Abstract
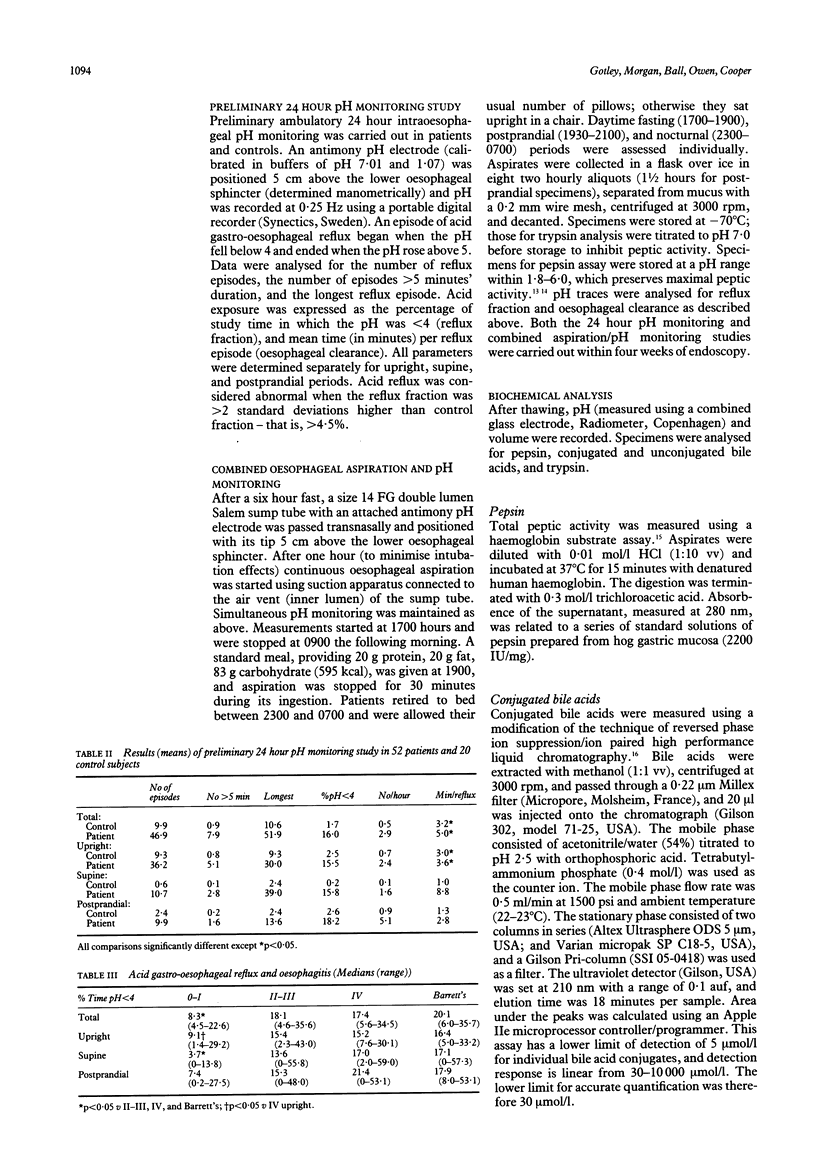
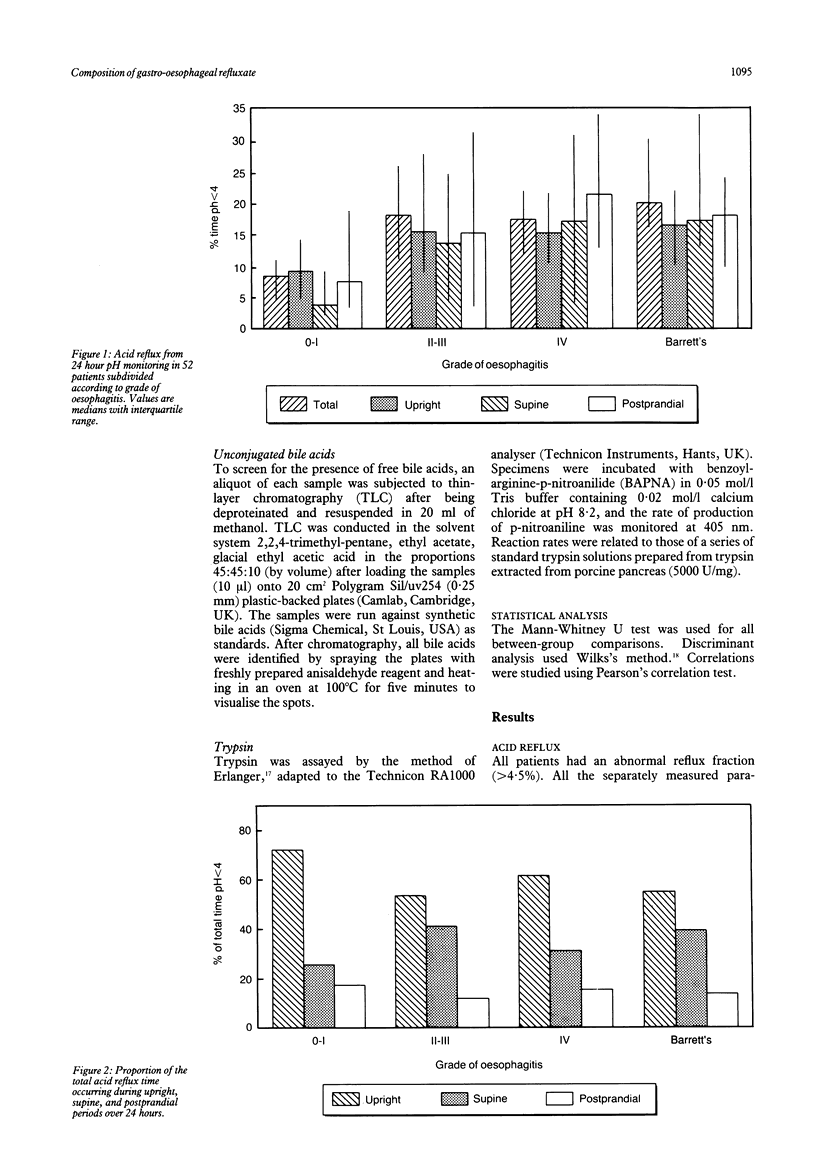
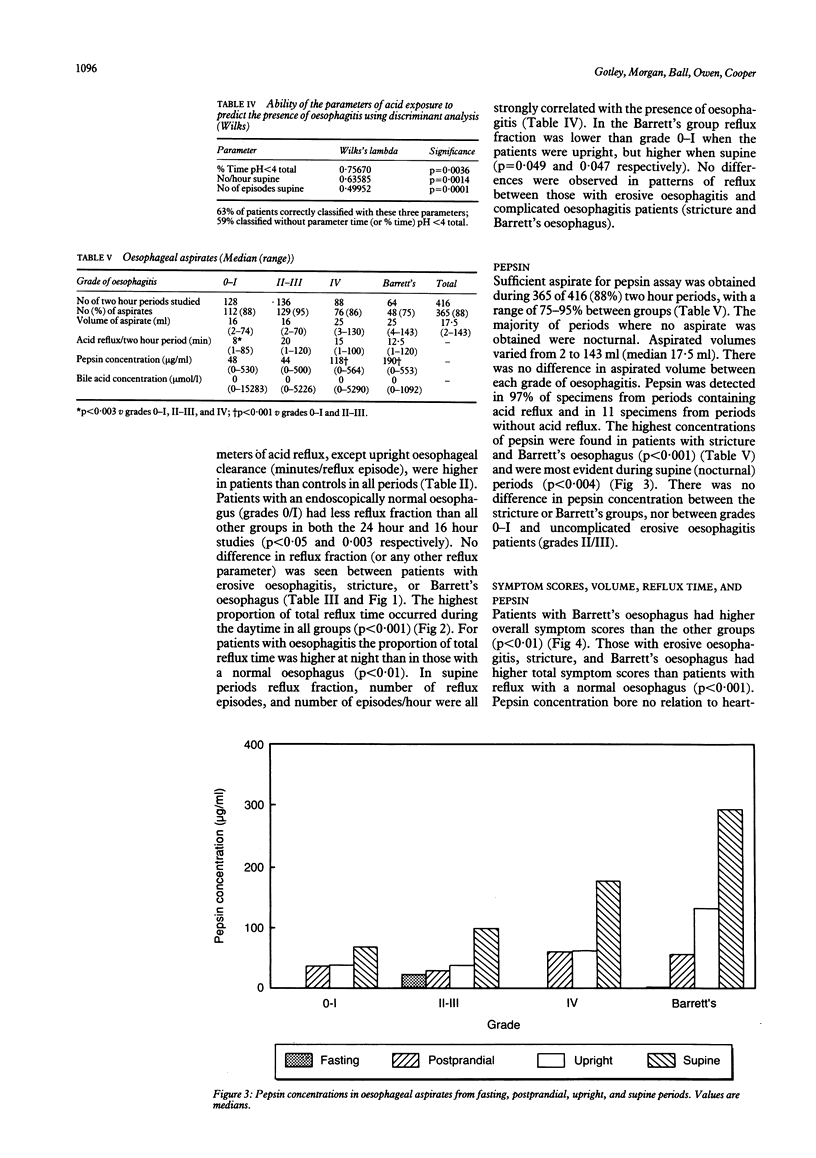
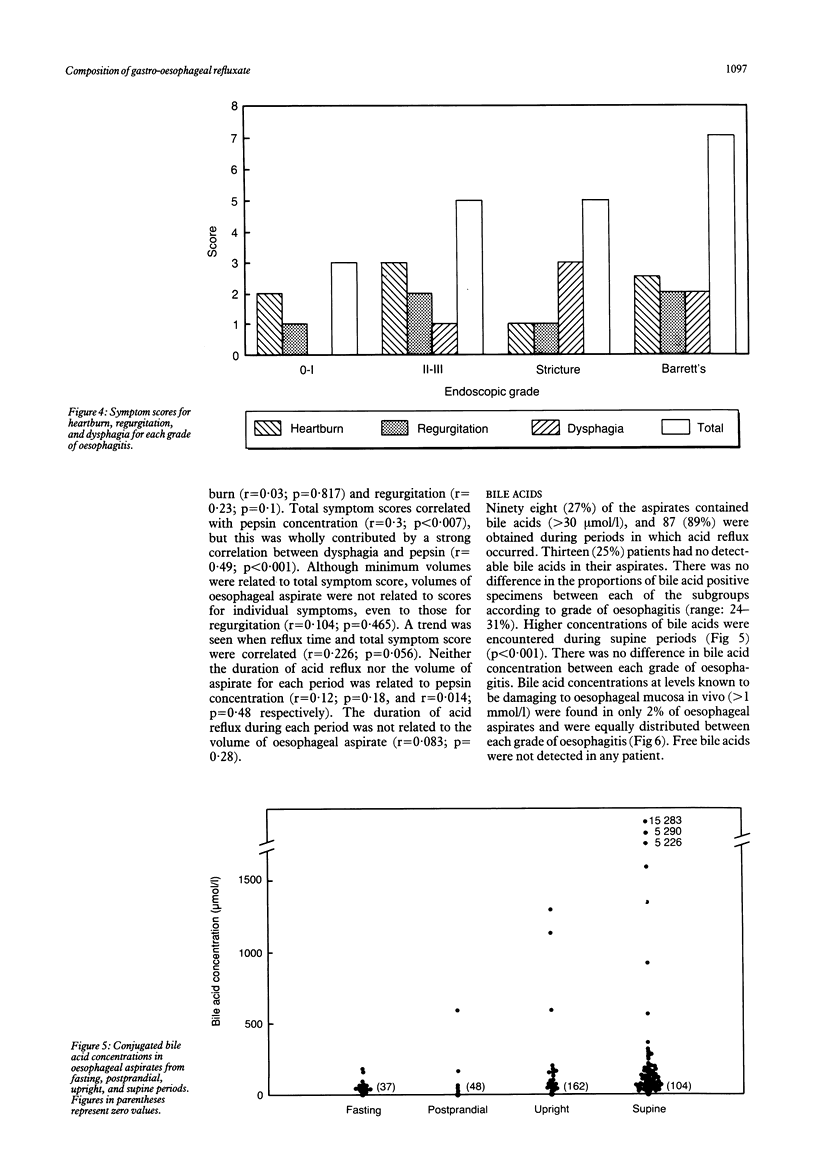
Fifty two patients with abnormal acid gastro-oesophageal reflux were studied by simultaneous oesophageal pH monitoring and continuous aspiration for 16 hours. Aspirates (from discrete two hour periods) were analysed for volume, pH, bile acids (conjugated and unconjugated), trypsin, and pepsin. The results were compared with pH changes and degree of oesophagitis. Patients with oesophagitis had greater acid reflux than those without, but patients with stricture and Barrett's oesophagus had similar acid reflux to those with uncomplicated erosive oesophagitis. Pepsin concentrations were highest in patients with stricture and Barrett's oesophagus particularly during nocturnal periods. Conjugated bile acids were detected in 75% of patients, mainly during the night, but only 2% of aspirates contained concentrations likely to be cytotoxic. Unconjugated bile acids were not detected, and trypsin was seldom found. Reflux oesophagitis is caused by acid and pepsin. Bile acids and trypsin are probably unimportant.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AYLWIN J. A. The physiological basis of reflux oesophagitis in sliding hiatal diaphragmatic hernia. Thorax. 1953 Mar;8(1):38–45. doi: 10.1136/thx.8.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstad A. A modified hemoglobin substrate method for the estimation of pepsin in gastric juice. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1970;5(5):343–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS F. S., WANGENSTEEN O. H. Role of bile and pancreatic juice in production of esophageal erosions and anemia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Aug;77(4):862–866. doi: 10.3181/00379727-77-18950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Wang C. I., Wernly J. A., Pellegrini C. A., Little A. G., Klementschitsch P., Bermudez G., Johnson L. F., Skinner D. B. Technique, indications, and clinical use of 24 hour esophageal pH monitoring. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980 May;79(5):656–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demeester T. R., Johnson L. F., Joseph G. J., Toscano M. S., Hall A. W., Skinner D. B. Patterns of gastroesophageal reflux in health and disease. Ann Surg. 1976 Oct;184(4):459–470. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197610000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds W. J., Hogan W. J., Helm J. F., Dent J. Pathogenesis of reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1981 Aug;81(2):376–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domellöf L., Reddy B. S., Weisburger J. H. Microflora and deconjugation of bile acids in alkaline reflux after partial gastrectomy. Am J Surg. 1980 Aug;140(2):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., KOKOWSKY N., COHEN W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Nov;95:271–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillison E. W., Capper W. M., Airth G. R., Gibson M. J., Bradford I. Hiatus hernia and heartburn. Gut. 1969 Aug;10(8):609–613. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.8.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg H. I., Dodds W. J., Gee S., Montgomery C., Zboralske F. F. Role of acid and pepsin in acute experimental esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1969 Feb;56(2):223–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotthard R., Bodemar G., Tjädermo M., Tobiasson P., Walan A. High gastric bile acid concentration in prepyloric ulcer patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 May;20(4):439–446. doi: 10.3109/00365528509089677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEIZER W. D., CLEAVELAND C. R., IBER F. L. GASTRIC INACTIVATION OF PANCREATIC SUPPLEMENTS. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1965 Apr;116:261–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetzel D. J., Dent J., Reed W. D., Narielvala F. M., Mackinnon M., McCarthy J. H., Mitchell B., Beveridge B. R., Laurence B. H., Gibson G. G. Healing and relapse of severe peptic esophagitis after treatment with omeprazole. Gastroenterology. 1988 Oct;95(4):903–912. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelz H. R., Birchler R., Bretholz A., Bron B., Capitaine Y., Delmore G., Fehr H. F., Fumagalli I., Gehrig J., Gonvers J. J. Healing and relapse of reflux esophagitis during treatment with ranitidine. Gastroenterology. 1986 Nov;91(5):1198–1205. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(86)80017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillemoe K. D., Johnson L. F., Harmon J. W. Taurodeoxycholate modulates the effects of pepsin and trypsin in experimental esophagitis. Surgery. 1985 Jun;97(6):662–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed R., Holden R. J., Hearns J. B., McKibben B. M., Buchanan K. D., Crean G. P. Effects of eight weeks' continuous treatment with oral ranitidine and cimetidine on gastric acid secretion, pepsin secretion, and fasting serum gastrin. Gut. 1983 Jan;24(1):61–66. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poxon V., Hogg B., Youngs D., Morris D. L., Keighley M. R. Incidence of bile reflux in gastric ulcer and after partial gastrectomy. Br J Surg. 1986 Apr;73(4):295–297. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800730416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. A., Aldersley M. A., Shepherd H., Lloyd R. S., Smith C. L. H2 antagonists in the treatment of reflux oesophagitis: can physiological studies predict the response? Gut. 1987 Aug;28(8):946–949. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.8.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindlbeck N. E., Heinrich C., König A., Dendorfer A., Pace F., Müller-Lissner S. A. Optimal thresholds, sensitivity, and specificity of long-term pH-metry for the detection of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jul;93(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildgrube H. J., Füssel U., Lauer H., Stockhausen H. Measurement of conjugated bile acids by ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1983 Dec 30;282:603–608. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)91637-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gara C. J., Burget D. W., Sivakumaran T., Hunt R. H. The effect of temperature and pH on the stability of human pepsin in stored gastric juice. A method to prevent activity loss. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986 Aug;21(6):650–654. doi: 10.3109/00365528609011096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


