Abstract
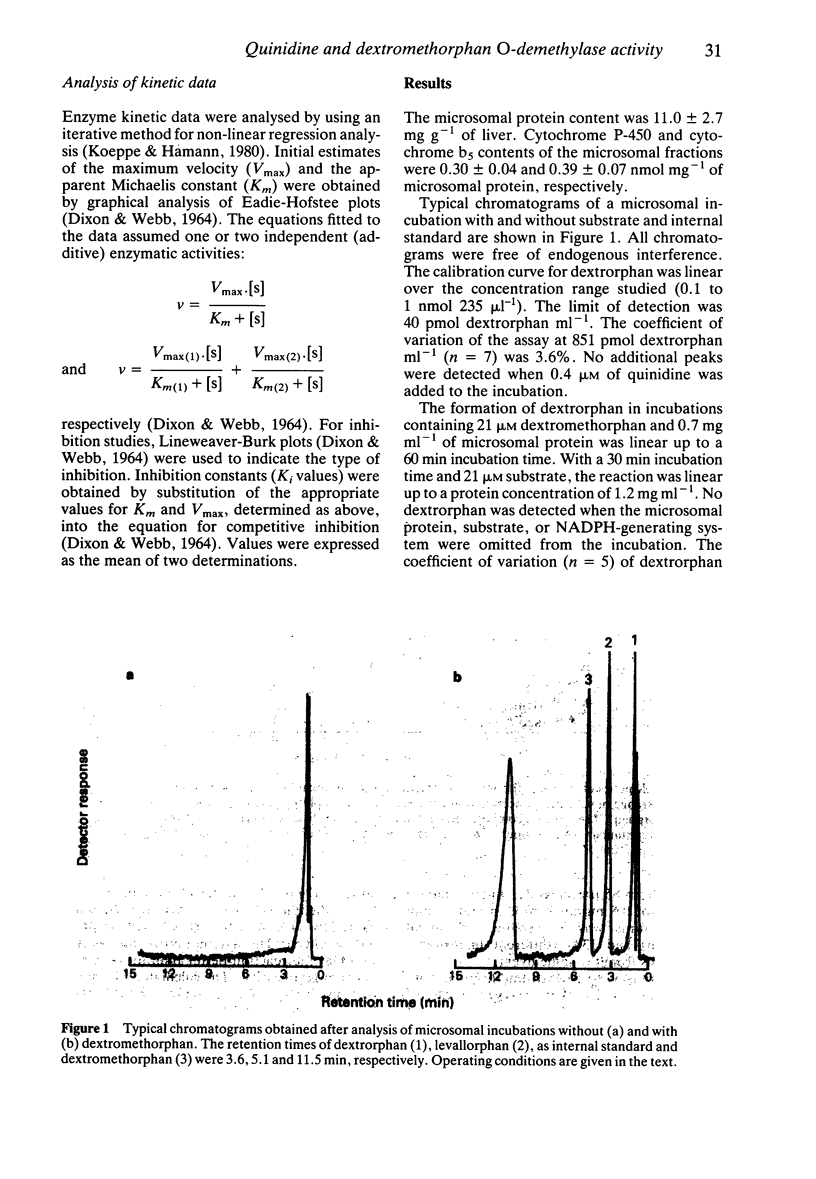
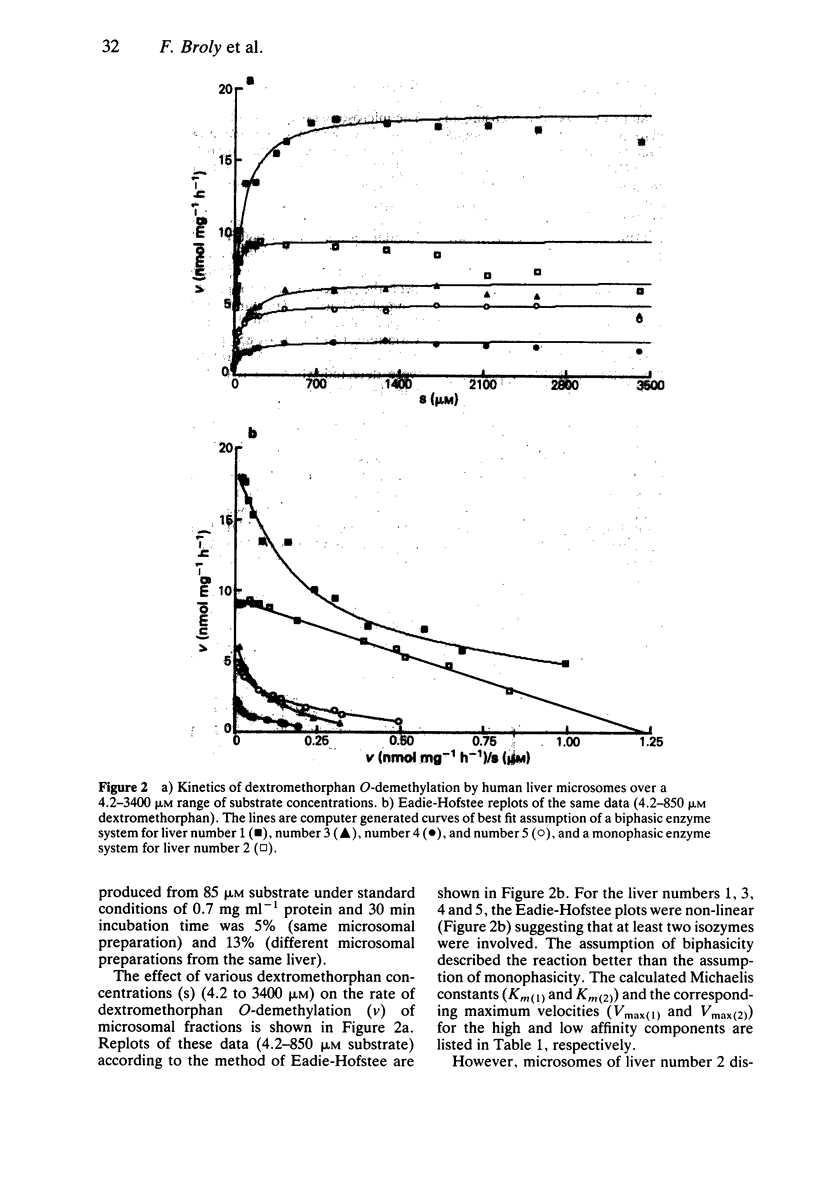
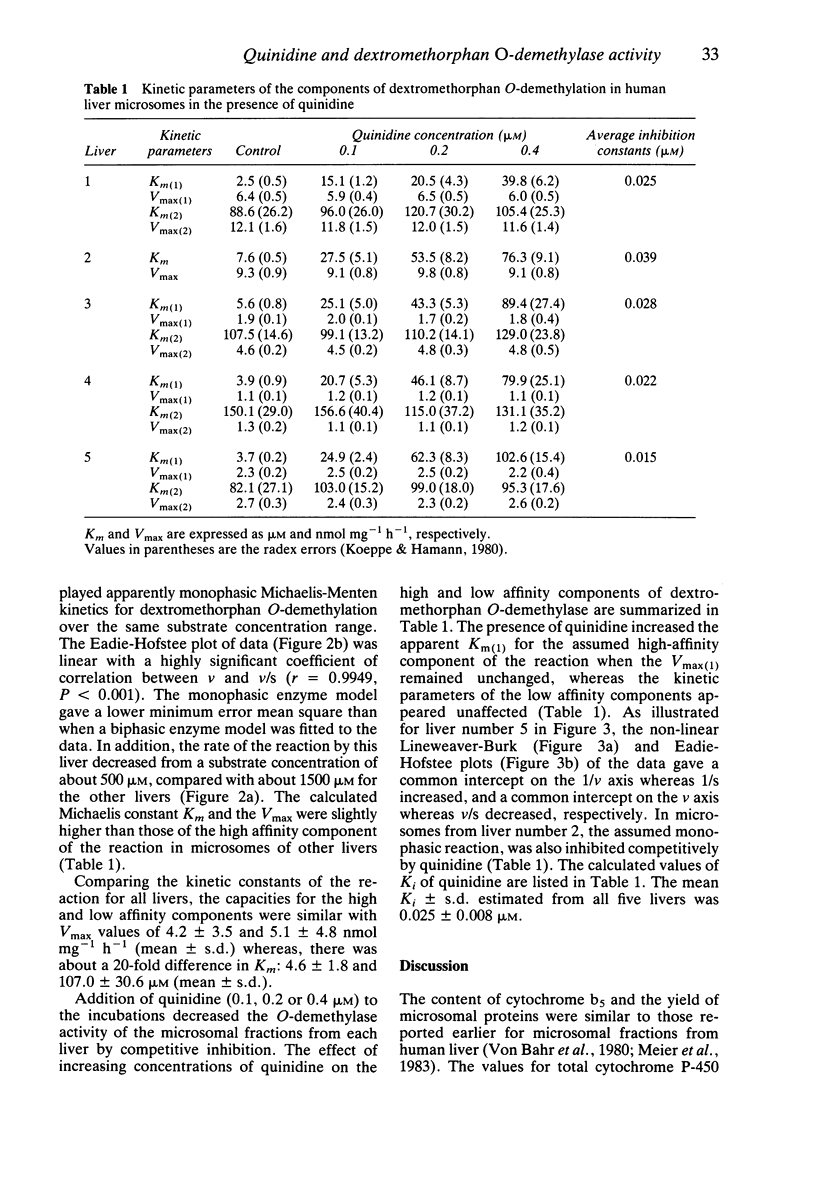
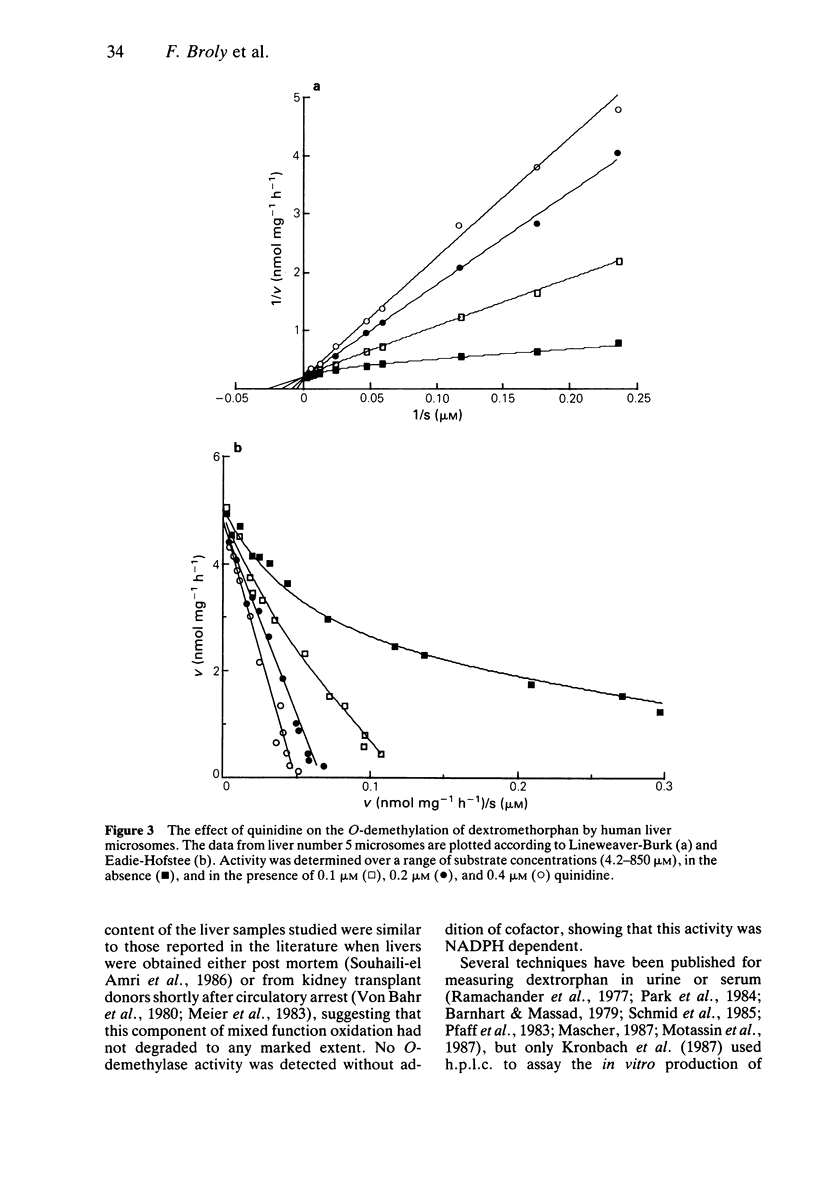
1. The kinetics of dextromethorphan O-demethylation were measured in microsomes prepared from five human livers, both in the absence and in the presence of quinidine. 2. For each liver and over the concentration range of dextromethorphan examined (4.2-3400 microM), this reaction involved an enzymatic component of high affinity, with an apparent Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) of 4.6 +/- 1.8 microM (mean +/- s.d.) and a maximum velocity (Vmax) of 4.2 +/- 3.5 nmol mg-1 h-1 (mean +/- s.d.). 3. Quinidine was a potent and competitive inhibitor of the activity of this component (mean Ki +/- s.d. of 0.025 +/- 0.008 microM) as it is for other oxidation reactions which have already been found to co-segregate with the debrisoquine-type polymorphism. 4. With microsomes from four of the five livers studied, there was evidence of a second enzymatic component of activity characterized by a similar Vmax and about 20-fold higher Km compared with the high affinity component. The activity of this low affinity component was unaffected by quinidine in the concentrations studied.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnhart J. W., Massad E. N. Determination of dextromethorphan in serum by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1979 Aug 21;163(4):390–395. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81642-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinn R., Brøsen K., Gram L. F., Haghfelt T., Otton S. V. Sparteine oxidation is practically abolished in quinidine-treated patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;22(2):194–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb05250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brøsen K., Gram L. F., Haghfelt T., Bertilsson L. Extensive metabolizers of debrisoquine become poor metabolizers during quinidine treatment. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987 Apr;60(4):312–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1987.tb01758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. S., Kahn G. C., Murray S., Brodie M. J., Boobis A. R. Evidence for an enzymatic defect in the 4-hydroxylation of debrisoquine by human liver. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;11(1):89–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distlerath L. M., Reilly P. E., Martin M. V., Davis G. G., Wilkinson G. R., Guengerich F. P. Purification and characterization of the human liver cytochromes P-450 involved in debrisoquine 4-hydroxylation and phenacetin O-deethylation, two prototypes for genetic polymorphism in oxidative drug metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):9057–9067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelbaum M. Defective oxidation of drugs: pharmacokinetic and therapeutic implications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1982 Jan-Feb;7(1):1–22. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198207010-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelbaum M. Polymorphic oxidation of debrisoquine and sparteine. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1986;214:157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. A., Mahgoub A., Sloan T. P., Idle J. R., Smith R. L. A family and population study of the genetic polymorphism of debrisoquine oxidation in a white British population. J Med Genet. 1980 Apr;17(2):102–105. doi: 10.1136/jmg.17.2.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Skoda R. C., Kimura S., Umeno M., Zanger U. M., Nebert D. W., Gelboin H. V., Hardwick J. P., Meyer U. A. Characterization of the common genetic defect in humans deficient in debrisoquine metabolism. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):442–446. doi: 10.1038/331442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Müller-Enoch D., Blair I. A. Oxidation of quinidine by human liver cytochrome P-450. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;30(3):287–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gut J., Catin T., Dayer P., Kronbach T., Zanger U., Meyer U. A. Debrisoquine/sparteine-type polymorphism of drug oxidation. Purification and characterization of two functionally different human liver cytochrome P-450 isozymes involved in impaired hydroxylation of the prototype substrate bufuralol. