Abstract
The effects of the abnormal innervation in Hirschsprung's disease on colonic ion transport were examined in vitro using Ussing chambers. The response of the mucosal/submucosal preparations to different secretagogues were investigated in aganglionic and ganglionic rectosigmoid and transverse colon from children with Hirschsprung's disease and compared with normally innervated colon from children with anorectal anomalies. Basal values were similar in aganglionic and ganglionic rectosigmoid colon. Neurally mediated secretion with iloprost (10(-6) M) and acetylcholine (900 and 9 microM) was considerably reduced in aganglionic colon compared with normally innervated ganglionic colon. The ganglionic colon proximal to the aganglionic colon also had a reduced response to acetylcholine despite a normal acetylcholinesterase staining pattern. The responses to Escherichia coli STa enterotoxin (50 MU/ml) and isobutylmethylxanthine (10(-3) M) were similar in ganglionic and aganglionic colon. The response to STa enterotoxin was not changed by the nerve blocking agent tetrodotoxin (10(-6) M). The data show that colonocytes from aganglionic colon are capable of a normal secretory response if stimulated directly by cAMP or cGMP acting secretagogues but secretion in response to neurally mediated secretagogues is impaired. The hypertrophied acetylcholinesterase positive nerve fibres that infiltrate the aganglionic colon are likely to contribute to the reduced secretion to acetylcholine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres H., Rock R., Bridges R. J., Rummel W., Schreiner J. Submucosal plexus and electrolyte transport across rat colonic mucosa. J Physiol. 1985 Jul;364:301–312. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. B., Guarino A., Shukla R., Giannella R. A. Age-related differences in receptors for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin in the small and large intestine of children. Gastroenterology. 1988 Feb;94(2):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90423-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobar E., Galindo F., Parisi M. Water handling in the human distal colon in vitro: role of Na+, Cl- and HCO3-. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 7;1027(3):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90316-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady G. F., Duhamel R. C., Moore E. W. Active transport of sodium by human colon in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1970 Oct;59(4):583–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawker P. C., Mashiter K. E., Turnberg L. A. Mechanisms of transport of Na, Cl, and K in the human colon. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jun;74(6):1241–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath A. L., Spitz L., Milla P. J. The absorptive function of colonic aganglionic intestine: are the Duhamel and Martin procedures rational? J Pediatr Surg. 1985 Feb;20(1):34–36. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(85)80388-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Burnstock G. Neuronal populations in the submucous plexus of the human colon. J Anat. 1989 Oct;166:7–22. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel K. A., Renquist K., Shirazi S. Ion transport in human cecum, transverse colon, and sigmoid colon in vitro. Baseline and response to electrical stimulation of intrinsic nerves. Gastroenterology. 