Abstract
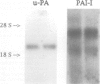
Urokinase is a neutral protease whose major site of action is the external surface of the plasma membrane of cells and whose major function seems to be modulation of cell adhesion, such as that which occurs during cell migration. This study aimed to determine whether colonic epithelium is involved with the urokinase system. The contents of urokinase and one of its specific inhibitors, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, were measured in culture supernatant and cell homogenates of isolated human colonic crypt cells. The amounts of both factors increased in supernatants over 24 hours, and approximately twice the amount was found in supernatants than in autologous cell homogenates. The secretion of both factors was similar in serum free and serum containing media. Northern blot analysis showed that messenger ribonucleic acid specific for urokinase and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 was present in colonic crypt cells and that expression over 18 hours of culture was increased 12 fold for urokinase type plasminogen activator and two to fourfold for the inhibitor compared with values found in autologous freshly isolated cells. Urokinase activity was detected in crypt cell homogenates and supernatants indicating that it was present in excess of its inhibitors. Control experiments indicated that the epithelial cells themselves were responsible for the observations and excluded artefactual effects of the isolation procedure. In conclusion, isolated human colonic epithelial cells secrete urokinase and at least one of its specific inhibitors. Further investigation of the role of urokinase in the physiology and pathophysiology of colonic epithelium is indicated.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan A., Bristol J. B., Williamson R. C. Crypt cell production rate in ulcerative proctocolitis: differential increments in remission and relapse. Gut. 1985 Oct;26(10):999–1003. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.10.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. B., Gronke R. S. Protease nexins and cellular regulation. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1986 Jul;12(3):216–220. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Florent G., Kim P., Brattain M. Determination of the levels of urokinase and its receptor in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 1;48(11):3112–3116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buø L., Lyberg T., Jørgensen L., Johansen H. T., Aasen A. O. Location of plasminogen activator (PA) and PA inhibitor in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. APMIS. 1993 Mar;101(3):235–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1993.tb00106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman P. L., Green G. D. A sensitive, coupled assay for plasminogen activator using a thiol ester substrate for plasmin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:617–626. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declerck P. J., Alessi M. C., Verstreken M., Kruithof E. K., Juhan-Vague I., Collen D. Measurement of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 in biologic fluids with a murine monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):220–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson P. R., Moeller I., Kagelari O., Folino M., Young G. P. Contrasting effects of butyrate on the expression of phenotypic markers of differentiation in neoplastic and non-neoplastic colonic epithelial cells in vitro. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1992 Mar-Apr;7(2):165–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1992.tb00956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson P. R., van de Pol E., Doe W. F. Cell associated urokinase activity and colonic epithelial cells in health and disease. Gut. 1991 Feb;32(2):191–195. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson P. R., van de Pol E., Maxwell L. E., Gabriel A., Doe W. F. Isolation of colonic crypts that maintain structural and metabolic viability in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1989 Feb;96(2 Pt 1):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91549-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. I., Schwimmer R., Quigley J. P. Human plasma fibronectin as a substrate for human urokinase. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):529–534. doi: 10.1042/bj2620529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Ralfkiaer E., Kirkeby L. T., Kristensen P., Lund L. R., Danø K. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in stromal cells in adenocarcinomas of the colon in humans. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):111–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. A., Rehemtulla A. Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors: regulators of extracellular proteolysis and cell function. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1988;90(4):691–708. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(88)90323-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollas W., Boyd D. Urokinase-dependent proteolysis in cultured colon cancer is directed by its receptor. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1991 Jul;17(3):225–230. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Binder B. R. Function of receptor-bound urokinase. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1991 Jul;17(3):246–250. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohga S., Harvey S. R., Weaver R. M., Markus G. Localization of plasminogen activators in human colon cancer by immunoperoxidase staining. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1787–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretz K., Möller P., Schwartz-Albiez R. Plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors in human colorectal carcinoma tissues are not expressed by the tumour cells. Eur J Cancer. 1993;29A(8):1184–1189. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(05)80312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen P., Eriksen J., Danø K. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator messenger RNA in the normal mouse by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Mar;39(3):341–349. doi: 10.1177/39.3.1899685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus G. S., Jensen P. J. Plasminogen activators in epithelial biology. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1991 Jul;17(3):210–216. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Sawdey M., Lawrence D., Millan J. L., Loskutoff D. J. Cloning and sequence of a cDNA coding for the human beta-migrating endothelial-cell-type plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6776–6780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Morain C. A., Abelow A. C., Chervu L. R., Fleischner G. M., Das K. M. Chromium 51-ethylenediaminetetraacetate test: a useful test in the assessment of inflammatory bowel disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Nov;108(5):430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöllänen J., Saksela O., Salonen E. M., Andreasen P., Nielsen L., Danø K., Vaheri A. Distinct localizations of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its type 1 inhibitor under cultured human fibroblasts and sarcoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1085–1096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M., Chucholowski N., Busch E., Hellmann D., Wagner B., Goretzki L., Jänicke F., Günzler W. A., Graeff H. Fluorescent probes as tools to assess the receptor for the urokinase-type plasminogen activator on tumor cells. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1991 Jul;17(3):291–302. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sier C. F., Fellbaum C., Verspaget H. W., Schmitt M., Griffioen G., Graeff H., Hôfler H., Lamers C. B. Immunolocalization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in adenomas and carcinomas of the colorectum. Histopathology. 1991 Sep;19(3):231–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1991.tb00027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengers E. D., Kluft C. Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. W., Pöllänen J., Tapiovaara H., Leung K. C., Sim P. S., Salonen E. M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Danø K., Vaheri A. Activation of pro-urokinase and plasminogen on human sarcoma cells: a proteolytic system with surface-bound reactants. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1987–1995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Deyashiki Y., Nishioka J., Toma K. Protein C inhibitor: structure and function. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Jun 30;61(3):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Ikeo K., Gojobori T., Tanifuji M. Local function of urokinase receptor at the adhesion contact sites of a metastatic tumor cell. Thromb Res Suppl. 1990;10:55–61. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90378-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Fukao H., Ueshima S., Okada K., Yasutomi M., Matsuo O. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 in human carcinoma tissues. Int J Cancer. 1991 Jun 19;48(4):481–484. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R. H., Jones J. K., Gabriel A., Lukies R. E. A new colon carcinoma cell line (LIM1863) that grows as organoids with spontaneous differentiation into crypt-like structures in vitro. Cancer Res. 1987 May 15;47(10):2683–2689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. A., Crama-Bohbouth G., Verspaget H. W., Verheijen J. H., Dooijewaard G., Weterman I. T., Lamers C. B. Plasminogen activators in the intestine of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Oct 31;60(2):262–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]