Abstract
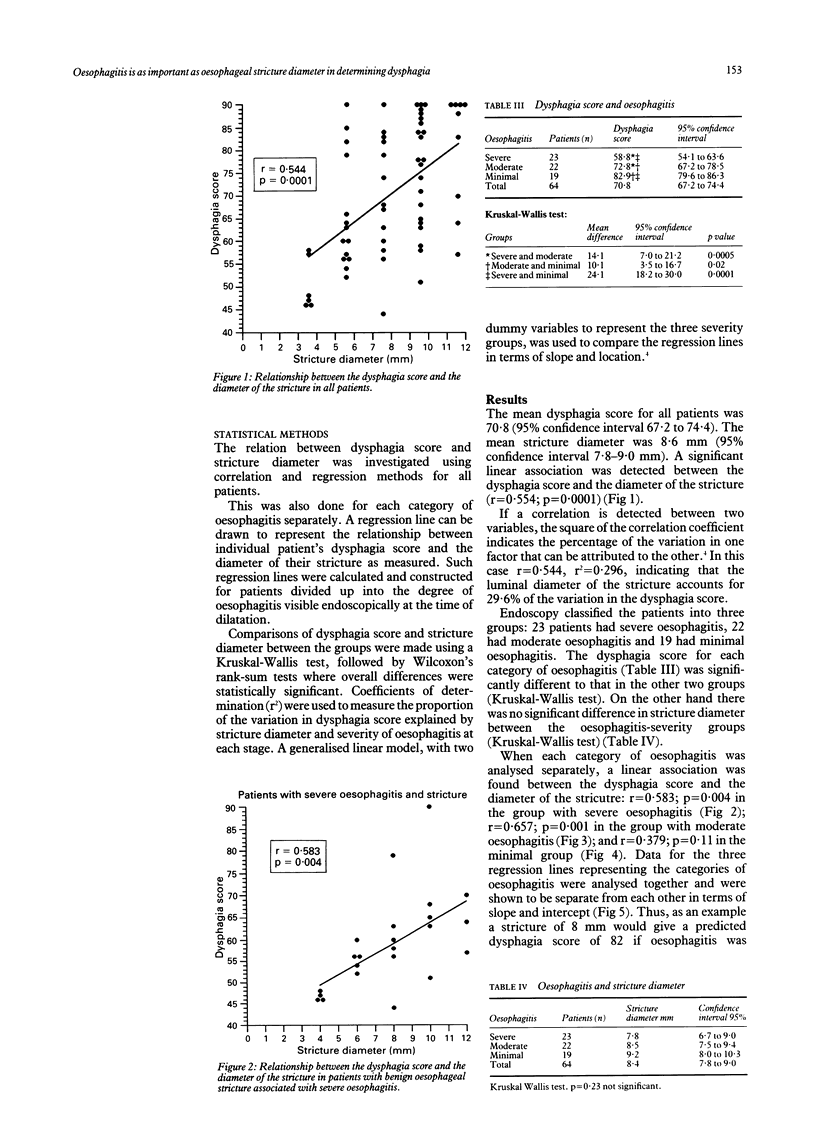
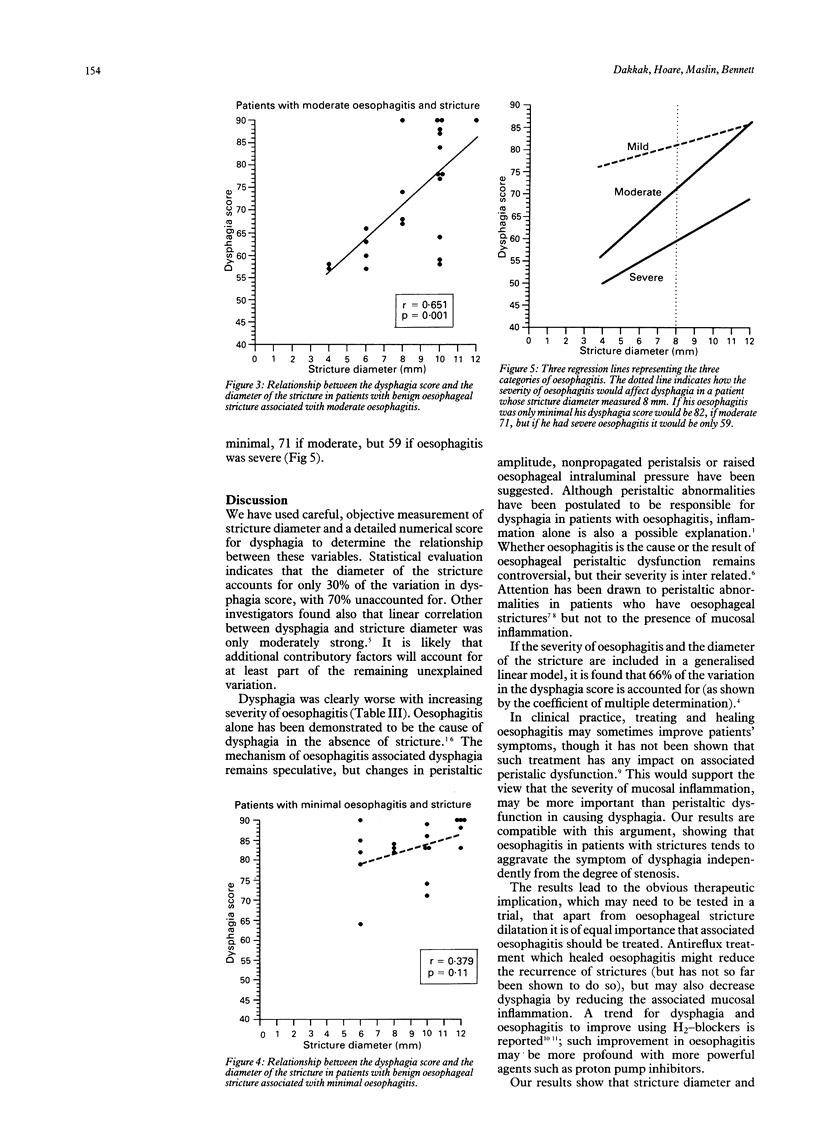
It is a common observation that stricture patients with severe dysphagia may have a wide lumen, while others with a narrow stricture have few swallowing complaints. In 64 patients with benign oesophageal stricture the dysphagia score (determined by questionnaire and by a test meal both based on nine different items of food scored according to their solidity) was compared with the diameter of the stricture measured radiologically by premeasured barium spheres. There was evidence of an association, but the correlation coefficient (r) was 0.544 (p = 0.0001), suggesting that the diameter of the stricture is an important, although not the sole, determinant of dysphagia. Stricture diameter explains 29.6% (r2) of variation in dysphagia score. The patients (mean dysphagia score 71 of a maximum possible 90) were divided into three groups according to the severity of oesophagitis (19 patients had minimal, 22 moderate and 23 severe oesophagitis). Analysis revealed the mean dysphagia score to be 83, 73, 59 in each group respectively. Dysphagia score of each group was significantly different from the others (Kruskal-Wallis test). Relating the dysphagia score to stricture diameter for each group gives correlation coefficient r = 0.379 (p = 0.110) in the minimal oesophagitis group, r = 0.651 (p = 0.001) in the moderate group, r = 0.583 (p = 0.004) in the severe group. If both diameter and severity of oesophagitis are included then 66.0% of the variation can be explained. It is concluded that the degree of oesophagitis is as important as luminal diameter in determining swallowing ability.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahtaridis G., Snape W. J., Jr, Cohen S. Clinical and manometric findings in benign peptic strictures of the esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Nov;24(11):858–861. doi: 10.1007/BF01324902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldi F., Ferrarini F., Longanesi A., Angeloni M., Ragazzini M., Miglioli M., Barbara L. Oesophageal function before, during, and after healing of erosive oesophagitis. Gut. 1988 Feb;29(2):157–160. