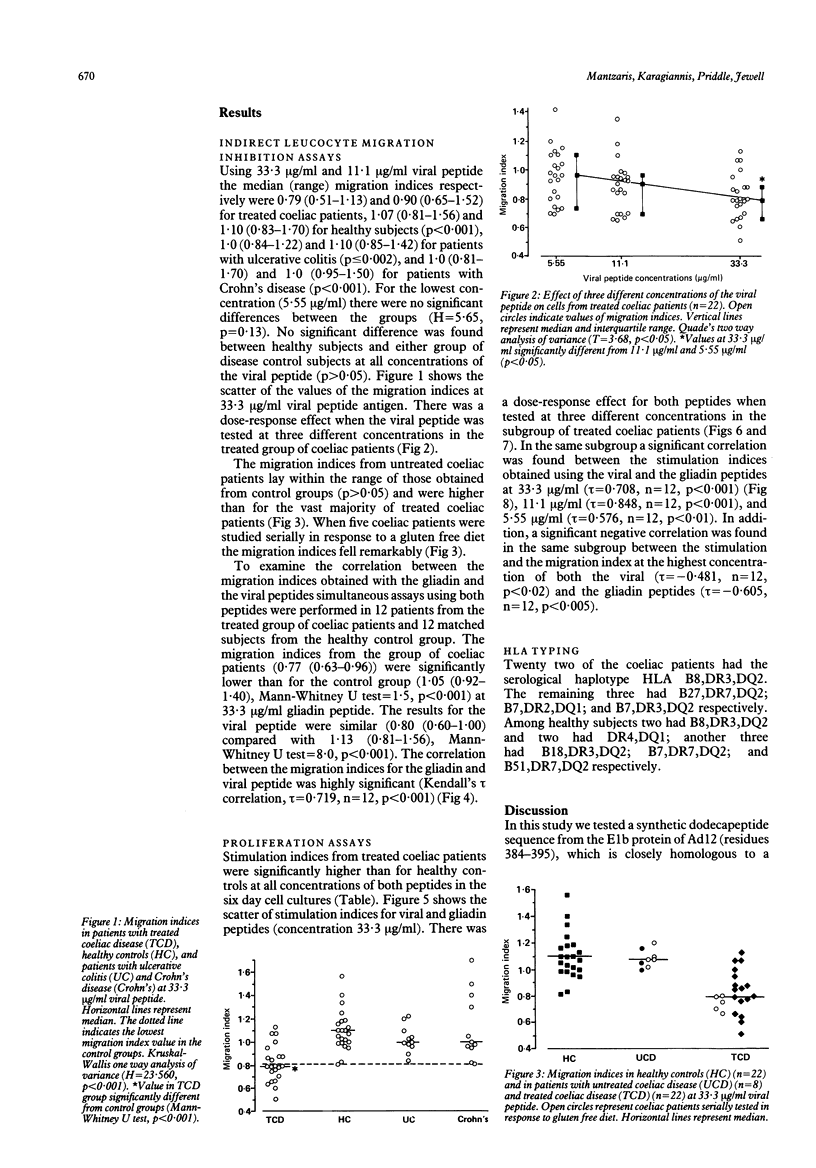
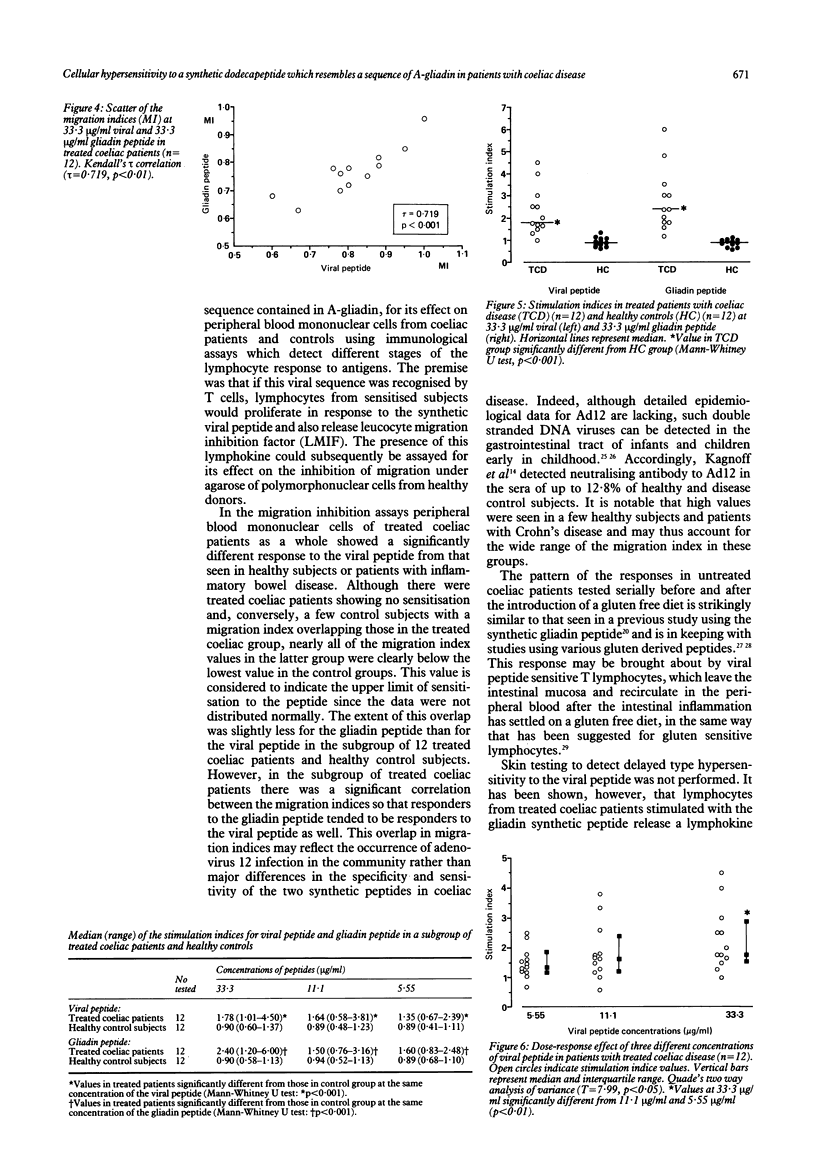
Abstract
The human intestinal adenovirus serotype 12 (Ad12) may be implicated in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease by virtue of immunological cross reactivity between epitopes shared by its early region E1b protein and A-gliadin. In the present study a synthetic dodecapeptide from the corresponding viral epitope (Ad12E1b, residues 384-395) was tested for its effect on peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 22 treated and eight untreated patients with coeliac disease, 22 healthy subjects, 11 patients with ulcerative colitis, and 11 patients with Crohn's disease by an indirect leucocyte migration inhibition assay. In addition, the effect of both the viral and the gliadin synthetic peptides was studied by proliferation and migration assays simultaneously performed in an unselected subgroup of 12 treated coeliac patients and 12 healthy subjects of the study. Coeliac patients with untreated disease showed no response to the viral peptide compared with treated patients (p greater than 0.1). Treated coeliac patients showed a significantly different response from healthy control subjects and control patients with disease (p less than 0.001) which was dependent on the concentration of the viral peptide. In the subgroup of the treated coeliac patients (n = 12) there was a significant correlation between the responses in the migration and the proliferation assay using either the viral (p less than 0.02) or the gliadin (p less than 0.005) peptide at the highest concentration (33.3 micrograms/ml). Furthermore, the responses obtained using viral peptide correlated significantly with the responses obtained with gliadin peptide in both the migration (p less than 0.001) and the proliferation (p less than 0.001) assays. These results show that in coeliac patients there is pronounced cross reactivity at the level of T cell recognition between synthetic peptides derived from the Ad12 and A-gliadin. This antigenic cross reactivity may be involved in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert E. D., Harms K., Wank R., Steinbauer-Rosenthal I., Scholz S. Segregation analysis of HL-A antigens and haplotypes in 50 families of patients with coeliac disease. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1785–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen A. W., Losowsky M. S. Cell-mediated immunity to gluten fraction III in adult coeliac disease. Gut. 1978 Feb;19(2):126–131. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen J. E. Migration inhibitory effect of cell-free supernatants from tuberculin-stimulated cultures of human mononuclear leukocytes demonstrated by two-step MIF agarose assay. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):546–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan R., Rawcliffe P. M., Priddle J. D., Jewell D. P. Cellular hypersensitivity to gluten derived peptides in coeliac disease. Gut. 1987 Apr;28(4):426–434. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.4.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. K., Asquith P., Cooke W. T. Cell-mediated immunity to gluten fraction III in adult coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):259–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell M. D., Austin R. K., Kelleher D., Nepom G. T., Kagnoff M. F. An HLA-D region restriction fragment length polymorphism associated with celiac disease. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Austin R. K., Hubert J. J., Bernardin J. E., Kasarda D. D. Possible role for a human adenovirus in the pathogenesis of celiac disease. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1544–1557. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Austin R. K., Johnson H. C., Bernardin J. E., Dietler M. D., Kasarda D. D. Celiac sprue: correlation with murine T cell responses to wheat gliadin components. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2693–2697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Paterson Y. J., Kumar P. J., Kasarda D. D., Carbone F. R., Unsworth D. J., Austin R. K. Evidence for the role of a human intestinal adenovirus in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease. Gut. 1987 Aug;28(8):995–1001. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.8.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karagiannis J. A., Priddle J. D., Jewell D. P. Cell-mediated immunity to a synthetic gliadin peptide resembling a sequence from adenovirus 12. Lancet. 1987 Apr 18;1(8538):884–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92859-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasarda D. D., Okita T. W., Bernardin J. E., Baecker P. A., Nimmo C. C., Lew E. J., Dietler M. D., Greene F. C. Nucleic acid (cDNA) and amino acid sequences of alpha-type gliadins from wheat (Triticum aestivum). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4712–4716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mearin M. L., Biemond I., Peña A. S., Polanco I., Vazquez C., Schreuder G. T., de Vries R. R., van Rood J. J. HLA-DR phenotypes in Spanish coeliac children: their contribution to the understanding of the genetics of the disease. Gut. 1983 Jun;24(6):532–537. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.6.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niven M. J., Caffrey C., Sachs J. A., Cassell P. G., Gallagher R. B., Kumar P., Hitman G. A. Susceptibility to coeliac disease involves genes in HLA-DP region. Lancet. 1987 Oct 3;2(8562):805–805. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92544-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrelly C., Feighery C., Greally J. F., Weir D. G. Cellular response to alpha-gliadin in untreated coeliac disease. Gut. 1982 Jan;23(1):83–87. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrelly C., Whelan C. A., Feighery C. F., Weir D. G. Suppressor-cell activity in coeliac disease induced by alpha-gliadin, a dietary antigen. Lancet. 1984 Dec 8;2(8415):1305–1307. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90822-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polanco I., Mearin M. L., Larrauri J., Biemond I., Wipkink-Bakker A., Peña A. S. Effect of gluten supplementation in healthy siblings of children with celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Mar;92(3):678–681. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shale D. J., Johnston D. G., Hall R., Roberts D. F. Coeliac disease in monozygotic twins. Postgrad Med J. 1982 Dec;58(686):797–798. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.58.686.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikora K., Anand B. S., Truelove S. C., Ciclitira P. J., Offord R. E. Stimulation of lymphocytes from patients with coeliac disease by a subfraction of gluten. Lancet. 1976 Aug 21;2(7982):389–391. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92406-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson F. G., Bullen A. W., Robertson D. A., Losowsky M. S. HLA-B8 and cell-mediated immunity to gluten. Gut. 1981 Aug;22(8):633–636. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.8.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes P. L., Asquith P., Holmes G. K., Mackintosh P., Cooke W. T. Histocompatibility antigens associated with adult coeliac disease. Lancet. 1972 Jul 22;2(7769):162–164. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki P. I., Bernoco D., Park M. S., Ozturk G., Iwaki Y. Microdroplet testing for HLA-A, -B, -C, and -D antigens. The Phillip Levine Award Lecture. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Feb;69(2):103–120. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.2.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOYCHIK J. H., BOUNDY J. A., DIMLER R. J. Starch gel electrophoresis of wheat gluten proteins with concentrated urea. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:477–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ritis G., Auricchio S., Jones H. W., Lew E. J., Bernardin J. E., Kasarda D. D. In vitro (organ culture) studies of the toxicity of specific A-gliadin peptides in celiac disease. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jan;94(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90607-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


