Abstract
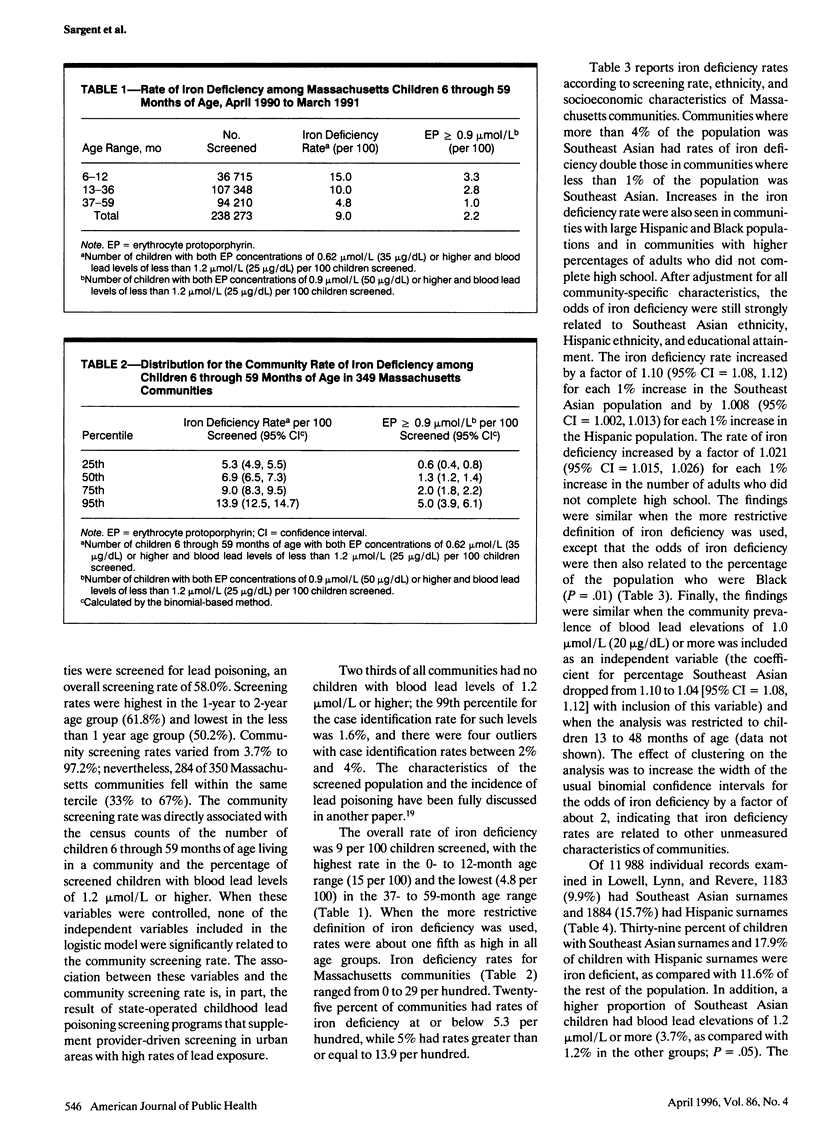
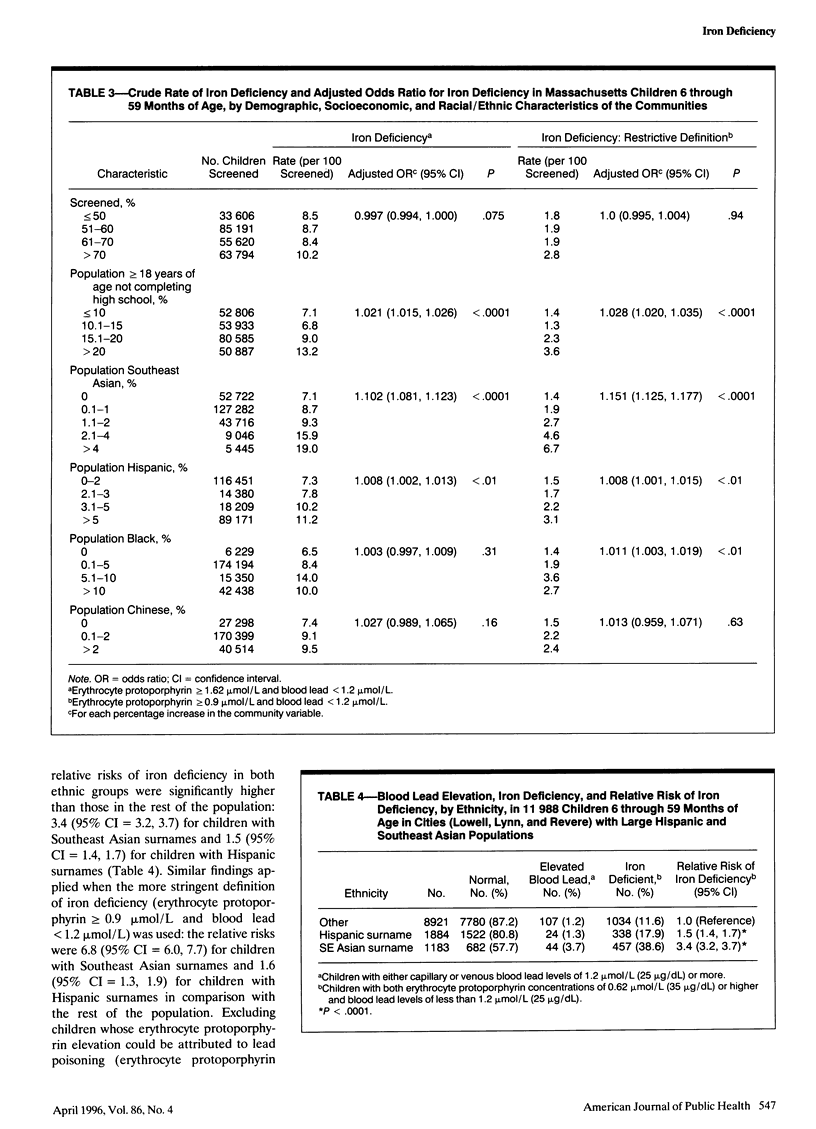
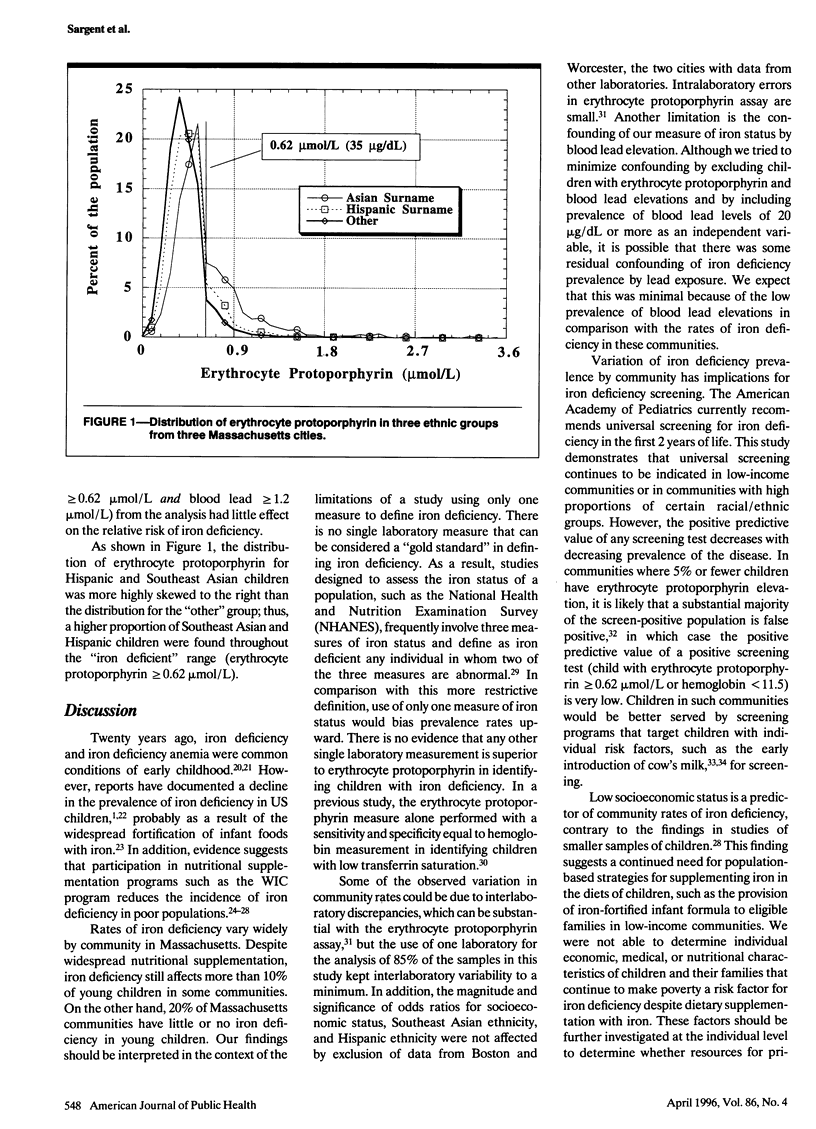
OBJECTIVES: This study examined the association between community rates of iron deficiency in children and sociodemographic characteristics of Massachusetts communities. METHODS: Between April 1990 and March 1991, 238 273 Mssachusetts children 6 through 59 months of age were screened; iron deficiency was defined as an erythrocyte protopophyrin concentration of 0.62 micromol/L or higher and a blood lead level of less than 1.2 micromol/L. Sociodemographic data were obtained from the 1990 US Census. RESULTS: Five percent of communities had iron deficiency rates greater than 13.9 per 100 children screened. Iron deficiency rate was positively associated with proportion of Southeast Asians (odds ratio [OR] = 1.10, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.08, 1.12), proportion of Hispanics (OR = 1.008, 95% CI = 1.002, 1.013), and high school incompletion (OR = 1.028, 95% CI = 1.020, 1.035). Similarly, an examination of three Massachusetts cities indicated that the iron deficiency rate was higher for children with Southeast Asian (relative risk [RR] = 3.6, 95% CI = 3.3, 3.8) and Hispanic (RR = 1.6, 95% CI = 1.5, 1.8) surnames than for all other children. CONCLUSIONS: Wide variation exists in iron deficiency rates for children in Massachusetts communities. Community iron deficiency was associated with low socioeconomic status and high proportions of Southeast Asians and Hispanics.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. E., Serdula M., Cairns K., Godes J. R., Jacobs D. R., Jr, Elmer P., Trowbridge F. L. Ethnic group differences in nutritional status of young children from low-income areas of an urban county. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 Dec;44(6):938–944. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/44.6.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraccio C. L., Bergman G. E., Daley B. P. Combined iron deficiency and lead poisoning in children. Effect on FEP levels. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1987 Dec;26(12):644–647. doi: 10.1177/000992288702601206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M., Royal J., Seeler R. Interaction of iron deficiency and lead and the hematologic findings in children with severe lead poisoning. Pediatrics. 