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dakkak M., Bennett J. R. A new dysphagia score with objective validation. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1992 Mar;14(2):99–100. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199203000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyet J. F., Bennett J. R., Buckton G., Ashworth D. The radiological measurement of oesophageal stricture diameter. Clin Radiol. 1983 Nov;34(6):647–649. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(83)80414-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson R., Dronfield M. W., Atkinson M. Cimetidine in treatment of reflux oesophagitis with peptic stricture. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 25;2(6188):472–474. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6188.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmid S., Boyce H. W., Jr, Brown J. I., Brady P. G., Nord H. J., Lyman G. H. A new objective measurement of esophageal lumen patency. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Oct;84(10):1255–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahrilas P. J., Dodds W. J., Hogan W. J., Kern M., Arndorfer R. C., Reece A. Esophageal peristaltic dysfunction in peptic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):897–904. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90692-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little A. G., Correnti F. S., Calleja I. J., Montag A. G., Chow Y. C., Ferguson M. K., Skinner D. B. Effect of incomplete obstruction on feline esophageal function with a clinical correlation. Surgery. 1986 Aug;100(2):430–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxton D. G., Ainley C. C., Grainger S. L., Morris R. W., Thompson R. P. Teeth and benign oesophageal stricture. Gut. 1987 Jan;28(1):61–63. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triadafilopoulos G. Nonobstructive dysphagia in reflux esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Jun;84(6):614–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesdorp E., Bartelsman J., Pape K., Dekker W., Tytgat G. N. Oral cimetidine in reflux esophagitis: a double blind controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 1978 May;74(5 Pt 1):821–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


