Abstract
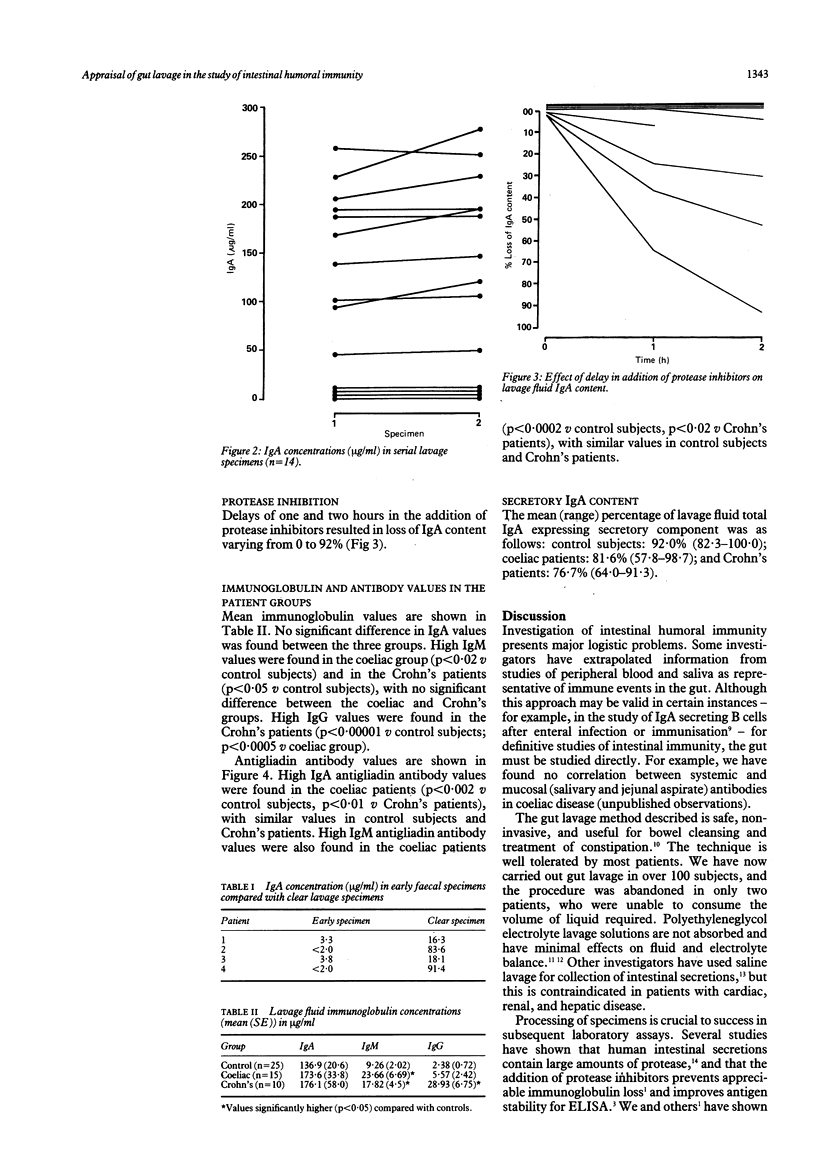
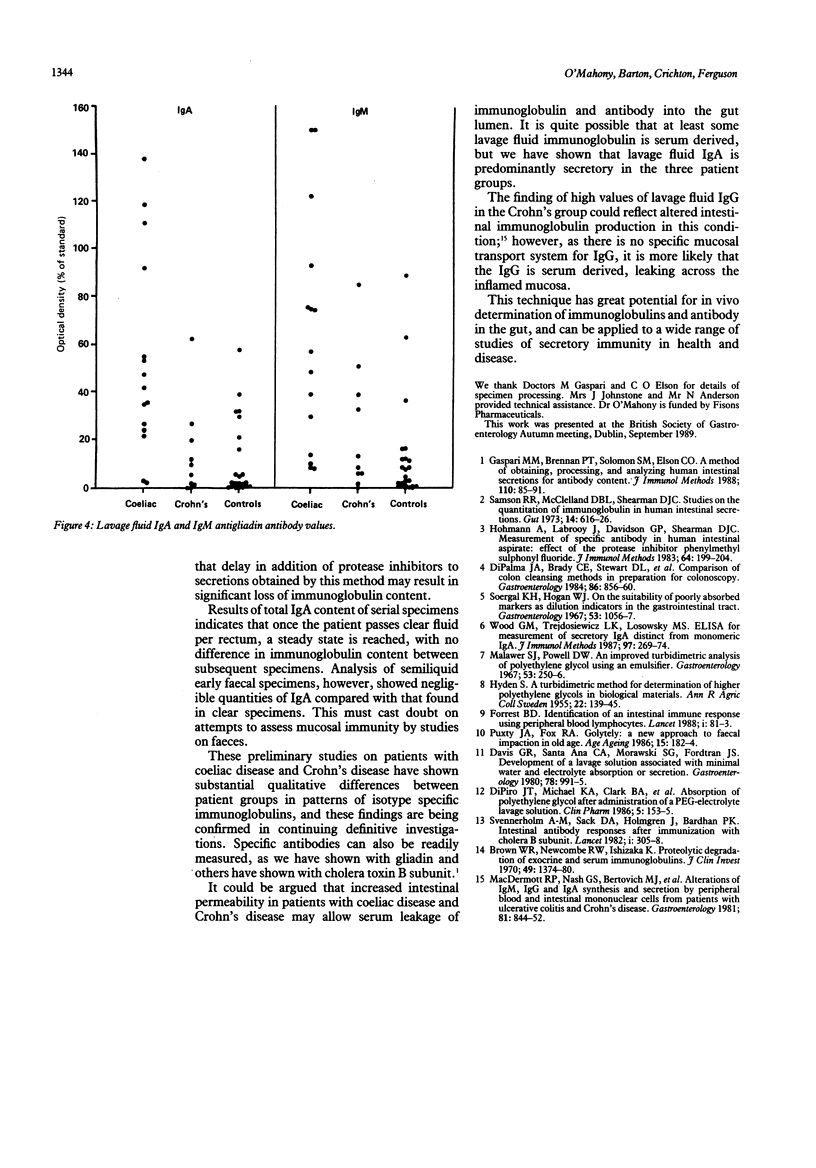
Direct investigation of intestinal humoral immunity requires collection of intestinal secretions or mucosal biopsy specimens, or both. A non-invasive technique of gut lavage, with a polyethyleneglycol electrolyte lavage solution as a means of collecting intestinal secretions for immunoglobulin and antibody studies, was evaluated. Fifty patients were studied--25 immunologically normal patients or volunteers, 15 patients with untreated coeliac disease, and 10 patients with active Crohn's disease. Protease inhibitors were added promptly to samples to prevent proteolysis of immunoglobulin content. Treated lavage samples were assayed by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin and antibody content. Studies of serial lavage specimens showed that early, faecally contaminated specimens contained negligible quantities of immunoglobulin, but once the specimens became clear a steady state was reached, with little variation in immunoglobulin content between serial specimens and with a uniform dilution (around 20%) of the ingested polyethyleneglycol. Gut lavage fluid IgA was predominantly secretory, comprising 92%, 81.6%, and 76.7% respectively of the total IgA gut lavage fluid content in the control, coeliac, and Crohn's groups. High values of total IgM and IgA and IgM antigliadin antibodies were detected in the coeliac group, and high values of IgG in the Crohn's disease group. This method of gut lavage is not only an effective bowel cleanser, but also a noninvasive means of obtaining intestinal secretions for the study of humoral immunity in gastrointestinal disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown W. R., Newcomb R. W., Ishizaka K. Proteolytic degradation of exocrine and serum immunoglobulins. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jul;49(7):1374–1380. doi: 10.1172/JCI106354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. R., Santa Ana C. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Development of a lavage solution associated with minimal water and electrolyte absorption or secretion. Gastroenterology. 