1987 Feb;92(2):501–507. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huott P. A., Liu W., McRoberts J. A., Giannella R. A., Dharmsathaphorn K. Mechanism of action of Escherichia coli heat stable enterotoxin in a human colonic cell line. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):514–523. doi: 10.1172/JCI113626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins H. R., Fenton T. R., McIntosh N., Dillon M. J., Milla P. J. Development of colonic sodium transport in early childhood and its regulation by aldosterone. Gut. 1990 Feb;31(2):194–197. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins H. R., Milla P. J. The development of colonic transport mechanisms in early life: evidence for reduced anion exchange. Early Hum Dev. 1988 Mar;16(2-3):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(88)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J., ROOTS L. A "DIRECT-COLORING" THIOCHOLINE METHOD FOR CHOLINESTERASES. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Mar;12:219–221. doi: 10.1177/12.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwahara A., Cooke H. J., Carey H. V., Mekhjian H., Ellison E. C., McGregor B. Effects of enteric neural stimulation on chloride transport in human left colon in vitro. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Feb;34(2):206–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01536052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask-Madsen J., Hjelt K. Effect of amiloride on electrical activity and electrolyte transport in human colon. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., Higgs N., Crowe P., Marsh M. N., Venkatesan S., Peters T. J. Cellular basis for defective electrolyte transport in inflamed human colon. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jul;99(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I., McGlone F. Segmental variability of membrane conductances in rat and human colonic epithelia. Implications for Na, K and Cl transport. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Sep;410(1-2):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00581912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandle G. I. Segmental heterogeneity of basal and aldosterone-induced electrogenic Na transport in human colon. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Sep;414(6):706–712. doi: 10.1007/BF00582139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
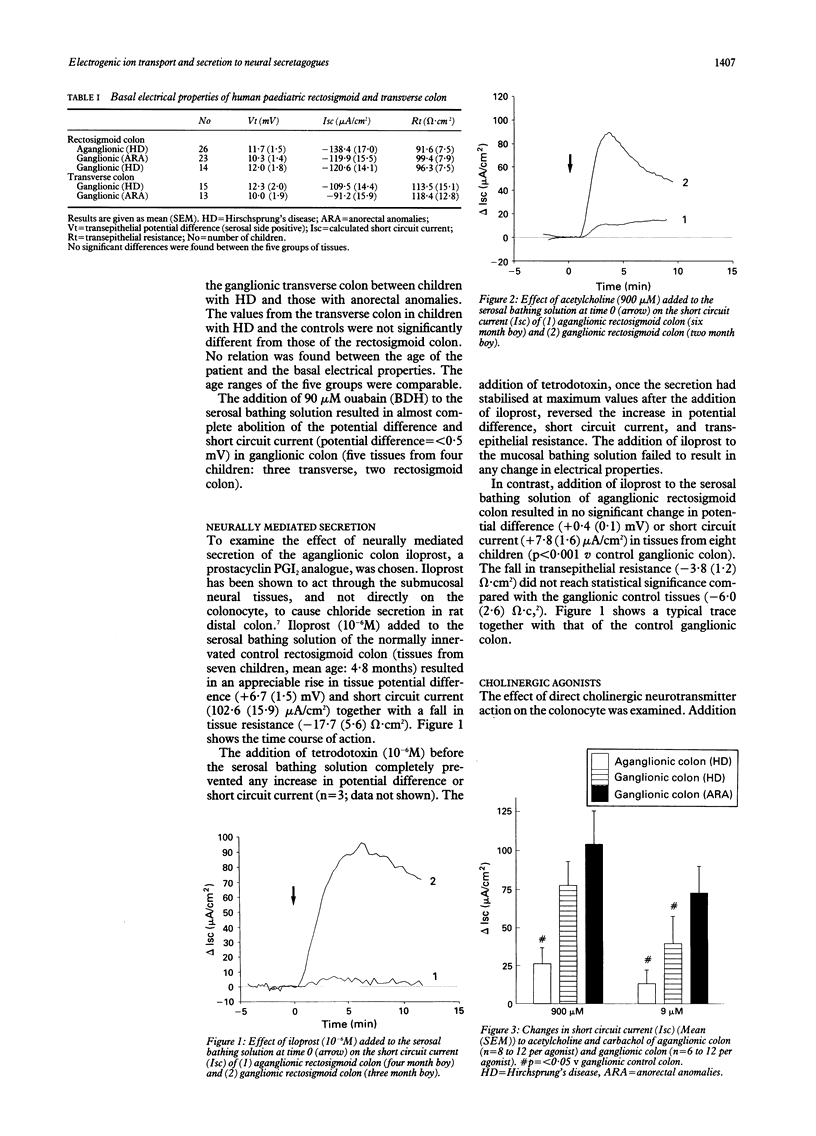
- Sandle G. I., Wills N. K., Alles W., Binder H. J. Electrophysiology of the human colon: evidence of segmental heterogeneity. Gut. 1986 Sep;27(9):999–1005. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.9.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellin J. H., De Soignie R. Ion transport in human colon in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1987 Sep;93(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90904-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills N. K., Alles W. P., Sandle G. I., Binder H. J. Apical membrane properties and amiloride binding kinetics of the human descending colon. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 1):G749–G757. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.6.G749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]