Abstract
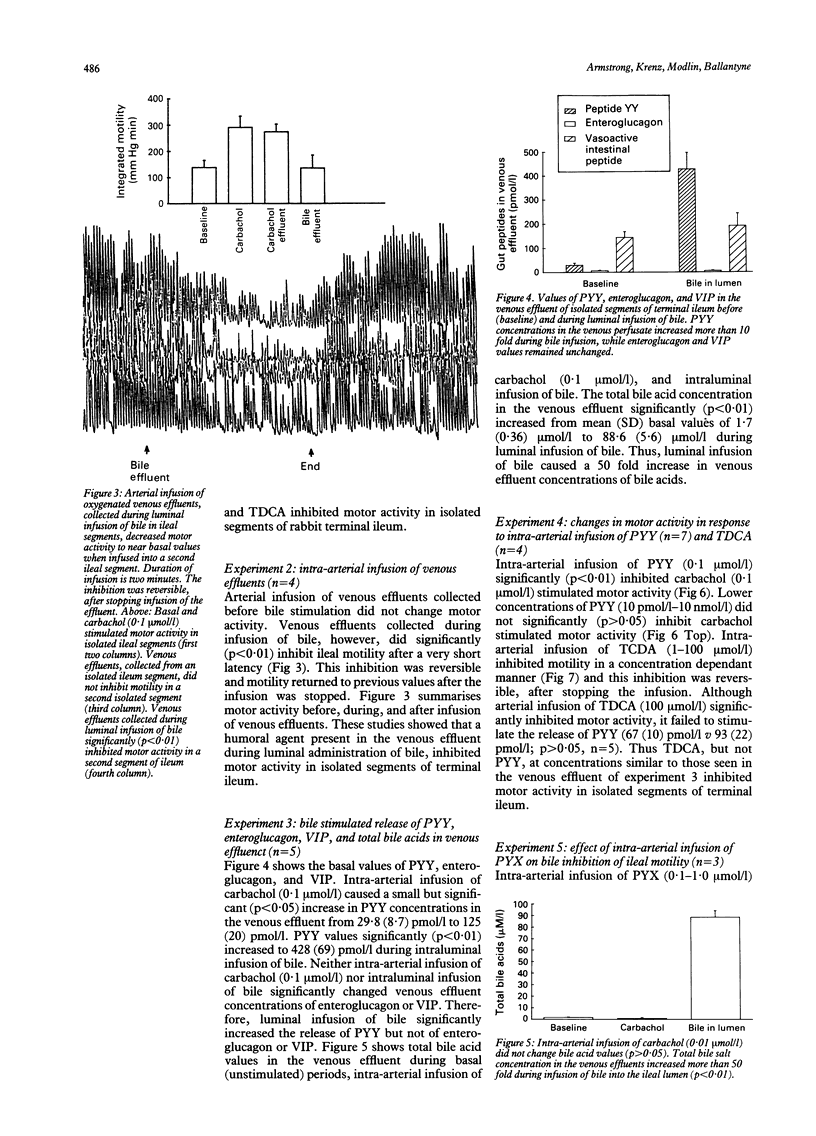
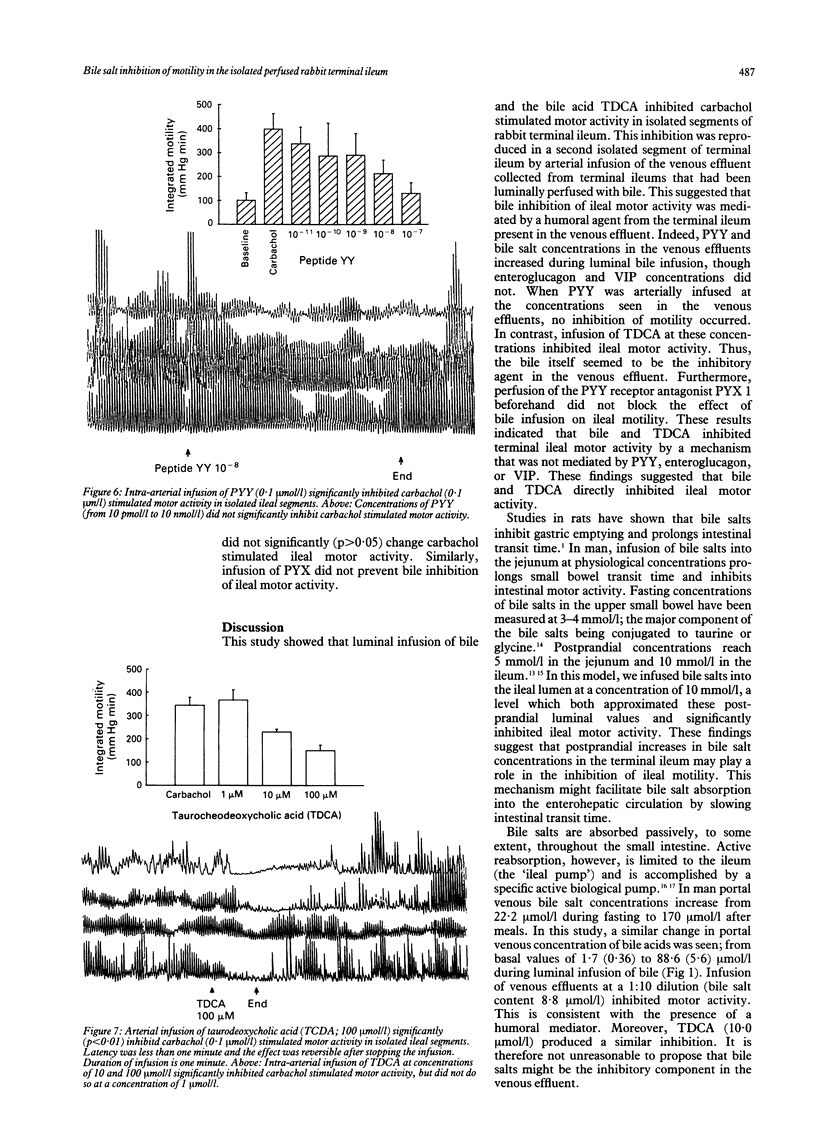
The effects of bile on small bowel motility were studied in isolated, perfused rabbit terminal ileum. It was proposed that bile delivery into the distal ileum would inhibit ileal motor activity, by peptide YY (PYY) release and therefore the effect of luminal bile on motor activity was examined and PYY release measured. Luminal bile and taurocheodeoxycholic acid (10 mmol) inhibited ileal motor activity. Arterial infusion of venous effluents from a bile inhibited ileum suppressed motor activity in a second isolated ileum. This shows the presence of a humoral inhibitor of ileal motor activity. Luminal bile increased venous PYY concentrations (42.5 (8.5) to 502 (46.2) pmol/l; p < 0.01) and increased bile salt values (1.7 (0.36) to 88.6 (5.6) 10 mumol/l/l; p < 0.005). Arterial infusion of taurocheodeoxycholic acid at concentrations found in the venous effluent (100 mumol/l/l) suppressed motility (p < 0.001) but infusion of PYY at concentrations in the venous effluent (500.0 pmol/l) failed to inhibit motility. Furthermore, PYY antagonist, PYX 1, failed to reverse the bile induced inhibition of motility. Luminal bile salts inhibit terminal ileal motility and this is independent of PYY release. By slowing motility, bile salts may participate in their own absorption by the 'ileal pump' and in the 'ileal brake' mechanism.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian T. E., Ferri G. L., Bacarese-Hamilton A. J., Fuessl H. S., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Human distribution and release of a putative new gut hormone, peptide YY. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):1070–1077. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian T. E., Savage A. P., Bacarese-Hamilton A. J., Wolfe K., Besterman H. S., Bloom S. R. Peptide YY abnormalities in gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterology. 1986 Feb;90(2):379–384. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90936-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne G. H., Longo W. E., Savoca P. E., Adrian T. E., Vukasin A. P., Bilchik A. J., Sussman J., Modlin I. M. Deoxycholate-stimulated release of peptide YY from the isolated perfused rabbit left colon. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 1):G715–G724. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.5.G715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chijiiwa Y., Misawa T., Ibayashi H. Evidence of local mechanism involvement in vasoactive intestinal polypeptide release from canine small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jun;90(6):1877–1881. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M. Mechanisms for the intestinal absorption of bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):297–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domschke S., Domschke W., Bloom S. R., Mitznegg P., Mitchell S. J., Lux G., Strunz U. Vasoactive intestinal peptide in man: pharmacokinetics, metabolic and circulatory effects. Gut. 1978 Nov;19(11):1049–1053. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.11.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S., Gibaldi M. Effect of bile salts on gastric emptying and intestinal transit in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1968 May;54(5):918–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Daniel E. E., Jury J., Robotham H. Muscarinic inhibition of canine small intestinal motility in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):G526–G531. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.5.G526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grider J. R., Makhlouf G. M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide. Transmitter of inhibitory motor neurons of the gut. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;527:369–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb26993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman L. Y., Sayadi H., Bass B., Moody T. W., Harmon J. W. Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and substance P receptors in human colon and small intestine. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Jul;34(7):1100–1108. doi: 10.1007/BF01536382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northfield T. C., McColl I. Postprandial concentrations of free and conjugated bile acids down the length of the normal human small intestine. Gut. 1973 Jul;14(7):513–518. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.7.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penagini R., Misiewicz J. J., Frost P. G. Effect of jejunal infusion of bile acids on small bowel transit and fasting jejunal motility in man. Gut. 1988 Jun;29(6):789–794. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.6.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penagini R., Spiller R. C., Misiewicz J. J., Frost P. G. Effect of ileal infusion of glycochenodeoxycholic acid on segmental transit, motility, and flow in the human jejunum and ileum. Gut. 1989 May;30(5):609–617. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.5.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam W. S., Liddle R. A., Williams J. A. Inhibitory regulation of rat exocrine pancreas by peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):G698–G703. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.4.G698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SJOVALL J., AKESSON I. Intestinal absorption of taurocholic acid in the rat. Bile acids and steroids, 26. Acta Physiol Scand. 1955 Oct 27;34(2-3):273–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1955.tb01246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna S. K., Soergel K. H., Harig J. M., Loo F. D., Wood C. M., Donahue K. M., Ryan R. P., Arndorfer R. C. Spatial and temporal patterns of human jejunal contractions. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):G423–G432. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.3.G423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage A. P., Adrian T. E., Carolan G., Chatterjee V. K., Bloom S. R. Effects of peptide YY (PYY) on mouth to caecum intestinal transit time and on the rate of gastric emptying in healthy volunteers. Gut. 1987 Feb;28(2):166–170. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiller R. C., Trotman I. F., Higgins B. E., Ghatei M. A., Grimble G. K., Lee Y. C., Bloom S. R., Misiewicz J. J., Silk D. B. The ileal brake--inhibition of jejunal motility after ileal fat perfusion in man. Gut. 1984 Apr;25(4):365–374. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.4.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. W., Anuras S., Green J. Jejunal manometry patterns in health, partial intestinal obstruction, and pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1290–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y and its receptor antagonists. Use of an analog mixture-screening strategy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;611:1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb48917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. W., Lu Y. X., Chung O. Y. Mechanism of action of peptide YY to inhibit gastric motility. Gastroenterology. 1991 Apr;100(4):865–872. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90257-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


