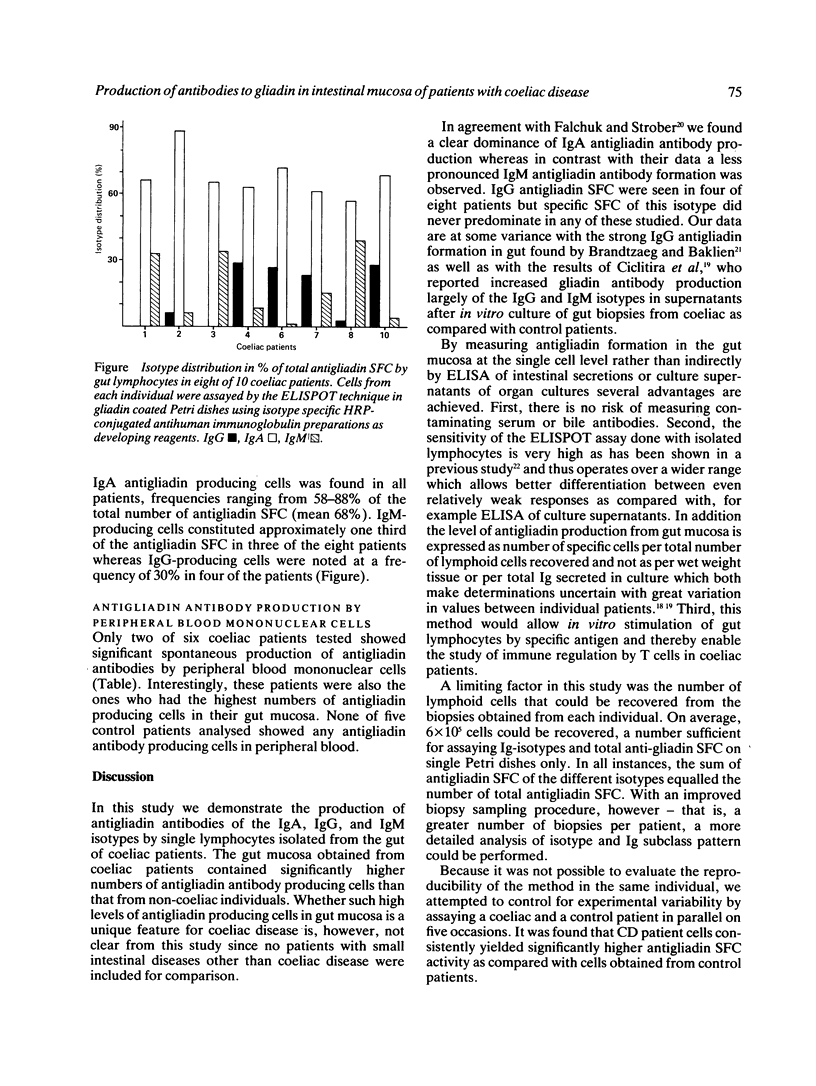
Abstract
Lymphocytes obtained after enzymatic digestion of intestinal biopsies from patients with coeliac disease were examined for the presence of gliadin specific antibody secreting cells by means of the ELISPOT technique. This technique permits enumeration of gliadin antibody secreting immunocytes, differentiated with regard to immunoglobulin class. Patients with coeliac disease were found to have high (834/10(6) cells) numbers of antigliadin spot forming cells (SFC) in gut mucosa. IgG and IgM antigliadin antibody secreting cells were infrequently shown whereas IgA antigliadin SFC predominated in all patients tested (average 68% of total SFC). Ten control patients were investigated in parallel with the coeliac patients and showed only low numbers of gliadin antibody secreting cells in gut mucosa (49/10(6) isolated cells). Antigliadin antibody secretion by peripheral blood mononuclear cells was shown in only two of six coeliac patients tested and in none of the control patients. The findings suggest that the intestinal mucosa is a major site for antigliadin antibody production and that IgA is the dominating Ig-class of these antibodies. The high sensitivity and accuracy of the ELISPOT technique may provide a useful instrument for future studies of antibody production and regulation of the gut immune response to gluten and other alimentary antigens in coeliac and other intestinal diseases.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asquith P., Thompson R. A., Cooke W. T. Serum-immunoglobulins in adult coeliac disease. Lancet. 1969 Jul 19;2(7612):129–131. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baklien K., Brandtzaeg P., Fausa O. Immunoglobulins in jejunal mucosa and serum from patients with adult coeliac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(2):149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Baklien K. Immunohistochemical studies of the formation and epithelial transport of immunoglobulins in normal and diseased human intestinal mucosa. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1976;36:1–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciclitira P. J., Ellis H. J., Wood G. M., Howdle P. D., Losowsky M. S. Secretion of gliadin antibody by coeliac jejunal mucosal biopsies cultured in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):119–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corazza G. R., Sarchielli P., Londei M., Frisoni M., Gasbarrini G. Gluten specific suppressor T cell dysfunction in coeliac disease. Gut. 1986 Apr;27(4):392–398. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.4.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerkinsky C. C., Nilsson L. A., Nygren H., Ouchterlony O., Tarkowski A. A solid-phase enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay for enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Dec 16;65(1-2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M., Strober W. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy: synthesis of antigliadin antibody in vitro. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):947–952. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluge G., Aksnes L. Quantification of immunoglobulins after organ culture of human duodenal mucosa. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(1):62–70. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198302010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillberg R., Ahrén C. Coeliac disease diagnosed by means of duodenoscopy and endoscopic duodenal biopsy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(8):911–916. doi: 10.3109/00365527709181349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby S., Foged N., Oxelius V. A., Svehag S. E. Serum IgG subclass antibodies to gliadin and other dietary antigens in children with coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jun;64(3):526–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilander A. F., Dotevall G., Fällström S. P., Gillberg R. E., Nilsson L. A., Tarkowski A. Evaluation of gliadin antibodies for detection of coeliac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 May;18(3):377–383. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilander A. F., Nilsson L. A., Gillberg R. Serum antibodies to gliadin in coeliac disease after gluten withdrawal. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987 Jan;22(1):29–34. doi: 10.3109/00365528708991852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster-Smith M., Kumar P., Marks R., Clark M. L., Dawson A. M. Jejunal mucosal immunoglobulin-containing cells and jejunal fluid immunoglobulins in adult coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis. Gut. 1974 May;15(5):371–376. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.5.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg T., Nilsson L. A., Borulf S., Cavell B., Fällström S. P., Jansson U., Stenhammar L., Stintzing G. Serum IgA and IgG gliadin antibodies and small intestinal mucosal damage in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1985 Dec;4(6):917–922. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198512000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb P. M., Strober W., Falchuk Z. M., Laster L. Incorporation of L-leucine-14C into immunoglobulins by jejunal biopsies of patients with celiac sprue and other gastrointestinal diseases. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):559–569. doi: 10.1172/JCI106525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N. A sensitive method for the detection of specific antibody production in different isotypes from single lamina propria plasma cells. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Oct;24(4):393–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb02127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Hellström U., Holmgren J. Circulating cholera antitoxin memory cells in the blood one year after oral cholera vaccination in humans. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Aug;26(2):207–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savilahti E. Intestinal immunoglobulins in children with coeliac disease. Gut. 1972 Dec;13(12):958–964. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.12.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savilahti E., Viander M., Perkkiö M., Vainio E., Kalimo K., Reunala T. IgA antigliadin antibodies: a marker of mucosal damage in childhood coeliac disease. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):320–322. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91627-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. B., Goodall A., Stephenson P., Jenkins D. Small intestinal plasma cells in coeliac disease. Gut. 1984 Jan;25(1):41–46. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Brandtzaeg P., Thorsby E., Baklien K., Fausa O., Ek J. Mucosal and systemic immune response patterns in celiac disease. Ann Allergy. 1983 Aug;51(2 Pt 2):233–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H., Fausa O., Ek J., Brandtzaeg P. Immune response patterns in coeliac disease. Serum antibodies to dietary antigens measured by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):25–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenhammar L., Kilander A. F., Nilsson L. A., Strömberg L., Tarkowski A. Serum gliadin antibodies for detection and control of childhood coeliac disease. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984 Sep;73(5):657–663. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1984.tb09991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsworth D. J., Walker-Smith J. A., Holborow E. J. Gliadin and reticulin antibodies in childhood coeliac disease. Lancet. 1983 Apr 16;1(8329):874–875. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91411-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. M., Shires S., Howdle P. D., Losowsky M. S. Immunoglobulin production by coeliac biopsies in organ culture. Gut. 1986 Oct;27(10):1151–1160. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.10.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


