Abstract
1. Serum and salivary concentrations of caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine) and its dimethylxanthine metabolites were measured in 10 healthy control subjects and in 19 patients with cirrhosis, for up to 96 h following a 400 mg oral caffeine load. 2. Serum and salivary caffeine concentrations correlated significantly (r = 0.954; P less than 0.001) and no significant differences were observed in the pharmacokinetic data derived from the respective concentration-time curves. 3. In the control subjects, basal salivary caffeine concentrations did not exceed 0.4 mg l-1. The median (range) basal salivary caffeine concentrations in patients with compensated cirrhosis (n = 10), 0.2 (0-0.7) mg l-1 and decompensated cirrhosis (n = 9), 0.7 (0-5.8) mg l-1, were not significantly different from control values, although three patients with decompensated cirrhosis had basal salivary caffeine values above 2.0 mg l-1. 4. In the patients with compensated cirrhosis, the median peak salivary caffeine concentration, 10.9 (8.2-16.5) mg l-1 was significantly greater than in controls, 7.1 (4.7-11.8) mg l-1 (P less than 0.01) and the median apparent volume of distribution was significantly reduced, 0.38 (0.19-0.49) vs 0.41 (0.23-0.63) l kg-1 (P less than 0.05).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



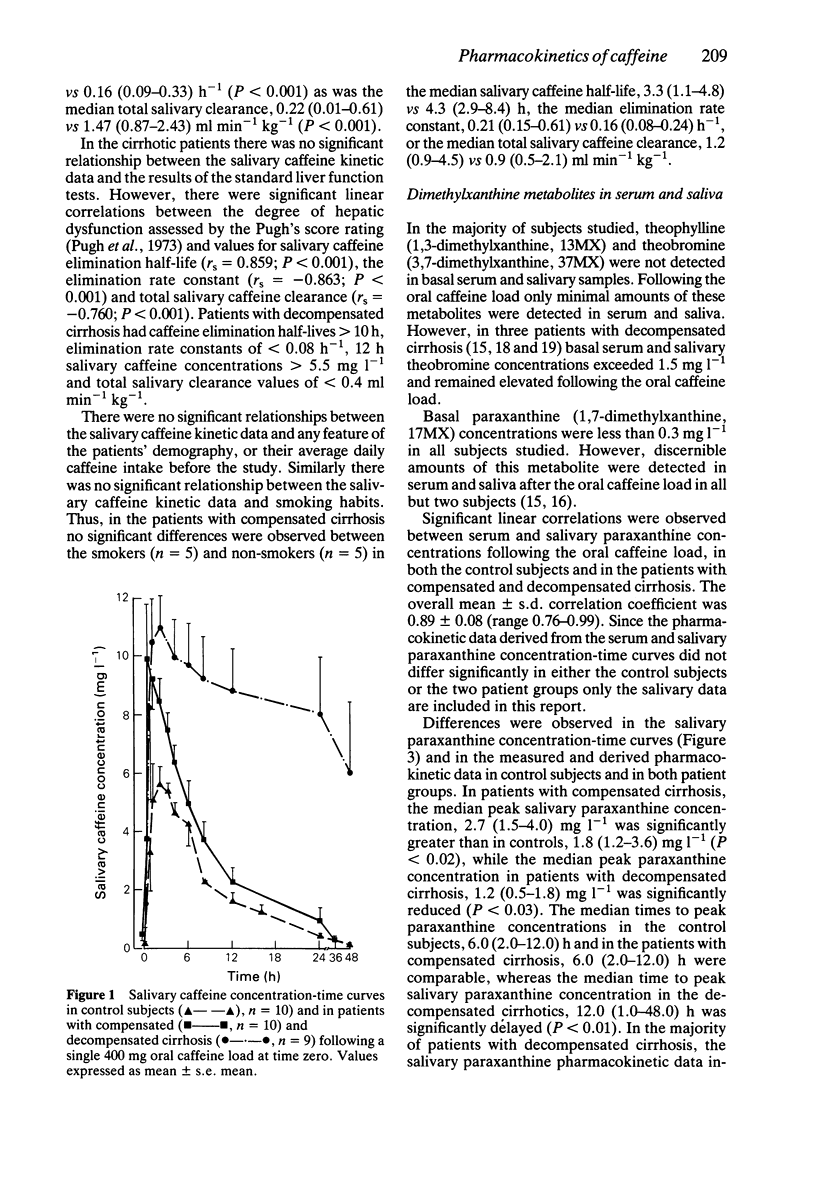
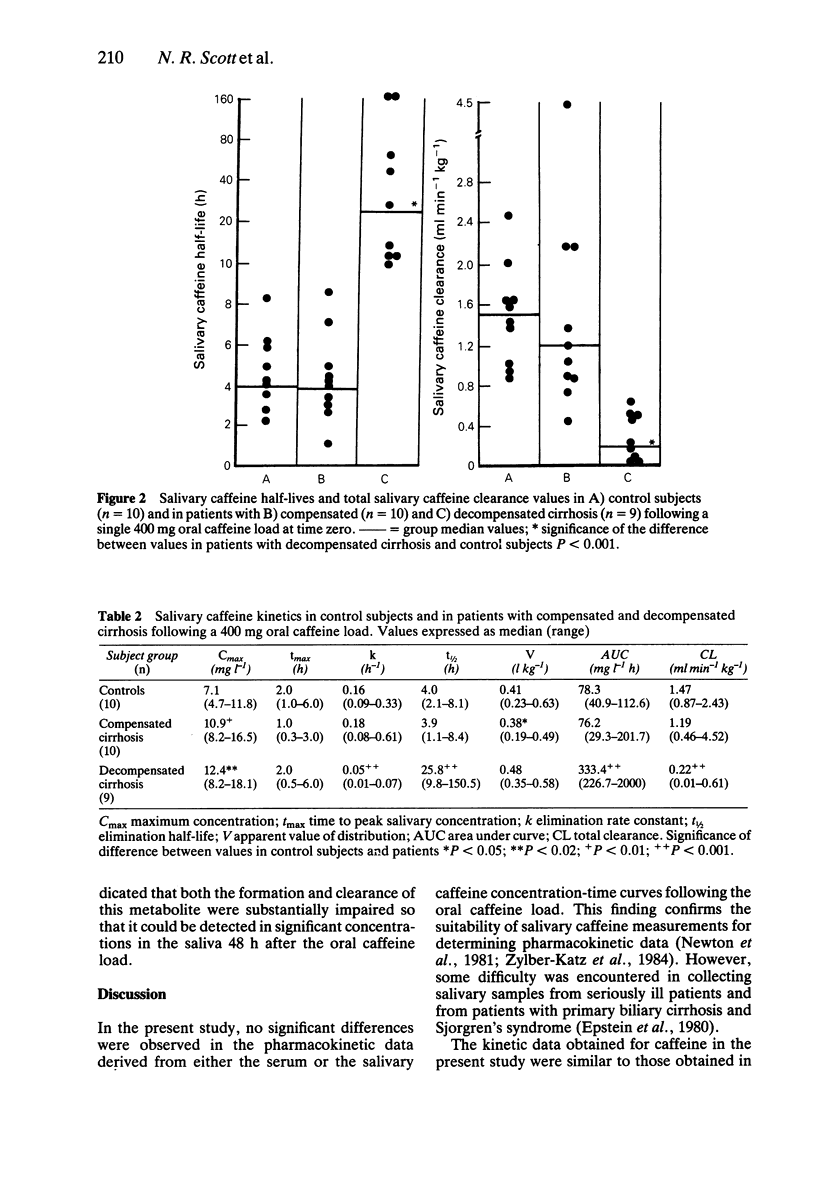
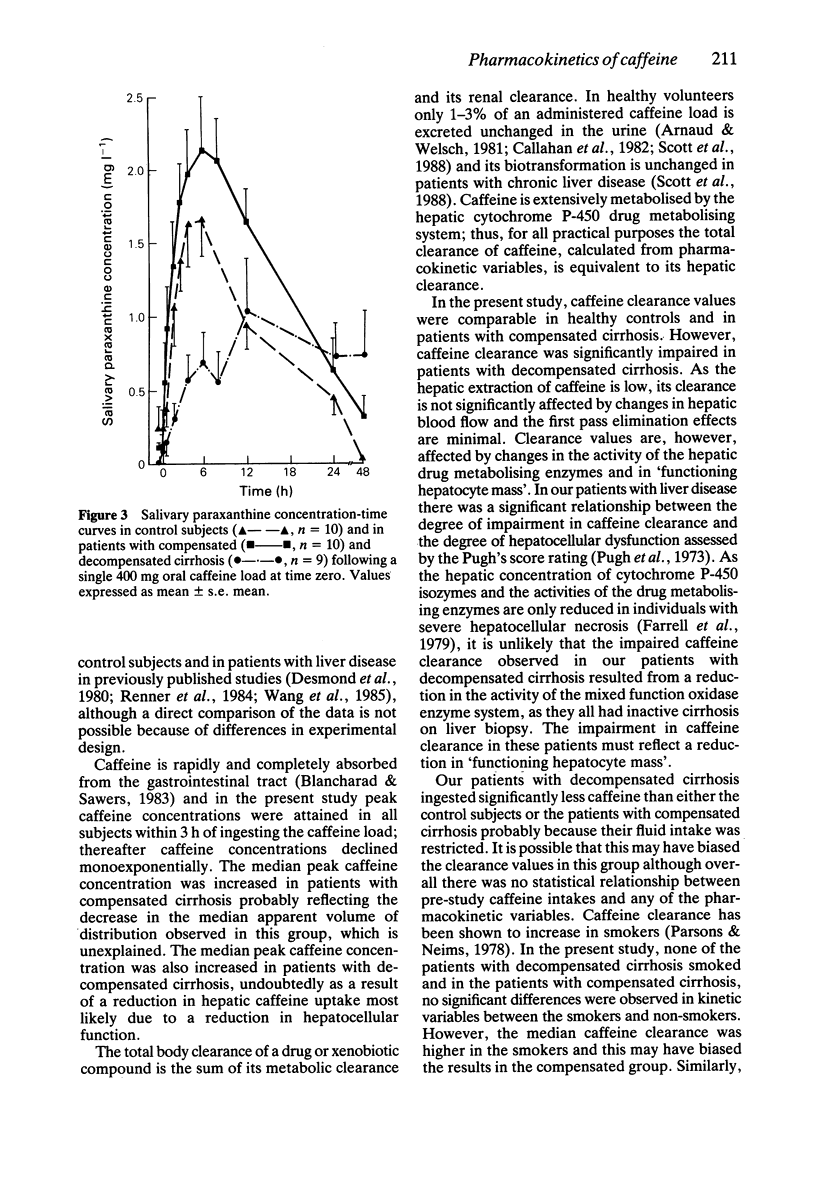


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bircher J., Küpfer A., Gikalov I., Preisig R. Aminopyrine demethylation measured by breath analysis in cirrhosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Oct;20(4):484–492. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976204484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard J., Sawers S. J. The absolute bioavailability of caffeine in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;24(1):93–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00613933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan M. M., Robertson R. S., Arnaud M. J., Branfman A. R., McComish M. F., Yesair D. W. Human metabolism of [1-methyl-14C]- and [2-14C]caffeine after oral administration. Drug Metab Dispos. 