Abstract
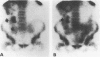
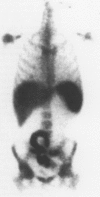
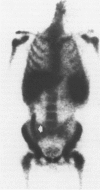
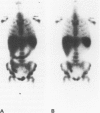
Scintigraphy with autologous granulocytes labelled by technetium-99m hexamethyl, propylene amine oxime (99mTc-HMPAO) was performed in 103 Crohn's disease patients and 52 healthy controls. In 31 patients endoscopic and histologic activity was compared with scan activity index. In the 98 patients with a positive scan, the extent of Crohn's disease, assessed by scintigraphy, was compared with that evaluated by small bowel x ray or colonoscopy with biopsies. In 48 patients, Crohn's disease activity index, activity index, simple index, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein were correlated with the scan results. In 16 patients the five parameters and scan were repeated after treatment with methyl-prednisolone (10 cases), enteral nutrition (3), and 5-acetylsalicylic acid (3). The results showed that 99mTc-HMPAO granulocyte scan had a 95% sensitivity and 100% specificity to detect active inflammation; it correctly showed an abscess or a fistula in all the 24 cases found. The correlation between histological inflammatory activity and scan activity index was highly significant (r = 0.85; p < 0.01), less significant (r = 0.65; p < 0.01) between endoscopy and scan activity index. The evaluation for the extent of Crohn's disease by scan was completely correct in the small bowel (100%) and 93% correct in the large bowel. No correlation was seen between the three clinical activity parameters and scanning; in more than 80% of the cases in remission on the basis of a clinical or laboratory index, scintigraphy remained positive. Medical treatment was effective on the clinical indices but not on the active inflammation in the ileum, whereas it led to a negative scan in 5/11 cases in the large intestine. Scintigraphy with 99mTc-HMPAO granulocyte plays an important part in Crohn's disease for the diagnosis of complications, for activity and assessment of the extent, and for the treatment results evaluation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andre C., Descos L., Landais P., Fermanian J. Assessment of appropriate laboratory measurements to supplement the Crohn's disease activity index. Gut. 1981 Jul;22(7):571–574. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.7.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker W. S., Saptogino A., Wolf F. G. The single late 99Tcm granulocyte antibody scan in inflammatory diseases. Nucl Med Commun. 1992 Mar;13(3):186–192. doi: 10.1097/00006231-199203000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker W., Fischbach W., Reiners C., Börner W. Three-phase white blood cell scan: diagnostic validity in abdominal inflammatory diseases. J Nucl Med. 1986 Jul;27(7):1109–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best W. R., Becktel J. M., Singleton J. W. Rederived values of the eight coefficients of the Crohn's Disease Activity Index (CDAI). Gastroenterology. 1979 Oct;77(4 Pt 2):843–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brignola C., Campieri M., Bazzocchi G., Farruggia P., Tragnone A., Lanfranchi G. A. A laboratory index for predicting relapse in asymptomatic patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1986 Dec;91(6):1490–1494. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll B., Silverman P. M., Goodwin D. A., McDougall I. R. Ultrasonography and indium 111 white blood cell scanning for the detection of intraabdominal abscesses. Radiology. 1981 Jul;140(1):155–160. doi: 10.1148/radiology.140.1.7244219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crama-Bohbouth G. E., Peña A. S., Arndt J. W., Tjon R. T., Tham A., Verspaget H. W., Weterman I. T., Pauwels E. K., Lamers C. B. Value of indium-111 tropolonate autologous granulocyte scintigraphy in the assessment of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1990;178:93–98. doi: 10.3109/00365529009093157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crama-Bohbouth G., Pena A. S., Biemond I., Verspaget H. W., Blok D., Arndt J. W., Weterman I. T., Pauwels E. K., Lamers C. B. Are activity indices helpful in assessing active intestinal inflammation in Crohn's disease? Gut. 1989 Sep;30(9):1236–1240. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.9.1236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Optimal conditions for simultaneous purification of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the Hypaque-Ficoll method. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson P., Lichtenstein M., Salehi N., Hebbard G., Andrews J. Value of positive technetium-99m leucocyte scans in predicting intestinal inflammation. Gut. 1991 Dec;32(12):1502–1507. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.12.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Bradshaw J. M. A simple index of Crohn's-disease activity. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):514–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarzian A., Price Y. E., Peters A. M., Lavender J. P., Wright N. A., Hodgson H. J. Specificity of indium-111 granulocyte scanning and fecal excretion measurement in inflammatory bowel disease--an autoradiographic study. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Dec;30(12):1156–1160. doi: 10.1007/BF01314050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantto E. H. Leucocytes labelled with 99mTc-HMPAO in the detection of abdominal abscesses. Eur J Surg. 1991 Aug;157(8):469–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantto E., Järvi K., Krekelä I., Lantto T., Taavitsainen M., Vedenkangas H., Vorne M. Technetium-99m hexamethyl propylene amine oxine leucocytes in the assessment of disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Nucl Med. 1992;19(1):14–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00178302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard-Jones J. E. Classification of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1989;170:2–19. doi: 10.3109/00365528909091339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow H., Ewe K., Brandes J. W., Goebell H., Ehms H., Sommer H., Jesdinsky H. European Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study (ECCDS): results of drug treatment. Gastroenterology. 