Abstract
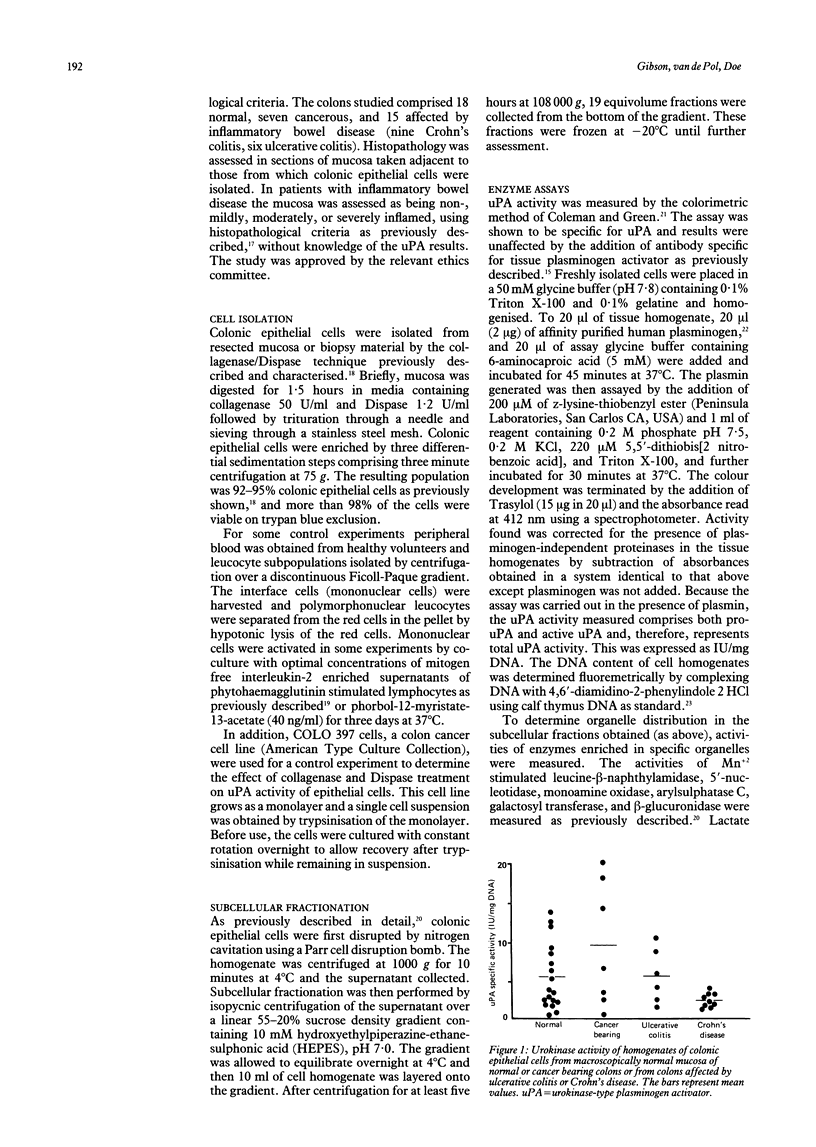
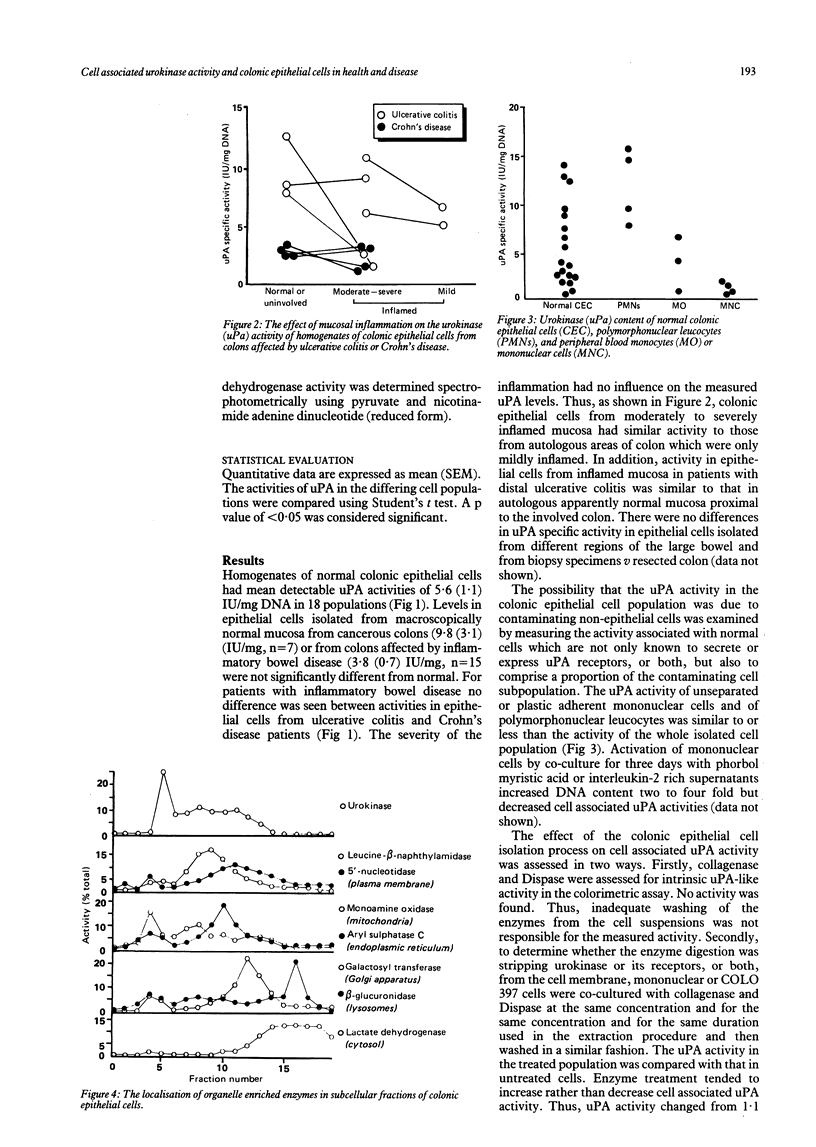
It is not known if urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) is associated with normal colonic epithelial cells. The aims of this study were to determine if normal colonic epithelial cells have uPA activity and whether this is concentrated at the cell membrane. In addition, the contribution of colonic epithelial cell associated uPA activity to disease related pertubations of mucosal uPA activity were examined. A highly enriched population of colonic epithelial cells was isolated from resected colon or biopsy specimens by an enzymatic technique. uPA activity was measured in cell homogenates by a specific and sensitive colorimetric method and expressed relative to cellular DNA. In two experiments subcellular fractionation of colonic epithelial cells was performed by nitrogen cavitation followed by ultracentrifugation over a linear sucrose gradient. The fractions collected were analysed for uPA and organelle-specific enzyme activities. Normal colonic epithelial cells have cell associated uPA activity (mean (SEM) 5.6 (1.1) IU/mg, n = 18). This colocalised with fractions enriched for leucine-beta-naphthylamidase and 5'-nucleotidase, markers of plasma membrane. uPA activities in epithelial cells from cancerous colons (9.8 (3.1) n = 7) or from mucosa affected by inflammatory bowel disease (3.8 (0.7) n = 15) were not significantly different from normal (paired t test), while that in epithelial cells from greatly inflamed mucosa was similar to that from autologous normal or mildly inflamed areas (4.4 (1.2) v 5.9 (3.6), n = 9). Thus normal colonic epithelial cells have cell associated uPA activity which is concentrated on the plasma membranes, suggesting the presence of uPA receptors. Increased mucosal levels of uPA previously reported in patients with inflammatory bowel disease are not due to increased colonic epithelial cell associated uPA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd D., Florent G., Kim P., Brattain M. Determination of the levels of urokinase and its receptor in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 1;48(11):3112–3116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtin P., Chavanel G., Foidart J. M., Martin E. Antigens of the basement membrane and the peritumoral stroma in human colonic adenocarcinomas: an immunofluorescence study. Int J Cancer. 1982 Jul 15;30(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman P. L., Green G. D. A sensitive, coupled assay for plasminogen activator using a thiol ester substrate for plasmin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:617–626. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corasanti J. G., Celik C., Camiolo S. M., Mittelman A., Evers J. L., Barbasch A., Hobika G. H., Markus G. Plasminogen activator content of human colon tumors and normal mucosae: separation of enzymes and partial purification. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Aug;65(2):345–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayle D. R., Sim P. S., Irvine D. K., Doe W. F. Isolation of plasma membrane from human blood monocytes. Subcellular fractionation and marker distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 1;147(2):409–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelister J. S., Lewin M. R., Driver H. E., Savage F., Mahmoud M., Gaffney P. J., Boulos P. B. Plasminogen activators in experimental colorectal neoplasia: a role in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence? Gut. 1987 Jul;28(7):816–821. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.7.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson P. R., van de Pol E., Barratt P. J., Doe W. F. Ulcerative colitis--a disease characterised by the abnormal colonic epithelial cell? Gut. 1988 Apr;29(4):516–521. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.4.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson P. R., van de Pol E., Maxwell L. E., Gabriel A., Doe W. F. Isolation of colonic crypts that maintain structural and metabolic viability in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1989 Feb;96(2 Pt 1):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91549-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson P. R., van de Pol E., Pullman W., Doe W. F. Lysis of colonic epithelial cells by allogeneic mononuclear and lymphokine activated killer cells derived from peripheral blood and intestinal mucosa: evidence against a pathogenic role in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1988 Aug;29(8):1076–1084. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.8.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Wojta J., Hienert G., Christ G., Heger M. E., Pflüger H., Binder B. R. Effect of urokinase on the proliferation of primary cultures of human prostatic cells. Thromb Res. 1987 Nov 1;48(3):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohga S., Harvey S. R., Weaver R. M., Markus G. Localization of plasminogen activators in human colon cancer by immunoperoxidase staining. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1787–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Goldfarb R. H., Brundage R., Siegal G. P., Terranova V., Garbisa S. Effect of plasminogen activator (urokinase), plasmin, and thrombin on glycoprotein and collagenous components of basement membrane. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4629–4636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Biegel D., Reich E. Mammary plasminogen activator: correlation with involution, hormonal modulation and comparison between normal and neoplastic tissue. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):929–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Quigley J. P., Kellerman G. M., Reich E. Fibrinolysis associated with oncogenic transformation. Requirement of plasminogen for correlated changes in cellular morphology, colony formation in agar, and cell migration. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1056–1064. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky D. K., Isselbacher K. J. Glycoprotein composition of colonic mucosa. Specific alterations in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1984 Nov;87(5):991–998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roediger W. E. The colonic epithelium in ulcerative colitis: an energy-deficiency disease? Lancet. 1980 Oct 4;2(8197):712–715. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91934-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim P. S., Stephens R. W., Fayle D. R., Doe W. F. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator in colorectal carcinomas and adenomatous polyps: quantitative expression of active and proenzyme. Int J Cancer. 1988 Oct 15;42(4):483–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Reich E., Sherman M. I. Plasminogen activator in early embryogenesis: enzyme production by trophoblast and parietal endoderm. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terpstra O. T., van Blankenstein M., Dees J., Eilers G. A. Abnormal pattern of cell proliferation in the entire colonic mucosa of patients with colon adenoma or cancer. Gastroenterology. 1987 Mar;92(3):704–708. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissot J. D., Hauert J., Bachmann F. Characterization of plasminogen activators from normal human breast and colon and from breast and colon carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1984 Sep 15;34(3):295–302. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. A., Crama-Bohbouth G., Verspaget H. W., Verheijen J. H., Dooijewaard G., Weterman I. T., Lamers C. B. Plasminogen activators in the intestine of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Oct 31;60(2):262–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin P. A., Griffioen G., Verspaget H. W., Verheijen J. H., Lamers C. B. Plasminogen activators and tumor development in the human colon: activity levels in normal mucosa, adenomatous polyps, and adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 1;47(17):4654–4657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