1988 Feb;81(2):247–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland J., van Ginneken J. Maternal schooling and childhood mortality. J Biosoc Sci Suppl. 1989;10:13–34. doi: 10.1017/s0021932000025244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J., Coleman D., Coulter H. O., Horwitz R., Barry M. Hematologic abnormalities in Southeast Asian refugees. JAMA. 1983 Jun 17;249(23):3204–3206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman P. R., Yip R., Johnson C. Prevalence and causes of anemia in the United States, 1976 to 1980. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984 Mar;39(3):437–445. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/39.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delves H. T. A micro-sampling method for the rapid determination of lead in blood by atomic-absorption spectrophotometry. Analyst. 1970 May;95(130):431–438. doi: 10.1039/an9709500431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner A., Donald A. Analysis of data arising from a stratified design with the cluster as unit of randomization. Stat Med. 1987 Jan-Feb;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780060106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein D. J. Racial and ethnic differences in U.S. census omission rates. Demography. 1990 May;27(2):285–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg L., Björn-Rasmussen E., Rossander L., Suwanik R. Iron absorption from Southeast Asian diets. II. Role of various factors that might explain low absorption. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 Apr;30(4):539–548. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.4.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg L., Garby L., Suwanik R., Bjorn-Rasmussen E. Iron absorption from Southeast Asian diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Aug;27(8):826–836. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.8.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamrick H. J. Whole cow's milk, iron deficiency anemia, and hypoproteinemia: an old problem revisited. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1994 Dec;148(12):1351–1352. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1994.02170120113025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko C., Konijn A. M., Link G., Moreb J., Grauer F., Weissenberg E. Combined use of zinc protoporphyrin (ZPP), mean corpuscular volume and haemoglobin measurements for classifying microcytic RBC disorders in children and young adults. Clin Lab Haematol. 