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11734–11743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba T., Jurima M., Mahon W. A., Kalow W. In vitro inhibition studies of two isozymes of human liver cytochrome P-450. Mephenytoin p-hydroxylase and sparteine monooxygenase. Drug Metab Dispos. 1985 Jul-Aug;13(4):443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba T., Tyndale R. E., Mahon W. A. Quinidine: potent inhibition of sparteine and debrisoquine oxidation in vivo. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;22(2):199–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb05251.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalow W. Genetic variation in the human hepatic cytochrome P-450 system. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;31(6):633–641. doi: 10.1007/BF00541288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe P., Hamann C. A program for non-linear regression analysis to be used on desk-top computers. Comput Programs Biomed. 1980 Dec;12(2-3):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(80)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronbach T., Mathys D., Gut J., Catin T., Meyer U. A. High-performance liquid chromatographic assays for bufuralol 1'-hydroxylase, debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase, and dextromethorphan O-demethylase in microsomes and purified cytochrome P-450 isozymes of human liver. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küpfer A., Preisig R. Inherited defects of hepatic drug metabolism. Semin Liver Dis. 1983 Nov;3(4):341–354. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küpfer A., Schmid B., Pfaff G. Pharmacogenetics of dextromethorphan O-demethylation in man. Xenobiotica. 1986 May;16(5):421–433. doi: 10.3109/00498258609050249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küpfer A., Schmid B., Preisig R., Pfaff G. Dextromethorphan as a safe probe for debrisoquine hydroxylation polymorphism. Lancet. 