Abstract
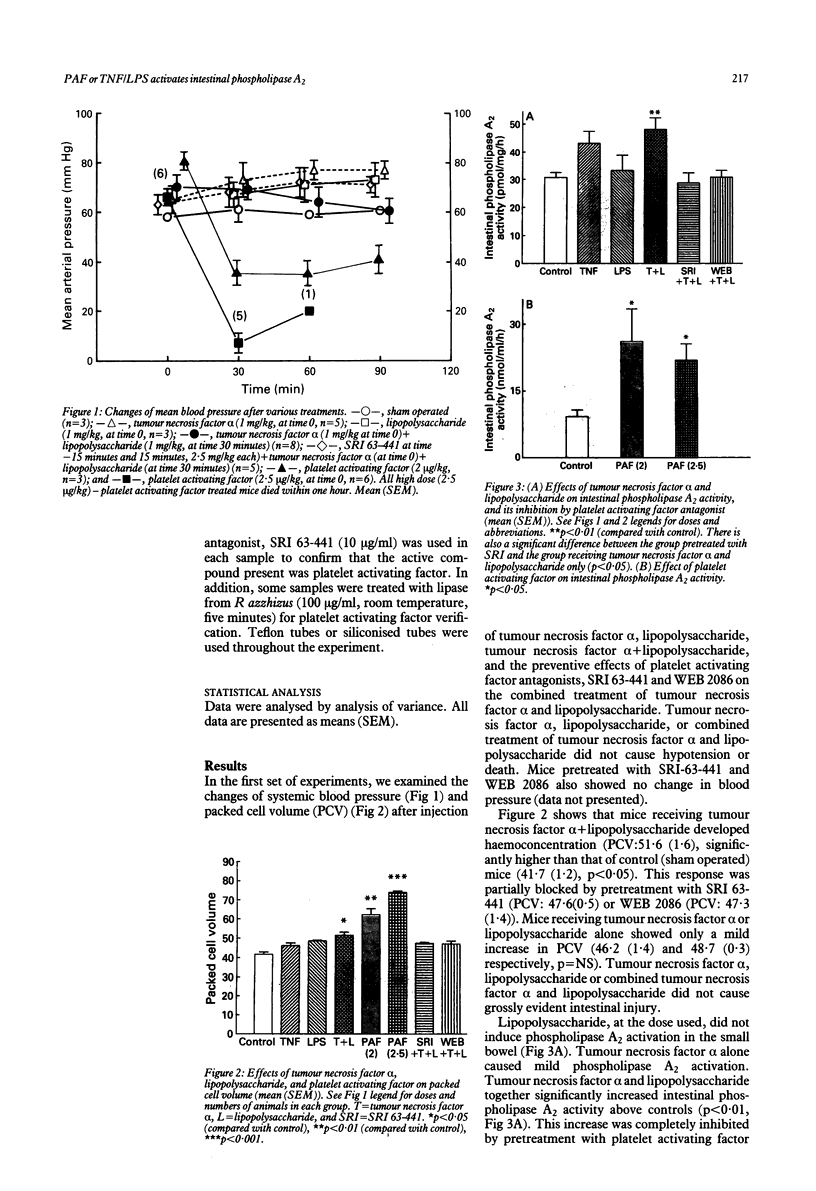
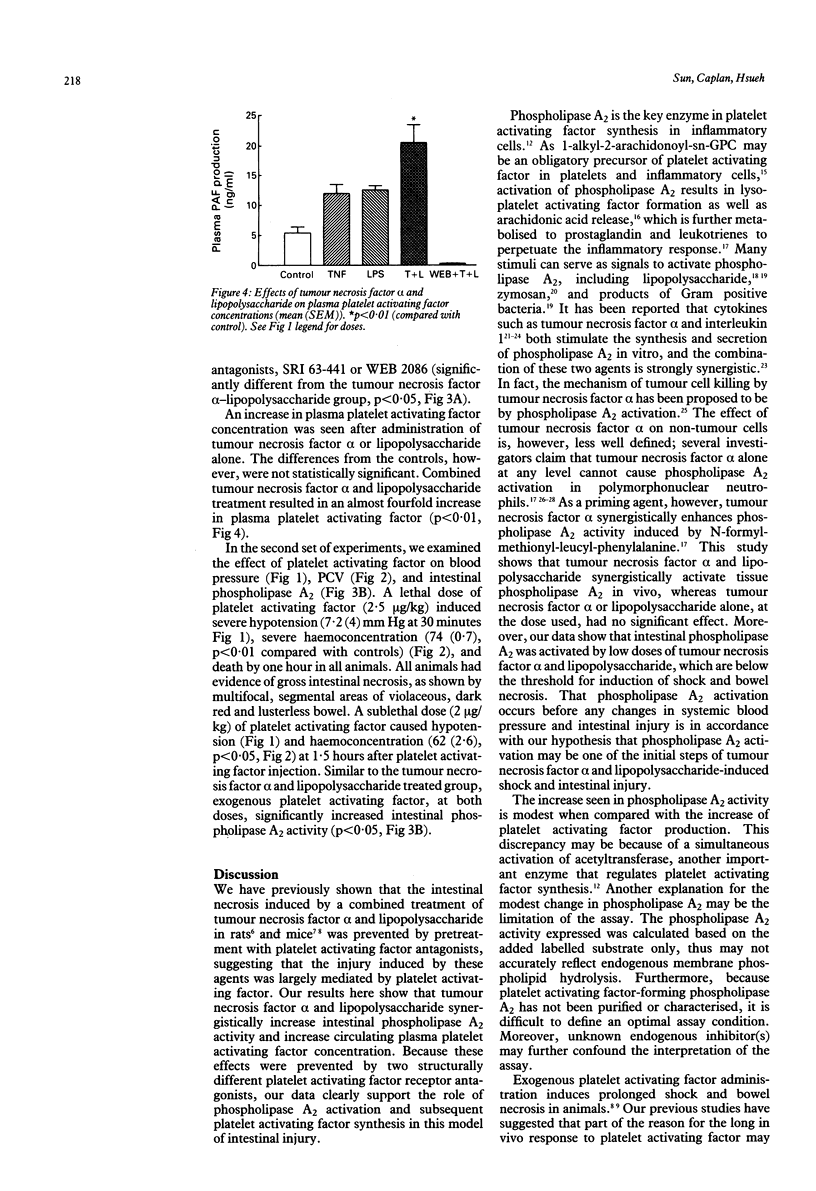
Previous studies have shown that: (a) platelet activating factor induces shock and intestinal injury, (b) exogenous platelet activating factor stimulates synthesis of endogenous platelet activating factor, and (c) tumour necrosis factor alpha and endotoxin synergise to induce shock and bowel injury in animals. These last two effects are largely mediated by platelet activating factor forming phospholipase A2 A2, a key enzyme for platelet activating factor synthesis, was examined in mouse intestine. It was found that tumour necrosis factor alpha and endotoxin synergise to stimulate platelet activating factor forming phospholipase A2 activity in the intestine, as well as platelet activating factor production, and these effects were blocked by pretreatment with platelet activating factor antagonists, SRI-63-441 and WEB 2086. In addition, exogenous platelet activating factor stimulates intestinal phospholipase A2 activity. These results show that tumour necrosis factor alpha and lipopolysaccharide synergistically activate the phospholipase A2 that participates in platelet activating factor formation, and this activation is largely mediated by endogenous platelet activating factor. Furthermore, platelet activating factor itself increases phospholipase A2 activity, suggesting that platelet activating factor induces its own synthesis, probably by phospholipase A2 activation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauldry S. A., McCall C. E., Cousart S. L., Bass D. A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha priming of phospholipase A2 activation in human neutrophils. An alternative mechanism of priming. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1277–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J. Paf-acether, an ether phospho-lipid with biological activity. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;282:73–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Bryant R. W., Siegel M. I. Lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid modulate biosynthesis of platelet-activating factor (1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) by human neutrophils via phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6899–6906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Gilman S. C., Lewis A. J. Interleukin 1 activates phospholipase A2 in rabbit chondrocytes: a possible signal for IL 1 action. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1283–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton F. H., Ellis J. M., Olson S. C., Wykle R. L. 1-O-alkyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. A common source of platelet-activating factor and arachidonate in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12014–12019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton F. H., O'Flaherty J. T., Walsh C. E., Thomas M. J., Wykle R. L., DeChatelet L. R., Waite B. M. Platelet activating factor. Stimulation of the lipoxygenase pathway in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5402–5407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diez E., Mong S. Purification of a phospholipase A2 from human monocytic leukemic U937 cells. Calcium-dependent activation and membrane association. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14654–14661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman S. C., Chang J., Zeigler P. R., Uhl J., Mochan E. Interleukin-1 activates phospholipase A2 in human synovial cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jan;31(1):126–130. