Abstract
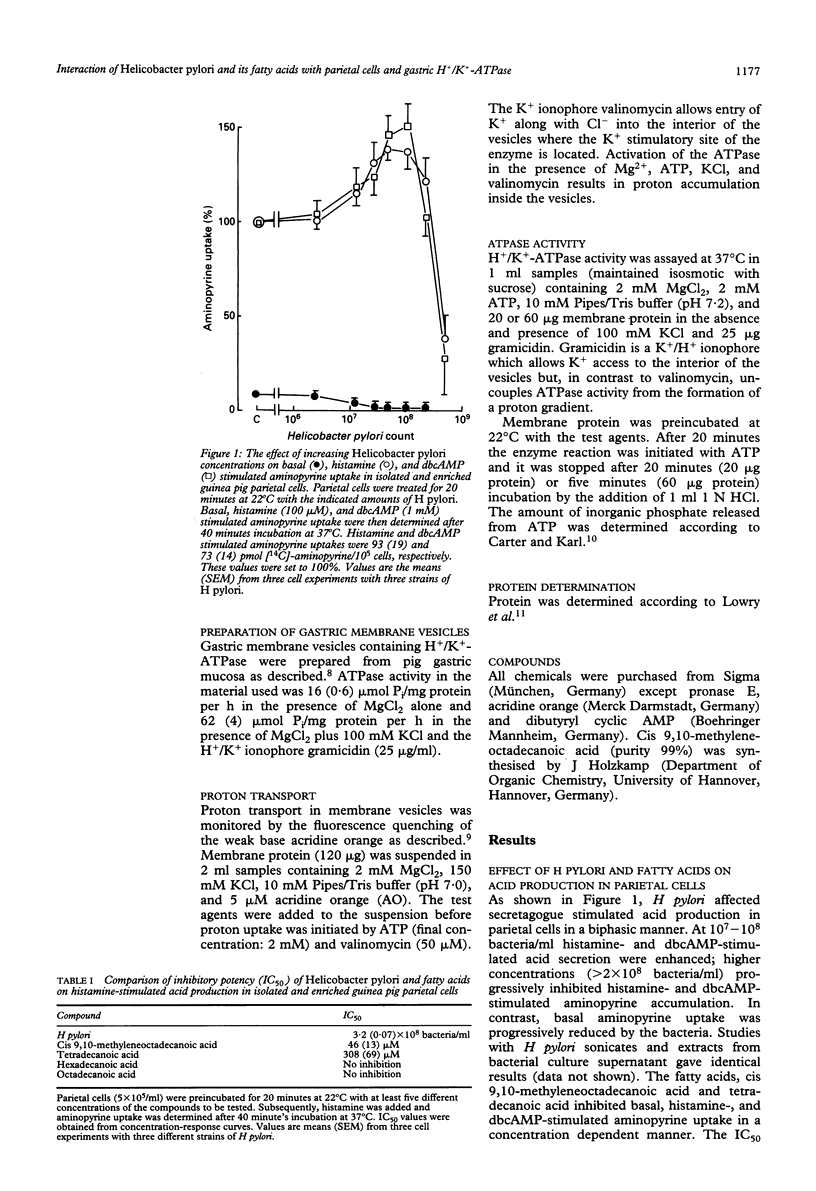
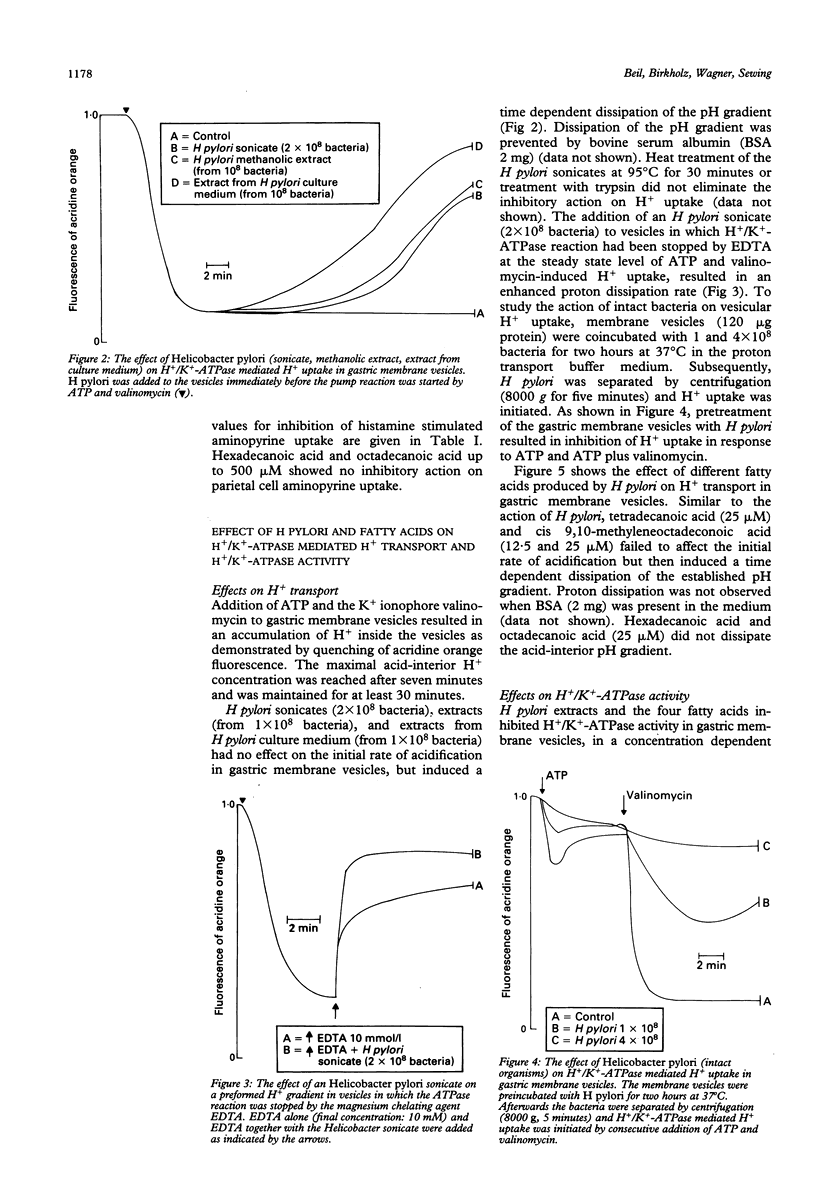
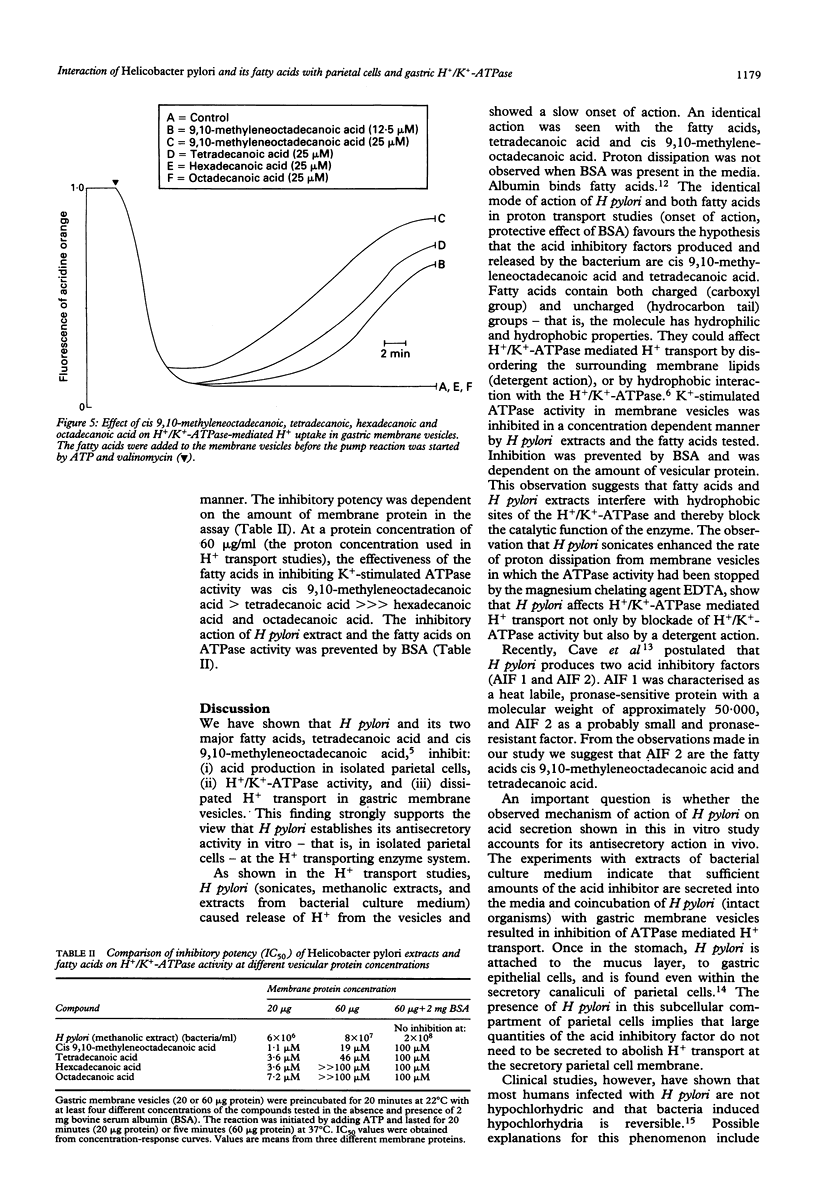
Helicobacter pylori and the fatty acids produced by this organism were compared for their acid inhibitory activity in isolated parietal cells and their interaction with gastric H+/K(+)-ATPase. H pylori (intact organisms, sonicates, methanolic extracts, and extracts from culture medium) and the fatty acids cis 9,10-methyleneoctadecanoic acid and tetradecanoic acid inhibited at fairly high concentrations histamine- and dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate stimulated acid production in isolated parietal cells, dissipated (with a slow onset) the H+/K(+)-ATPase created H+ gradient in gastric membrane vesicles, and inhibited H+/K(+)-ATPase activity in a concentration dependent manner. The inhibitory potency of H pylori and the fatty acids in relation to H+/K(+)-ATPase depended on the amount of membrane protein. Bovine serum albumin prevented enzyme inhibition and proton dissipation from gastric vesicles. The data indicate that H pylori establishes its antisecretory action in parietal cells by blocking H+/K(+)-ATPase activity and also by a detergent action at the apical parietal cell membrane. The fatty acids cis 9,10-methyleneoctadecanoic acid and tetradecanoic acid are probably the acid inhibitory factors secreted by H pylori.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beil W., Staar U., Schünemann P., Sewing K. F. Omeprazole, SCH 28080 and doxepin differ in their characteristics to inhibit H+/K+-ATPase driven proton accumulation by parietal cell membrane vesicles. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Dec 1;37(23):4487–4493. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90664-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. G., Karl D. W. Inorganic phosphate assay with malachite green: an improvement and evaluation. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1982 Dec;7(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(82)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cave D. R., Vargas M. Effect of a Campylobacter pylori protein on acid secretion by parietal cells. Lancet. 1989 Jul 22;2(8656):187–189. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. G., Correa P., Offerhaus J., Rodriguez E., Janney F., Hoffmann E., Fox J., Hunter F., Diavolitsis S. Ultrastructure of the gastric mucosa harboring Campylobacter-like organisms. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Nov;86(5):575–582. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.5.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin C. S., McCulloch R. K., Armstrong J. A., Wee S. H. Unusual cellular fatty acids and distinctive ultrastructure in a new spiral bacterium (Campylobacter pyloridis) from the human gastric mucosa. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Apr;19(2):257–267. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. Y., Alpert L. C., Smith J. L., Yoshimura H. H. Iatrogenic Campylobacter pylori infection is a cause of epidemic achlorhydria. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 Sep;83(9):974–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im W. B., Blakeman D. P. Inhibition of gastric (H+ + K+)-ATPase by unsaturated long-chain fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 22;692(3):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90384-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König B., Schönfeld W., Scheffer J., König W. Signal transduction in human platelets and inflammatory mediator release induced by genetically cloned hemolysin-positive and -negative Escherichia coli strains. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1591–1599. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1591-1599.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. C., Forte J. G. A study of H+ transport in gastric microsomal vesicles using fluorescent probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 4;508(2):339–356. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Nicholson G. Ingestion of Campylobacter pyloridis causes gastritis and raised fasting gastric pH. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Mar;82(3):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A., Olafsson A. S., Lancaster C., Zhang W. R. Interleukin-1 is cytoprotective, antisecretory, stimulates PGE2 synthesis by the stomach, and retards gastric emptying. Life Sci. 1991;48(2):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90405-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewing K. F., Harms P., Schulz G., Hannemann H. Effect of substituted benzimidazoles on acid secretion in isolated and enriched guinea pig parietal cells. Gut. 1983 Jun;24(6):557–560. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.6.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Fletcher J. E., Ashbrook J. D. Analysis of long-chain free fatty acid binding to bovine serum albumin by determination of stepwise equilibrium constants. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 17;10(17):3229–3232. doi: 10.1021/bi00793a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