1984 Sep 1;2(8401):517–518. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92591-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leemann T., Dayer P., Meyer U. A. Single-dose quinidine treatment inhibits metoprolol oxidation in extensive metabolizers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;29(6):739–741. doi: 10.1007/BF00615971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahgoub A., Idle J. R., Dring L. G., Lancaster R., Smith R. L. Polymorphic hydroxylation of Debrisoquine in man. Lancet. 1977 Sep 17;2(8038):584–586. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91430-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascher H. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of dextrorphan and 3-hydroxymorphinan in human plasma based on a selective pre-column sample clean-up. J Chromatogr. 1987 Sep 4;420(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., Mueller H. K., Dick B., Meyer U. A. Hepatic monooxygenase activities in subjects with a genetic defect in drug oxidation. Gastroenterology. 1983 Sep;85(3):682–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer U. A., Gut J., Kronbach T., Skoda C., Meier U. T., Catin T., Dayer P. The molecular mechanisms of two common polymorphisms of drug oxidation--evidence for functional changes in cytochrome P-450 isozymes catalysing bufuralol and mephenytoin oxidation. Xenobiotica. 1986 May;16(5):449–464. doi: 10.3109/00498258609050251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motassim N., Decolin D., Le Dinh T., Nicolas A., Siest G. Direct determination of dextromethorphan and its three metabolites in urine by high-performance liquid chromatography using a precolumn switching system for sample clean-up. J Chromatogr. 1987 Nov 27;422:340–345. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otton S. V., Inaba T., Kalow W. Competitive inhibition of sparteine oxidation in human liver by beta-adrenoceptor antagonists and other cardiovascular drugs. Life Sci. 1984 Jan 2;34(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park Y. H., Kullberg M. P., Hinsvark O. N. Quantitative determination of dextromethorphan and three metabolites in urine by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Sci. 1984 Jan;73(1):24–29. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600730107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachander G., Williams F. D., Emele J. F. Determination of dextrorphan in plasma and evaluation of bioavailability of dextromethorphan hydrobromide in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1977 Jul;66(7):1047–1048. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600660740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid B., Bircher J., Preisig R., Küpfer A. Polymorphic dextromethorphan metabolism: co-segregation of oxidative O-demethylation with debrisoquin hydroxylation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985 Dec;38(6):618–624. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1985.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhaili-el Amri H., Batt A. M., Siest G. Comparison of cytochrome P-450 content and activities in liver microsomes of seven animal species, including man. Xenobiotica. 1986 Apr;16(4):351–358. doi: 10.3109/00498258609043538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner E., Iselius L., Alván G., Lindsten J., Sjöqvist F. A family study of genetic and environmental factors determining polymorphic hydroxylation of debrisoquin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985 Oct;38(4):394–401. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1985.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr C., Groth C. G., Jansson H., Lundgren G., Lind M., Glaumann H. Drug metabolism in human liver in vitro: establishment of a human liver bank. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 Jun;27(6):711–725. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr C., Spina E., Birgersson C., Ericsson O., Göransson M., Henthorn T., Sjöqvist F. Inhibition of desmethylimipramine 2-hydroxylation by drugs in human liver microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 15;34(14):2501–2505. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90533-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