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh W., Gonzalez-Crussi F., Arroyave J. L. Platelet-activating factor-induced ischemic bowel necrosis. An investigation of secondary mediators in its pathogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):231–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh W., Gonzalez-Crussi F., Arroyave J. L. Release of leukotriene C4 by isolated, perfused rat small intestine in response to platelet-activating factor. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):108–114. doi: 10.1172/JCI112538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh W., Gonzalez-Crussi F., Arroyave J. L. Sequential release of leukotrienes and norepinephrine in rat bowel after platelet-activating factor. A mechanistic study of platelet-activating factor-induced bowel necrosis. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jun;94(6):1412–1418. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90680-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh W., González-Crussi F., Arroyave J. L. Platelet-activating factor: an endogenous mediator for bowel necrosis in endotoxemia. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):403–405. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.5.3678700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh W., Sun X., Rioja L. N., Gonzalez-Crussi F. The role of the complement system in shock and tissue injury induced by tumour necrosis factor and endotoxin. Immunology. 1990 Jul;70(3):309–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi H., Yasuda H. Effect of platelet-activating factor on arachidonic acid metabolism in renal epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 28;875(3):525–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Jakubowski J. A., Deykin D. Hydrolysis of 1-alkyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, a common precursor of platelet-activating factor and eicosanoids, by human platelet phospholipase A2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 15;959(3):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudanna C., Miron S., Berton G., Rossi F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha/cachectin activates the O2(-)-generating system of human neutrophils independently of the hydrolysis of phosphoinositides and the release of arachidonic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):308–315. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91946-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luedke E. S., Humes J. L. Effect of tumor necrosis factor on granule release and LTB4 production in adherent human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Agents Actions. 1989 Jun;27(3-4):451–454. doi: 10.1007/BF01972850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima S., Suganuma A., Sato M., Tohmatsu T., Nozawa Y. Mechanism of arachidonic acid liberation in platelet-activating factor-stimulated human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1295–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Pignat W., Vosbeck K., Märki F. Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor synergistically stimulate prostaglandin synthesis and phospholipase A2 release from rat renal mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):385–394. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubin R., Elsas P. P., Fiers W., Dessein A. J. Recombinant human tumour necrosis factor (rTNF)2 enhances leukotriene biosynthesis in neutrophils and eosinophils stimulated with the Ca2+ ionophore A23187. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Nov;70(2):484–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder F. Biochemistry of platelet-activating factor: a unique class of biologically active phospholipids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Feb;190(2):125–135. doi: 10.3181/00379727-190-42839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs D. R., Sherman M. L., Imamura K., Mohri M., Rodriguez C., Robbins G., Kufe D. W. Phospholipase A2 activation and autoinduction of tumor necrosis factor gene expression by tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 15;50(22):7101–7107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suffys P., Beyaert R., Van Roy F., Fiers W. Reduced tumour necrosis factor-induced cytotoxicity by inhibitors of the arachidonic acid metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):735–743. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Hsueh W. Bowel necrosis induced by tumor necrosis factor in rats is mediated by platelet-activating factor. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1328–1331. doi: 10.1172/JCI113459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. M., Hsueh W. Platelet-activating factor produces shock, in vivo complement activation, and tissue injury in mice. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):509–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessner T. G., O'Flaherty J. T., Wykle R. L. Stimulation of platelet-activating factor synthesis by a nonmetabolizable bioactive analog of platelet-activating factor and influence of arachidonic acid metabolites. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4794–4799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynor J. R., Authi K. S. Phospholipase A2 activity of lysosomal origin secreted by polymorphonuclear leucocytes during phagocytosis or on treatment with calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 24;665(3):571–577. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Hay J. B. Involvement of circulating phospholipase A2 in the pathogenesis of the hemodynamic changes in endotoxin shock. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;61(6):561–566. doi: 10.1139/y83-086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W., Stefanski E., Sternby B., Mustard R., Bohnen J., Fraser I., Farewell V., Bombardier C. Pathogenesis of hypotension in septic shock: correlation of circulating phospholipase A2 levels with circulatory collapse. Crit Care Med. 1988 Jan;16(1):1–7. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198801000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelkel N. F., Worthen S., Reeves J. T., Henson P. M., Murphy R. C. Nonimmunological production of leukotrienes induced by platelet-activating factor. Science. 1982 Oct 15;218(4569):286–289. doi: 10.1126/science.7123233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C., Hsueh W., Caplan M. S., Kelly A. Platelet activating factor-induced shock and intestinal necrosis in the rat: role of endogenous platelet-activating factor and effect of saline infusion. Crit Care Med. 1991 Aug;19(8):1067–1072. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199108000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