1980 May;78(5 Pt 1):991–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPalma J. A., Brady C. E., 3rd, Stewart D. L., Karlin D. A., McKinney M. K., Clement D. J., Coleman T. W., Pierson W. P. Comparison of colon cleansing methods in preparation for colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 1984 May;86(5 Pt 1):856–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPiro J. T., Michael K. A., Clark B. A., Dickson P., Vallner J. J., Bowden T. A., Jr, Tedesco F. J. Absorption of polyethylene glycol after administration of a PEG-electrolyte lavage solution. Clin Pharm. 1986 Feb;5(2):153–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest B. D. Identification of an intestinal immune response using peripheral blood lymphocytes. Lancet. 1988 Jan 16;1(8577):81–83. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90284-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaspari M. M., Brennan P. T., Solomon S. M., Elson C. O. A method of obtaining, processing, and analyzing human intestinal secretions for antibody content. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 25;110(1):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A., LaBrooy J., Davidson G. P., Shearman D. J. Measurement of specific antibodies in human intestinal aspirate: effect of the protease inhibitor phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 11;64(1-2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Nash G. S., Bertovich M. J., Seiden M. V., Bragdon M. J., Beale M. G. Alterations of IgM, IgG, and IgA Synthesis and secretion by peripheral blood and intestinal mononuclear cells from patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1981 Nov;81(5):844–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puxty J. A., Fox R. A. Golytely: a new approach to faecal impaction in old age. Age Ageing. 1986 May;15(3):182–184. doi: 10.1093/ageing/15.3.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson R. R., McClelland D. B., Shearman D. J. Studies on the quantitation of immunoglobulin in human intestinal secretions. Gut. 1973 Aug;14(8):616–626. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.8.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Sack D. A., Holmgren J., Bardhan P. K. Intestinal antibody responses after immunisation with cholera B subunit. Lancet. 1982 Feb 6;1(8267):305–308. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91568-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. M., Trejdosiewicz L. K., Losowsky M. S. ELISA for measurement of secretory IgA distinct from monomeric IgA. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Mar 12;97(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


