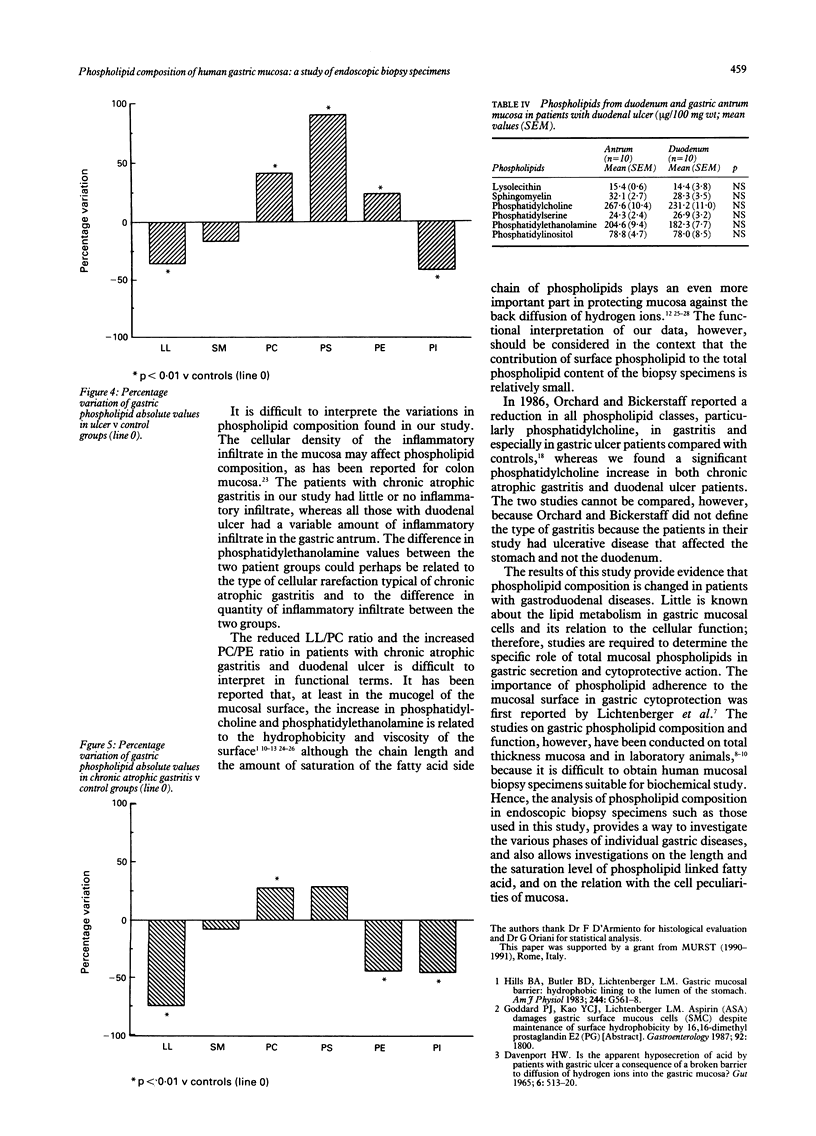
Abstract
Gastric mucosal phospholipids, and in particular those of the surface layer, play an important part in mucosal barrier function. This study examined whether the phospholipid composition of the full thickness gastric mucosa is changed in peptic ulcer disease and gastritis. The phospholipid composition of gastric mucosa from endoscopic biopsy specimens in 28 subjects (eight healthy controls, 12 patients with duodenal ulcer, and eight with chronic atrophic gastritis) was studied. In addition, the phospholipid composition of gastric mucosa was compared with that of duodenal mucosa in 10 patients with duodenal ulcer. As expected phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine prevailed in all three groups. Lysolecithin was the smallest component in the duodenal ulcer and chronic atrophic gastritis groups. The phosphatidylethanolamine value was higher in duodenal ulcer and lower in chronic atrophic gastritis compared with the control group. In chronic atrophic gastritis there was an appreciable amount of phosphatidylglycerol that was not present in patients with duodenal ulcer or in the control group. There was no significant difference in phospholipid composition between antral and duodenal sites in duodenal ulcer patients. In conclusion, the phospholipid composition of gastric mucosa changes in human gastrointestinal diseases but its relation to cellular functions needs further study.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butler B. D., Lichtenberger L. M., Hills B. A. Distribution of surfactants in the canine gastrointestinal tract and their ability to lubricate. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):G645–G651. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.6.G645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport H. W. Is the apparent hyposecretion of acid by patients with gastric ulcer a consequence of a broken barrier to diffusion of hydrogen ions into the gastric mucosa? Gut. 1965 Oct;6(5):513–513. doi: 10.1136/gut.6.5.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard P. J., Hills B. A., Lichtenberger L. M. Does aspirin damage canine gastric mucosa by reducing its surface hydrophobicity? Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 1):G421–G430. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.3.G421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong D. H., Turner B., Bhaskar K. R., Lamont J. T. Lipid binding to gastric mucin: protective effect against oxygen radicals. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):G681–G686. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.4.G681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills B. A., Butler B. D., Lichtenberger L. M. Gastric mucosal barrier: hydrophobic lining to the lumen of the stomach. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):G561–G568. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.5.G561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills B. A., Kirwood C. A. Surfactant approach to the gastric mucosal barrier: protection of rats by banana even when acidified. Gastroenterology. 1989 Aug;97(2):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills B. A., Lichtenberger L. M. Gastric mucosal barrier: hydrophobicity of stretched stomach lining. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 1):G643–G647. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.6.G643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills B. A. Water repellency induced by pulmonary surfactants. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:175–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiviluoto T., Paimela H., Mustonen H., Kivilaakso E. Exogenous surface-active phospholipid protects Necturus gastric mucosa against luminal acid and barrier-breaking agents. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):38–46. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90580-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laccetti P., Grollman E. F., Aloj S. M., Kohn L. D. Ganglioside dependent return of TSH receptor function in a rat thyroid tumor with a TSH receptor defect. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 10;110(3):772–778. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberger L. M., Graziani L. A., Dial E. J., Butler B. D., Hills B. A. Role of surface-active phospholipids in gastric cytoprotection. Science. 1983 Mar 18;219(4590):1327–1329. doi: 10.1126/science.6828859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberger L. M., Richards J. E., Hills B. A. Effect of 16,16-dimethyl prostaglandin E2 on the surface hydrophobicity of aspirin-treated canine gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jan;88(1 Pt 2):308–314. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murty V. L., Sarosiek J., Slomiany A., Slomiany B. L. Effect of lipids and proteins on the viscosity of gastric mucus glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90213-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida T., Miwa H., Shigematsu A., Yamamoto M., Iida M., Fujishima M. Increased arachidonic acid composition of phospholipids in colonic mucosa from patients with active ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1987 Aug;28(8):1002–1007. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.8.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarosiek J., Slomiany A., Takagi A., Slomiany B. L. Hydrogen ion diffusion in dog gastric mucus glycoprotein: effect of associated lipids and covalently bound fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 30;118(2):523–531. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. G., Renooij W. Phospholipids from rat, human, and canine gastric mucosa. Composition and metabolism of molecular classes of phosphatidylcholine. Gastroenterology. 1990 Nov;99(5):1292–1296. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91152-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany A., Yano S., Slomiany B. L., Glass G. B. Lipid composition of the gastric mucous barrier in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3785–3791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassef M. K., Lin Y. N., Horowitz M. I. Molecular species of phosphatidylcholine from rat gastric mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 27;573(1):222–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90191-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]