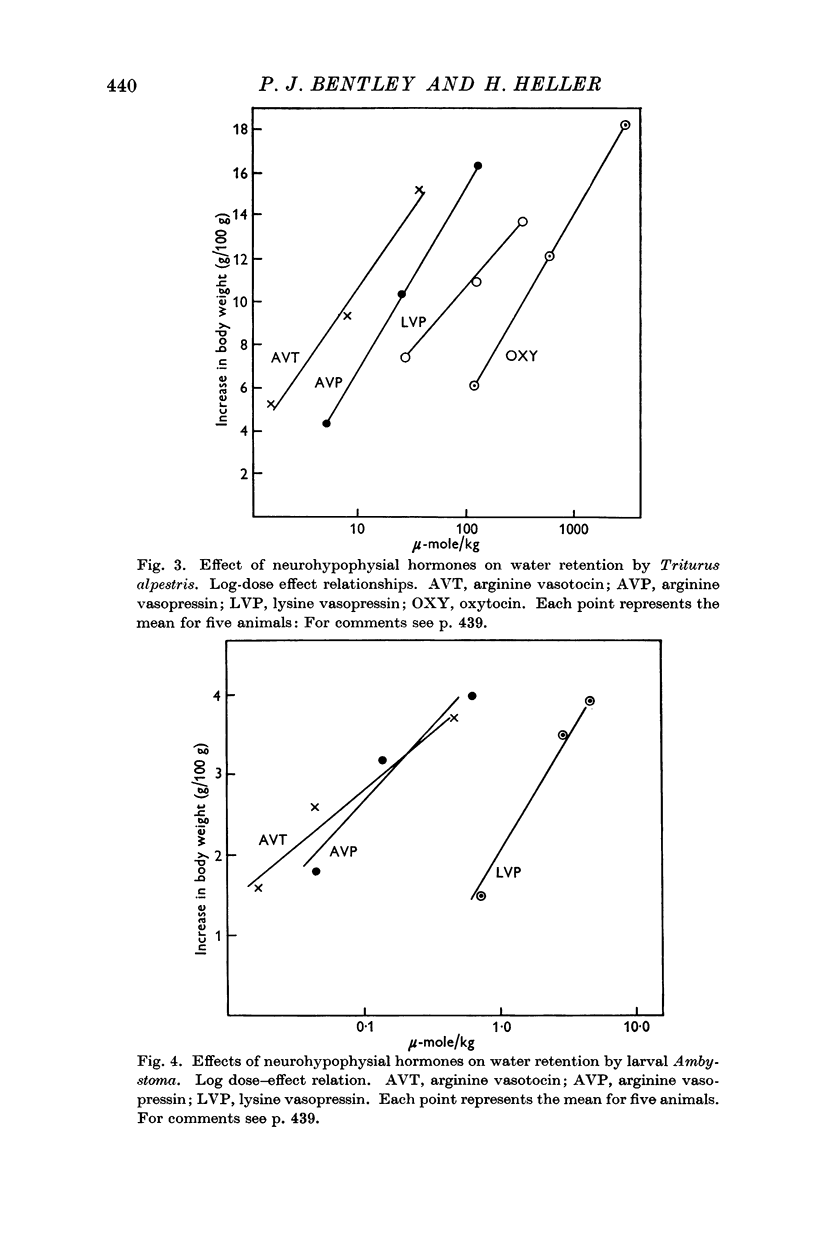



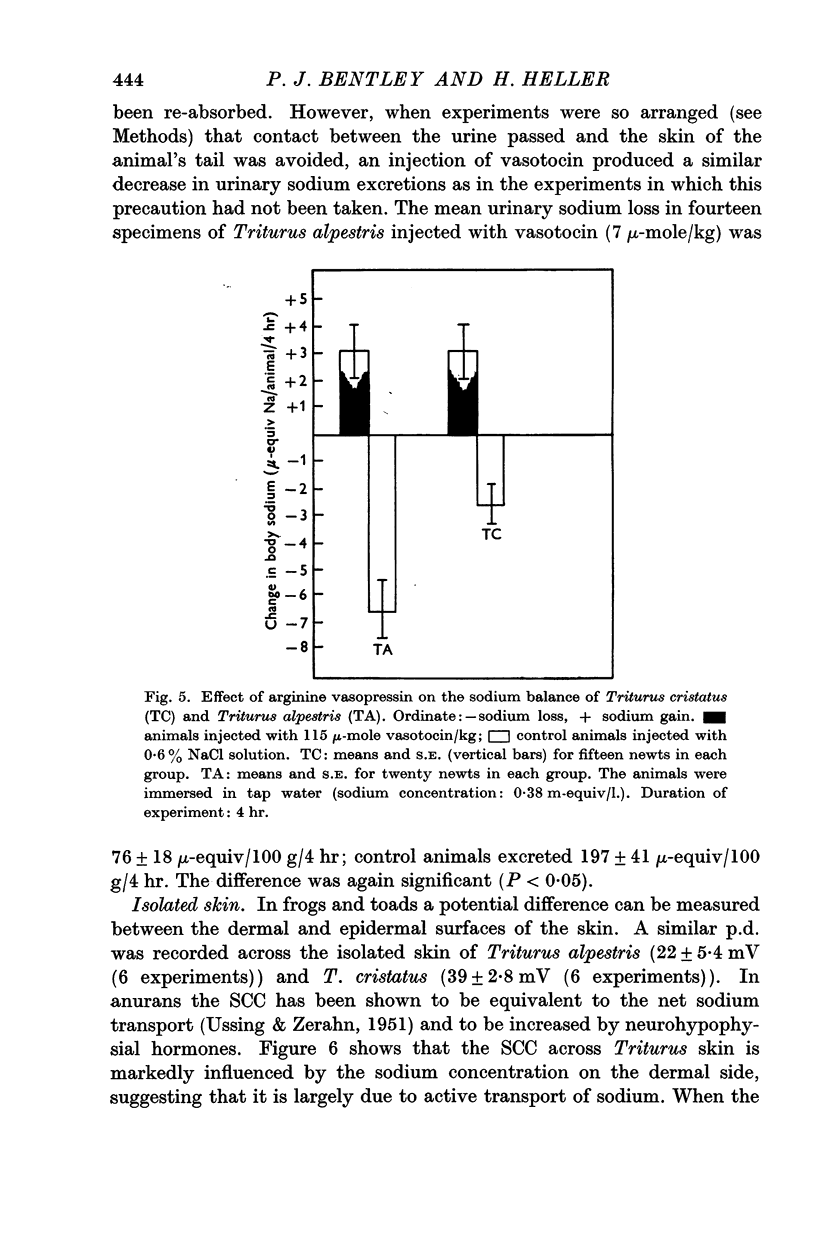
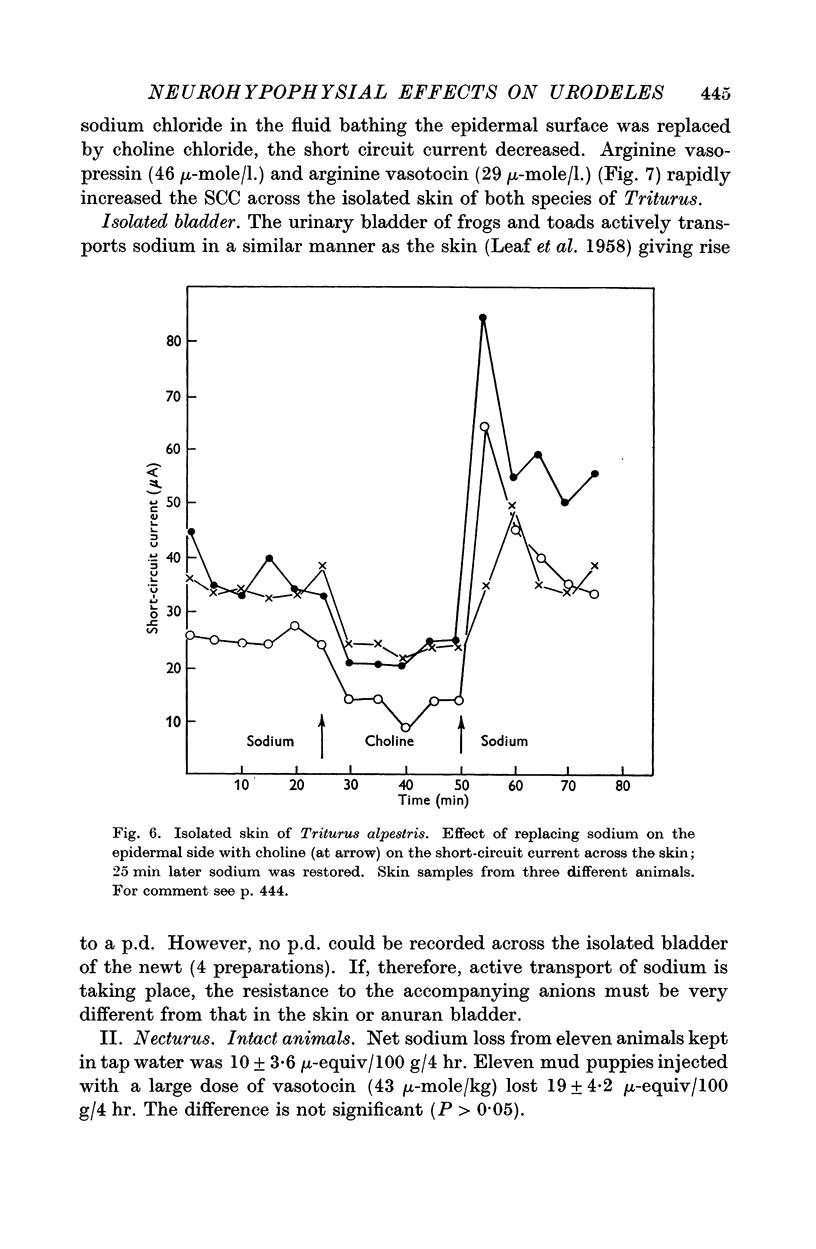
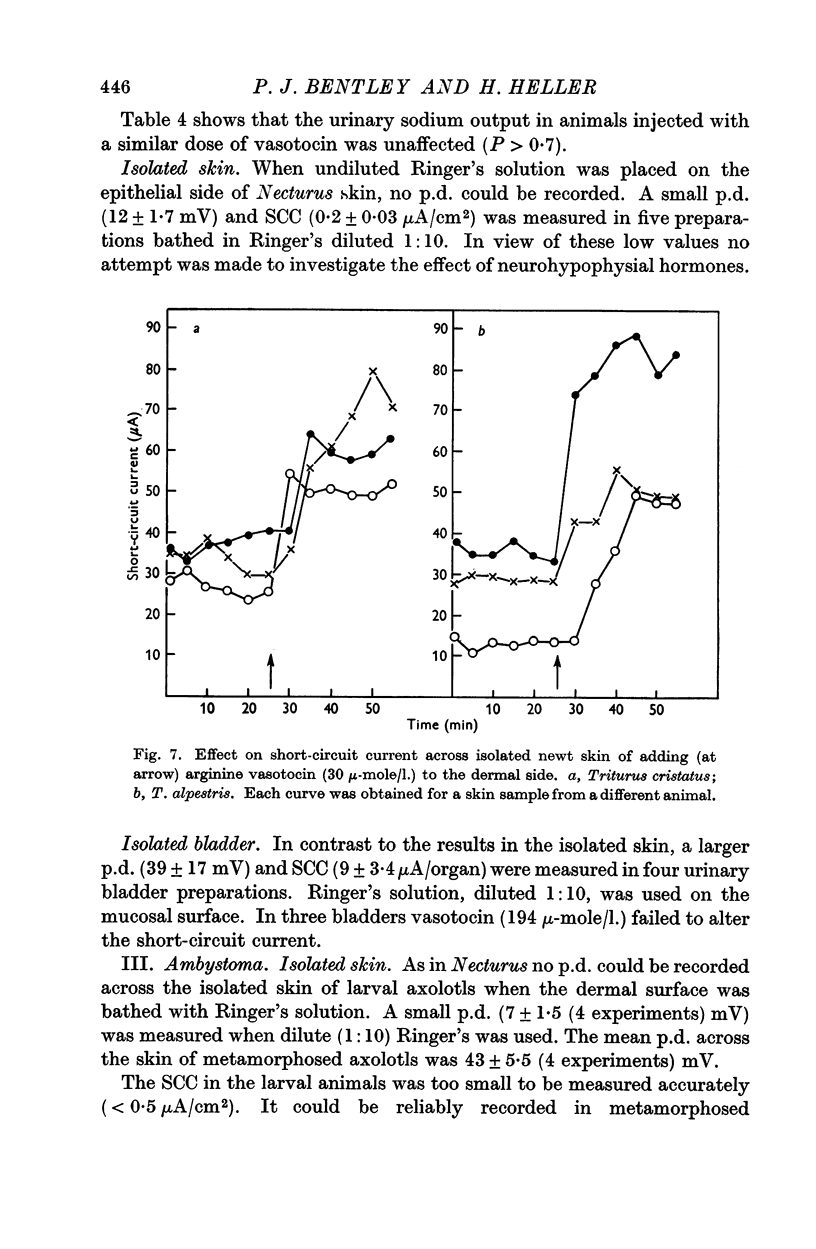







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENTLEY P. J. The effects of neurohypophysial extracts on the tadpole of the frog, Heleioporus eyrei. Endocrinology. 1959 Apr;64(4):609–610. doi: 10.1210/endo-64-4-609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENTLEY P. J. The effects of neurohypophysial extracts on the water transfer across the wall of the isolated urinary bladder of the toad Bufo marinus. J Endocrinol. 1958 Sep;17(3):201–209. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0170201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERDE B., HUGUENIN R., STURMER E. The biological activities of arginine-vasotocin obtained by a new synthesis. Experientia. 1962 Oct 15;18:444–445. doi: 10.1007/BF02175846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURGUET J., MAETZ J. [Arguments in favor of the independence of the mechanisms of action of various neurohypophyseal hormones on the osmotic flux of water and on the active transport of sodium in the same receptor; studies on the bladder and the skin of Rana esculenta L]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 30;52:552–565. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90414-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEKANSKI J. The quantitative assay of vasopressin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Dec;7(4):567–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb00723.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKER S. E., EGGLETON M. G. Renal excretion of hyaluronidase and calcium in man during the antidiuretic action of vasopressins and some analogues. J Physiol. 1961 Jul;157:351–362. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLLETT B. K., HELLER H. PHARMACOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF NEUROHYPOPHYSIAL HORMONES IN LUNGFISH AND AMPHIBIANS. Nature. 1963 Aug 10;199:611–612. doi: 10.1038/199611a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLER H., PICKERING B. T. Neurohypophysial hormones of non-mammalian vertebrates. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:98–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JARD S., MOREL F. Actions of vasotocin and some of its analogues on salt and water excretion by the frog. Am J Physiol. 1962 Feb;204:222–226. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATSOYANNIS P. G., DU VIGNEAUD V. Arginine-vasotocin, a synthetic analogue of the posterior pituitary hormones containing the ring of oxytocin and the side chain of vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1352–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A., ANDERSON J., PAGE L. B. Active sodium transport by the isolated toad bladder. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Mar 20;41(4):657–668. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A. Some actions of neurohypophyseal hormones on a living membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1960 May;43:175–189. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.5.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINSKY N. G., SAWYER W. H. Significance of the neurohypophysis in regulation of fluid balance in the frog. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Feb;82(2):272–274. doi: 10.3181/00379727-82-20089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIGHT A., STUDER R. O., DU VIGNEAUD V. Isolation of oxytocin and arginine vasopressin by way of a protein complex on a preparative scale. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Jul;83(1):84–87. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOREL F., MAETZ J., LUCARAIN C. Action des deux peptides neurohypophysalres sur le transport actif de sodium et le flux net d'eau à travers la peau de diverses espèces de batraciens anoures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Jun;28(3):619–626. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90529-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PICKERING B. T., HELLER H. Chromatographic and biological characteristics of fish and frog neuro-hypophysial extracts. Nature. 1959 Nov 7;184:1463–1464. doi: 10.1038/1841463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACHS H. Vasopressin biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Aug;34:572–573. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90319-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER W. H., MUNSICK R. A., VANDYKE H. B. Pharmacological evidence for the presence of arginine vasotocin and oxytocin in neurohypophysial extracts from cold-blooded vertebrates. Nature. 1959 Nov 7;184:1464–1465. doi: 10.1038/1841464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER W. H., SCHISGALL R. M. Increased permeability of the frog bladder to water in response to dehydration and neurohypophysial extracts. Am J Physiol. 1956 Nov;187(2):312–314. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHREIBER V., SCHREIBEROVA O. Réaction de Brunn chez les axolotls. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1951 Apr;145(7-8):619–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USSING H. H., ZERAHN K. Active transport of sodium as the source of electric current in the short-circuited isolated frog skin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1951 Aug 25;23(2-3):110–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1951.tb00800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