1982 Jul-Aug;10(4):417–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O., Leevy C. M., Vlahcevic Z. R., Rodgers J. B., Maddrey W. C., Seeff L., Levy L. L. Comparison of lactulose and neomycin in the treatment of chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy. A double blind controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 1977 Apr;72(4 Pt 1):573–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmond P. V., Patwardhan R. V., Johnson R. F., Schenker S. Impaired elimination of caffeine in cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 Mar;25(3):193–197. doi: 10.1007/BF01308138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein O., Thomas H. C., Sherlock S. Primary biliary cirrhosis is a dry gland syndrome with features of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Lancet. 1980 May 31;1(8179):1166–1168. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91621-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris R., Colombatti G., Fiorentini M. T., Carosso R., Arossa W., De La Pierre M. Diagnostic value of serum bile acids and routine liver function tests in hepatobiliary diseases. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive value. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Feb;28(2):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF01315142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant D. M., Tang B. K., Campbell M. E., Kalow W. Effect of allopurinol on caffeine disposition in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;21(4):454–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb05222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton R., Broughton L. J., Lind M. J., Morrison P. J., Rogers H. J., Bradbrook I. D. Plasma and salivary pharmacokinetics of caffeine in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;21(1):45–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00609587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons W. D., Neims A. H. Effect of smoking on caffeine clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Jul;24(1):40–45. doi: 10.1002/cpt197824140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh R. N., Murray-Lyon I. M., Dawson J. L., Pietroni M. C., Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renner E., Wietholtz H., Huguenin P., Arnaud M. J., Preisig R. Caffeine: a model compound for measuring liver function. Hepatology. 