1984 Feb;86(2):249–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mary J. Y., Modigliani R. Development and validation of an endoscopic index of the severity for Crohn's disease: a prospective multicentre study. Groupe d'Etudes Thérapeutiques des Affections Inflammatoires du Tube Digestif (GETAID). Gut. 1989 Jul;30(7):983–989. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.7.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAfee J. G., Samin A. In-111 labeled leukocytes: a review of problems in image interpretation. Radiology. 1985 Apr;155(1):221–229. doi: 10.1148/radiology.155.1.3919419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAfee J. G., Subramanian G., Gagne G., Schneider R. F., Zapf-Longo C. 99mTc-HM-PAO for leukocyte labeling--experimental comparison with 111In oxine in dogs. Eur J Nucl Med. 1987;13(7):353–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00252994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meignan M., Wirquin E. Lymphocyte radiolabeling: a challenge to their survival. J Nucl Med. 1987 Jul;28(7):1228–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers S., Wolke A., Field S. P., Feuer E. J., Johnson J. W., Janowitz H. D. Fecal alpha 1-antitrypsin measurement: an indicator of Crohn's disease activity. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):13–18. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90739-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modigliani R., Mary J. Y., Simon J. F., Cortot A., Soule J. C., Gendre J. P., Rene E. Clinical, biological, and endoscopic picture of attacks of Crohn's disease. Evolution on prednisolone. Groupe d'Etude Thérapeutique des Affections Inflammatoires Digestives. Gastroenterology. 1990 Apr;98(4):811–818. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90002-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaison G., Sjödahl R., Tagesson C. Glucocorticoid treatment in ileal Crohn's disease: relief of symptoms but not of endoscopically viewed inflammation. Gut. 1990 Mar;31(3):325–328. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. M., Danpure H. J., Osman S., Hawker R. J., Henderson B. L., Hodgson H. J., Kelly J. D., Neirinckx R. D., Lavender J. P. Clinical experience with 99mTc-hexamethylpropylene-amineoxime for labelling leucocytes and imaging inflammation. Lancet. 1986 Oct 25;2(8513):946–949. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90601-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saverymuttu S. H., Camilleri M., Rees H., Lavender J. P., Hodgson H. J., Chadwick V. S. Indium 111-granulocyte scanning in the assessment of disease extent and disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. A comparison with colonoscopy, histology, and fecal indium 111-granulocyte excretion. Gastroenterology. 1986 May;90(5 Pt 1):1121–1128. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saverymuttu S. H. Clinical remission in Crohn's disease--assessment using faecal 111In granulocyte excretion. Digestion. 1986;33(2):74–79. doi: 10.1159/000199277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saverymuttu S. H., Peters A. M., Lavender J. P., Pepys M. B., Hodgson H. J., Chadwick V. S. Quantitative fecal indium 111-labeled leukocyte excretion in the assessment of disease in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1983 Dec;85(6):1333–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schölmerich J., Schmidt E., Schümichen C., Billmann P., Schmidt H., Gerok W. Scintigraphic assessment of bowel involvement and disease activity in Crohn's disease using technetium 99m-hexamethyl propylene amine oxine as leukocyte label. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1287–1293. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabold J. E., Wilson D. G., Lieberman L. M., Boyd C. M. Unsuspected extra-abdominal sites of infection: scintigraphic detection with indium-111-labeled leukocytes. Radiology. 1984 Apr;151(1):213–217. doi: 10.1148/radiology.151.1.6701317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segarra I., Roca M., Baliellas C., Vilar L., Ricart Y., Mora J., Puchal R., Martin-Comin J. Granulocyte-specific monoclonal antibody technetium-99m-BW 250/183 and indium-111 oxine-labelled leucocyte scintigraphy in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Nucl Med. 1991;18(9):715–719. doi: 10.1007/BF00956711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D. T., Gray G. M., Gregory P. B., Anderson M., Goodwin D. A., McDougall I. R. Location and activity of ulcerative and Crohn's colitis by indium 111 leukocyte scan. A prospective comparison study. Gastroenterology. 1983 Feb;84(2):388–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Dombal F. T., Softley A. IOIBD report no 1: Observer variation in calculating indices of severity and activity in Crohn's disease. International Organisation for the Study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut. 1987 Apr;28(4):474–481. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.4.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hees P. A., van Elteren P. H., van Lier H. J., van Tongeren J. H. An index of inflammatory activity in patients with Crohn's disease. Gut. 1980 Apr;21(4):279–286. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.4.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]