Abstract
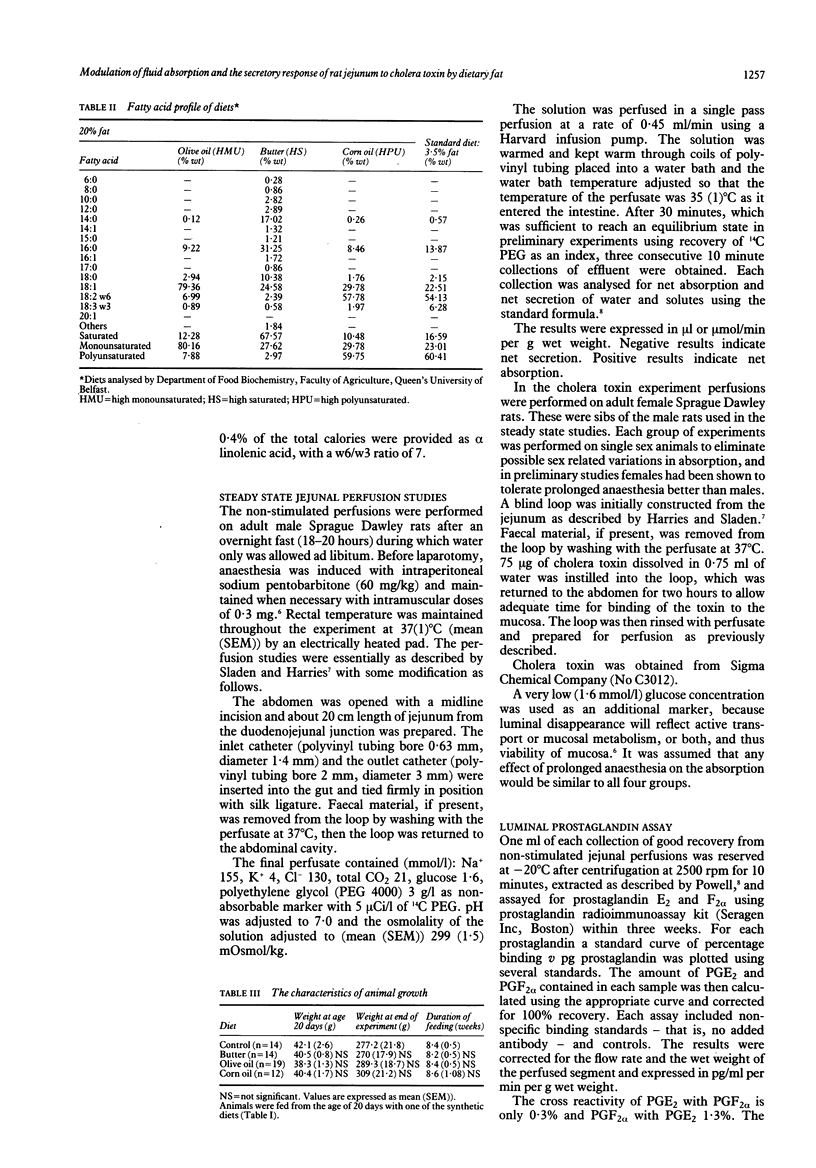
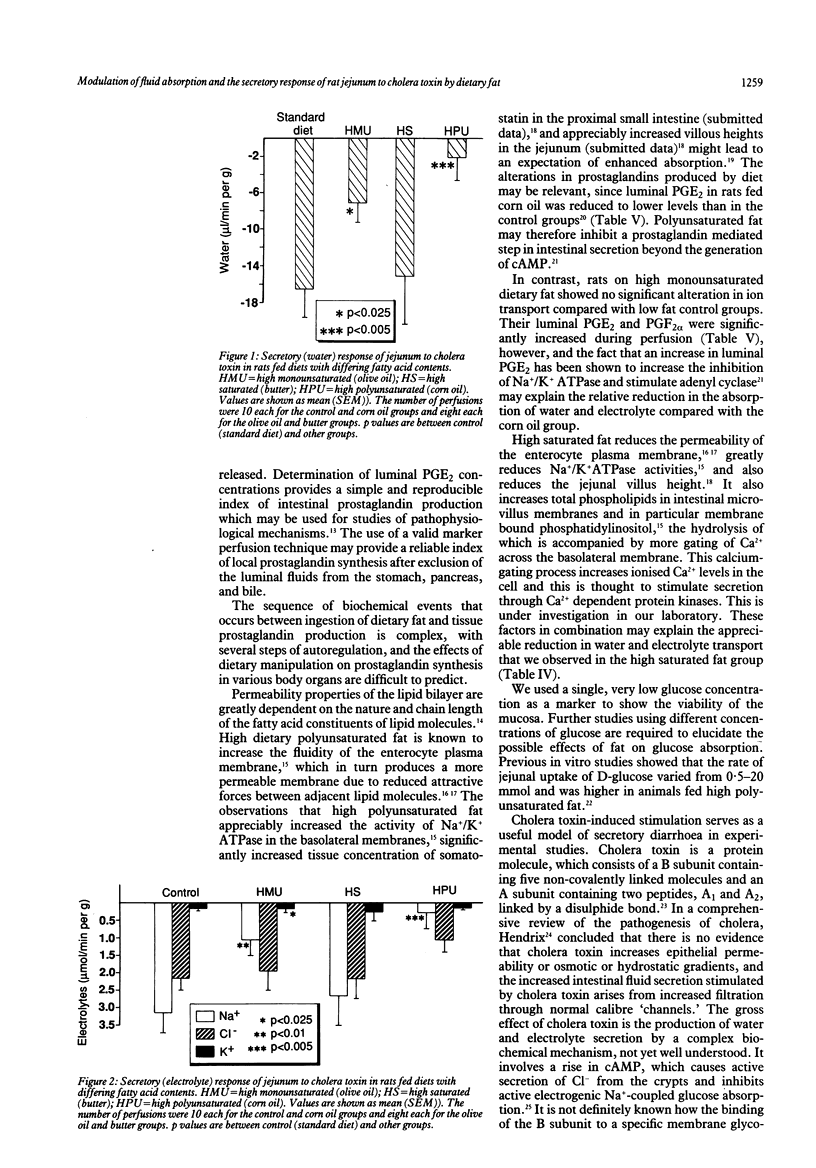
To study the effects of dietary fat on jejunal water and ion absorption and on cholera toxin-induced secretion, 3 week old Sprague Dawley rats were fed isocaloric diets. Forty per cent of the total calories were given as fat, as butter (high saturated fat), olive oil (high monounsaturated fat), or corn oil (high polyunsaturated fat), with one group on low fat (10% of calories) standard laboratory diet as controls. During in vivo jejunal perfusion studies we found that (i) a polyunsaturated fat (corn oil) supplemented diet improves jejunal absorption of water and electrolytes and these changes are independent of the observed concentrations of luminal prostaglandins; (ii) high dietary fat appreciably reduced the secretory response to cholera toxin, probably without fundamentally changing the mechanism by which cholera toxin induces secretion. We conclude that dietary fat composition altered the permeability and transport characteristics of the small intestine. This observation might have relevance to some human diarrhoeal disorders.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi S., Mirelman D. Nonimmunoglobulin fraction of human milk inhibits the adherence of certain enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains to guinea pig intestinal tract. Pediatr Res. 1987 Aug;22(2):130–134. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198708000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs J. M. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding between lipids: influence on organization and function of lipids in membranes. Can J Biochem. 1980 Oct;58(10):755–770. doi: 10.1139/o80-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasitus T. A., Davidson N. O., Schachter D. Variations in dietary triacylglycerol saturation alter the lipid composition and fluidity of rat intestinal plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 25;812(2):460–472. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasitus T. A., Davidson N. O., Schachter D. Variations in dietary triacylglycerol saturation alter the lipid composition and fluidity of rat intestinal plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 25;812(2):460–472. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresson J. L., Pang K. Y., Walker W. A. Microvillus membrane differentiation: quantitative difference in cholera toxin binding to the intestinal surface of newborn and adult rabbits. Pediatr Res. 1984 Oct;18(10):984–987. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198410000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhave K., Rask-Madsen J. Prostaglandin E2 in jejunal fluids and its potential diagnostic value for selecting patients with indomethacin-sensitive diarrhoea. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;11(3):191–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb01840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D. Phase transitions and fluidity characteristics of lipids and cell membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1975 May;8(2):185–235. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney A. N., Gots R. E., Giannella R. A. Na+-K+)-stimulated adenosinetriphosphatase in isolated intestinal villus tip and crypt cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 15;367(3):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Rosing E., Wiley K. S., Slater I. H. Somatostatin inhibits adrenergic and cholinergic neurotransmission in smooth muscle. Life Sci. 1978 Oct 23;23(16):1659–1664. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. A., Hendricks K. M., Mathis R. K., Laramee S., Walker W. A. Chronic nonspecific diarrhea: dietary relationships. Pediatrics. 1979 Oct;64(4):402–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Sherwin R. S., Dobbins J. W. Somatostatin inhibits fluid secretion in the rat jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jun;78(6):1554–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries J. T., Sladen G. E. The effects of different bile salts on the absorption of fluid, electrolytes, and monosaccharides in the small intestine of the rat in vivo. Gut. 1972 Aug;13(8):596–603. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.8.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaros W., Biller J., Greer S., O'Dorisio T., Grand R. Successful treatment of idiopathic secretory diarrhea of infancy with the somatostatin analogue SMS 201-995. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jan;94(1):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90629-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman J. S., Turkisk V. J., Monto A. S., Thompson F. E., Isaacson R. E. Milk fat and gastrointestinal illness. Am J Public Health. 1984 Dec;74(12):1371–1373. doi: 10.2105/ajph.74.12.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosky A., Markel D. E., Touchstone B., Peterson J. W. Chemical characterization of the structure of cholera toxin and its natural toxoid. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133 (Suppl):14–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_1.s14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mózsik G., Kutas J., Nagy L., Németh G. Inhibition of Mg2+-Na+-K+-dependent ATPase system from human gastric mucosa by prostaglandins E1 and E2. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Nov;29(1):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otnaess A. B., Svennerholm A. M. Non-immunoglobulin fraction of human milk protects rabbits against enterotoxin-induced intestinal fluid secretion. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):738–740. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.738-740.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W., Malawer S. J. Relationship between water and solute transport from isosmotic solutions by rat intestine in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):49–55. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. S. Rapid extraction of oxygenated metabolites of arachidonic acid from biological samples using octadecylsilyl silica. Prostaglandins. 1980 Nov;20(5):947–957. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(80)90144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz D., Karmeli F., Okon E. Effects of bisacodyl on cAMP and prostaglandin E2 contents, (Na + K) ATPase, adenyl cyclase, and phosphodiesterase activities of rat intestine. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Aug;25(8):602–608. doi: 10.1007/BF01318874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz D., Karmeli F., Okon E. Effects of bisacodyl on cAMP and prostaglandin E2 contents, (Na + K) ATPase, adenyl cyclase, and phosphodiesterase activities of rat intestine. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Aug;25(8):602–608. doi: 10.1007/BF01318874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu B. K., Tripp J. H., Candy D. C., Harries J. T. Loperamide: studies on its mechanism of action. Gut. 1981 Aug;22(8):658–662. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.8.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serebro H. A., Bayless T. M., Hendrix T. R., Iber F. L., McGonagle T. Absorption of d-glucose by the rabbit jejunum during cholera toxin-induced diarrhoea. Nature. 1968 Mar 30;217(5135):1272–1273. doi: 10.1038/2171272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Harries J. T. Studies on the effects of unconjugated dihydroxy bile salts on rat small intestinal function in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):443–456. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. S., Warhurst G., Turnberg L. A. Synthesis and degradation of prostaglandin E2 in the epithelial and sub-epithelial layers of the rat intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 13;713(3):684–687. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. B., Keelan M., Clandinin M. T., Walker K. Dietary fat selectively alters transport properties of rat jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):279–288. doi: 10.1172/JCI112288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollström T., Hellström P. M., Johansson C., Pernow B. Effects of prostaglandins E2 and F2 alpha on motility of small intestine in man. Dig Dis Sci. 1988 May;33(5):552–557. doi: 10.1007/BF01798356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