1984 Jan-Feb;4(1):38–46. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. K., Grice J., Wood L., Petroff V., McGuffie C. Cimetidine impairs the elimination of theophylline and antipyrine. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jul;81(1):19–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott N. R., Chakraborty J., Marks V. Determination of caffeine, theophylline and theobromine in serum and saliva using high-performance liquid chromatography. Ann Clin Biochem. 1984 Mar;21(Pt 2):120–124. doi: 10.1177/000456328402100208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott N. R., Stambuk D., Chakraborty J., Marks V., Morgan M. Y. Caffeine clearance and biotransformation in patients with chronic liver disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Apr;74(4):377–384. doi: 10.1042/cs0740377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYGSTRUP N. THE GALACTOSE ELIMINATION CAPACITY IN CONTROL SUBJECTS AND IN PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS OF THE LIVER. Acta Med Scand. 1964 Mar;175:281–289. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1964.tb00576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Kleber G., Stellaard F., Paumgartner G. Caffeine elimination: a test of liver function. Klin Wochenschr. 1985 Nov 4;63(21):1124–1128. doi: 10.1007/BF02291094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wietholtz H., Voegelin M., Arnaud M. J., Bircher J., Preisig R. Assessment of the cytochrome P-448 dependent liver enzyme system by a caffeine breath test. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;21(1):53–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00609588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylber-Katz E., Granit L., Levy M. Relationship between caffeine concentrations in plasma and saliva. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Jul;36(1):133–137. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


