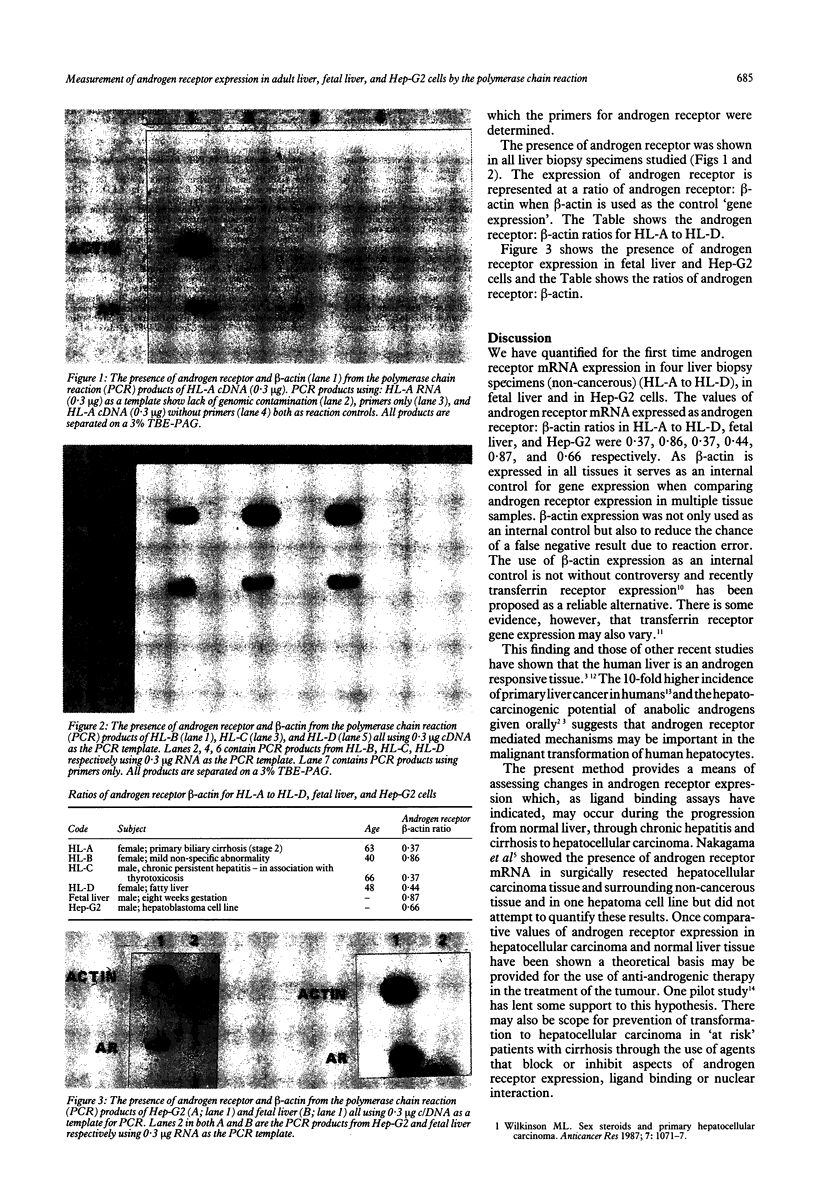
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most commonly fatal malignant tumour worldwide. The role of androgen receptors, which have been found in hepatocellular carcinoma, is controversial. Sequence specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to quantify, for the first time, the expression of androgen receptor in four adult liver biopsy specimens (HL-A to HL-D), fetal liver, and Hep-G2 cells. The measurement of androgen receptor is expressed as a ratio (androgen receptor: beta-actin) of the value of androgen receptor to the value of a control gene, beta-actin. The value of the androgen receptor: beta-actin ratios for HL-A, HL-B, HL-C, HL-D, fetal liver, and Hep-G2 were 0.37, 0.86, 0.37, 0.44, 0.87, and 0.66 respectively. To verify sequence specific amplification of the androgen receptor, the PCR androgen receptor fragment was sequenced. The resultant sequence data for both strands of the double stranded PCR androgen receptor fragment had 100% similarity with the published androgen receptor mRNA sequence (complete codons).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boix L., Bruix J., Castells A., Fuster J., Bru C., Visa J., Rivera F., Rodes J. Sex hormone receptors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Is there a rationale for hormonal treatment? J Hepatol. 1993 Feb;17(2):187–191. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomford A. B., Munro H. N. Transferrin and its receptor: their roles in cell function. Hepatology. 1985 Sep-Oct;5(5):870–875. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco D., Prieto M., Pallardó L., Moll J. L., Cruz J. M., Muñoz C., Berenguer J. Multiple hepatic adenomas after long-term therapy with testosterone enanthate. Review of the literature. J Hepatol. 1985;1(6):573–578. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(85)80001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes A., Wilkinson M. L., Iqbal M. J., Johnson P. J., Williams R. Response to cyproterone acetate treatment in primary hepatocellular carcinoma is related to fall in free 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Nov;23(11):1659–1664. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90446-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson D., Newbould M. J., Taylor P., McMahon R. F., Leahy B. C., Warnes T. W. Androgen associated hepatocellular carcinoma with an aggressive course. Gut. 1991 Sep;32(9):1084–1086. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.9.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindan M. V. Specific region in hormone binding domain is essential for hormone binding and trans-activation by human androgen receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):417–427. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji H. J., Zhang Q. Q., Leung B. S. Survey of oncogene and growth factor/receptor gene expression in cancer cells by intron-differential RNA/PCR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):569–575. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92129-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax E. R., Baumann P., Schriefers H. Changes in the activities of microsomal enzymes involved in hepatic steroid metabolism in the rat after administration of androgenic, estrogenic, progestational, anabolic and catatoxic steroids. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 15;33(8):1235–1241. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagama H., Gunji T., Ohnishi S., Kaneko T., Ishikawa T., Makino R., Hayashi K., Shiga J., Takaku F., Imawari M. Expression of androgen receptor mRNA in human hepatocellular carcinomas and hepatoma cell lines. Hepatology. 1991 Jul;14(1):99–102. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840140116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Ohtsuki T., Obata H., Tomimatsu M., Okazaki N., Hasegawa H., Nakajima Y., Ohnishi K. Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment. Study of 850 patients. Cancer. 1985 Aug 15;56(4):918–928. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850815)56:4<918::aid-cncr2820560437>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Ng S. Y., Engel J., Gunning P., Kedes L. Evolutionary conservation in the untranslated regions of actin mRNAs: DNA sequence of a human beta-actin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1687–1696. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson M. L. Sex-steroids and primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 1987 Sep-Oct;7(5B):1071–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





