Abstract
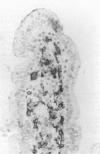
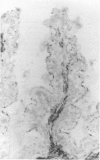
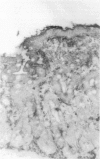
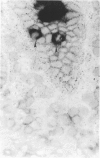
The staining of HLA class II antigens, the presence of cells positive for interleukin-2 receptors, the proportion of crypt cells in mitosis in the jejunal biopsy specimens, and the dose of coeliac disease marker HLA-DQ genes were studied in 75 healthy family members of coeliac disease patients. Eleven had silent coeliac disease; in the rest the morphology of the jejunum was normal. In the specimens from family members, staining of epithelial cells with HLA-DP and -DR antibodies was more widely distributed and stronger than in those from 19 controls. Interleukin-2 receptor+ cells were seen in the epithelium of all eight specimens from subjects with silent coeliac disease, and also in 24 morphologically normal specimens from family members, but not in the 19 control specimens. The proportion of crypt cells in mitosis was increased only in the specimens from the subjects with silent coeliac disease. The staining intensity of the epithelial cells with HLA-DP and -DR antibodies, the presence of interleukin-2 receptor+ cells and the percentage of crypt cells in mitosis were significantly associated with the number of coeliac disease marker DQB genes. Many family members of patients with coeliac disease have signs of inflammation even in morphologically normal jejunum; these inflammatory changes together with coeliac disease marker DQ genes may point to latent disease in these subjects.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmann D. M., Sansom D., Marsh S. G. What is the basis for HLA-DQ associations with autoimmune disease? Immunol Today. 1991 Aug;12(8):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90124-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud-Battandier F., Cerf-Bensussan N., Amsellem R., Schmitz J. Increased HLA-DR expression by enterocytes in children with celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1986 Nov;91(5):1206–1212. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(86)80018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerf-Bensussan N., Brousse N., Jarry A., Goulet O., Revillon Y., Ricour C., Guy-Grand D. Role of in vivo activated T cells in the mechanisms of villous atrophy in humans: study of allograft rejection. Digestion. 1990;46 (Suppl 2):297–301. doi: 10.1159/000200400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerf-Bensussan N., Schneeberger E. E., Bhan A. K. Immunohistologic and immunoelectron microscopic characterization of the mucosal lymphocytes of human small intestine by the use of monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2615–2622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty M., Barry R. E. Gluten-induced mucosal changes in subjects without overt small-bowel disease. Lancet. 1981 Mar 7;1(8219):517–520. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92860-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert E. C. Proliferative responses of human intraepithelial lymphocytes to various T-cell stimuli. Gastroenterology. 1989 Dec;97(6):1372–1381. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Blackwell J. N., Barnetson R. S. Effects of additional dietary gluten on the small-intestinal mucosa of volunteers and of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987 Jun;22(5):543–549. doi: 10.3109/00365528708991895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Lemke H., Baisch H., Wacker H. H., Schwab U., Stein H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1710–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Hendrix L. R. MHC class II structure, occupancy and surface expression determined by post-endoplasmic reticulum antigen binding. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):134–139. doi: 10.1038/353134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm K., Mäki M., Savilahti E., Lipsanen V., Laippala P., Koskimies S. Intraepithelial gamma delta T-cell-receptor lymphocytes and genetic susceptibility to coeliac disease. Lancet. 1992 Jun 20;339(8808):1500–1503. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91262-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeway C. A., Jr, Jones B., Hayday A. Specificity and function of T cells bearing gamma delta receptors. Immunol Today. 1988 Mar;9(3):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J., O'Farrelly C., O'Mahony C., Weir D. G., Feighery C. Immunoperoxidase demonstration of the cellular composition of the normal and coeliac small bowel. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Apr;68(1):177–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J., Weir D. G., Feighery C. Differential expression of HLA-D gene products in the normal and coeliac small bowel. Tissue Antigens. 1988 Mar;31(3):151–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1988.tb02076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kósnai I., Kárpati S., Savilahti E., Verkasalo M., Bucsky P., Török E. Gluten challenge in children with dermatitis herpetiformis: a clinical, morphological and immunohistological study. Gut. 1986 Dec;27(12):1464–1470. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.12.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Spencer J. Evidence that activated mucosal T cells play a role in the pathogenesis of enteropathy in human small intestine. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1341–1349. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley N. J., Macartney J. C., Ciclitira P. J. HLA-DR, DP and DQ expression in the small intestine of patients with coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Nov;70(2):386–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N., Bjarnason I., Shaw J., Ellis A., Baker R., Peters T. J. Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue. XIV--HLA status, mucosal morphology, permeability and epithelial lymphocyte populations in first degree relatives of patients with coeliac disease. Gut. 1990 Jan;31(1):32–36. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N. Gluten, major histocompatibility complex, and the small intestine. A molecular and immunobiologic approach to the spectrum of gluten sensitivity ('celiac sprue'). Gastroenterology. 1992 Jan;102(1):330–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N. Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue. XV. Histopathologic features suggestive of cell-mediated reactivity in jejunal mucosae of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1989;416(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF01606317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Eisenhardt D., Salomon P., Bauer W., Plous R., Piccinini L. Expression of class II molecules on intestinal epithelial cells in humans. Differences between normal and inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):3–12. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90575-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki M., Holm K., Collin P., Savilahti E. Increase in gamma/delta T cell receptor bearing lymphocytes in normal small bowel mucosa in latent coeliac disease. Gut. 1991 Nov;32(11):1412–1414. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.11.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki M., Holm K., Koskimies S., Hällström O., Visakorpi J. K. Normal small bowel biopsy followed by coeliac disease. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Oct;65(10):1137–1141. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.10.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki M., Holm K., Lipsanen V., Hällström O., Viander M., Collin P., Savilahti E., Koskimies S. Serological markers and HLA genes among healthy first-degree relatives of patients with coeliac disease. Lancet. 1991 Nov 30;338(8779):1350–1353. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92234-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony S., Vestey J. P., Ferguson A. Similarities in intestinal humoral immunity in dermatitis herpetiformis without enteropathy and in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1990 Jun 23;335(8704):1487–1490. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93029-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roep B. O., Bontrop R. E., Peña A. S., van Eggermond M. C., van Rood J. J., Giphart M. J. An HLA-DQ alpha allele identified at DNA and protein level is strongly associated with celiac disease. Hum Immunol. 1988 Dec;23(4):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(88)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savilahti E., Arato A., Verkasalo M. Intestinal gamma/delta receptor-bearing T lymphocytes in celiac disease and inflammatory bowel diseases in children. Constant increase in celiac disease. Pediatr Res. 1990 Dec;28(6):579–581. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199012000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer J. J., Mearin M. L., Peña A. S., Offerhaus G. J., Dreef E. J., Roep B. O., Bontrop R. E., Dooren L. J., Lamers C. B., Hoedemaeker P. J. Expression of HLA-DQ antigens in the small-intestinal mucosa of patients with coeliac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1991 Jun;26(6):605–610. doi: 10.3109/00365529109043634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Brandtzaeg P., Solheim B. G., Thorsby E. Relation between HLA-DR-like antigens and secretory component (SC) in jejunal epithelium of patients with coeliac disease or dermatitis herpetiformis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 May;44(2):233–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollid L. M., Markussen G., Ek J., Gjerde H., Vartdal F., Thorsby E. Evidence for a primary association of celiac disease to a particular HLA-DQ alpha/beta heterodimer. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):345–350. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J., Finn T., Isaacson P. G. Expression of HLA-DR antigens on epithelium associated with lymphoid tissue in the human gastrointestinal tract. Gut. 1986 Feb;27(2):153–157. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J., MacDonald T. T., Diss T. C., Walker-Smith J. A., Ciclitira P. J., Isaacson P. G. Changes in intraepithelial lymphocyte subpopulations in coeliac disease and enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma (malignant histiocytosis of the intestine). Gut. 1989 Mar;30(3):339–346. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.3.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Borst J., Giphart M., Coligan J., Terhorst C., De Vries J. E. HLA-DC antigens can serve as recognition elements for human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Apr;14(4):299–304. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein W. M. Latent celiac sprue. Gastroenterology. 1974 Apr;66(4):489–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N., Watson A., Morley A., Appleton D., Marks J. Cell kinetics in flat (avillous) mucosa of the human small intestine. Gut. 1973 Sep;14(9):701–710. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.9.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Silva H. J., Millard P. R., Kettlewell M., Mortensen N. J., Prince C., Jewell D. P. Mucosal characteristics of pelvic ileal pouches. Gut. 1991 Jan;32(1):61–65. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]