1985;7(3):259–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2257.1985.tb00034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson K. W. Interlaboratory comparison of results of erythrocyte protoporphyrin analysis. Clin Chem. 1978 Dec;24(12):2135–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsanis E., Luke K. H., Hsu E., Yates J. R. Hemoglobin E: a common hemoglobinopathy among children of Southeast Asian origin. CMAJ. 1987 Jul 1;137(1):39–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberatos P., Link B. G., Kelsey J. L. The measurement of social class in epidemiology. Epidemiol Rev. 1988;10:87–121. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looker A. C., Johnson C. L., McDowell M. A., Yetley E. A. Iron status: prevalence of impairment in three Hispanic groups in the United States. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989 Mar;49(3):553–558. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/49.3.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh W. L., Jr, Rogers Z. R., Nelson D. P., Vedvick T. S. Hematologic findings in Southeast Asian immigrants with particular reference to hemoglobin E. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1983 Jul-Aug;13(4):299–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V., Swaney S., Deinard A. Impact of the WIC program on the iron status of infants. Pediatrics. 1985 Jan;75(1):100–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monzon C. M., Fairbanks V. F., Burgert E. O., Jr, Sutherland J. E., Elliot S. C. Hematologic genetic disorders among Southeast Asian refugees. Am J Hematol. 1985 May;19(1):27–36. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830190105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern H. Uses of ecologic analysis in epidemiologic research. Am J Public Health. 1982 Dec;72(12):1336–1344. doi: 10.2105/ajph.72.12.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oski F. A. Iron deficiency in infancy and childhood. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 15;329(3):190–193. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307153290308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen G. M., Lubin A. H., Garry P. J. Preschool children in the United States: who has iron deficiency? J Pediatr. 1971 Oct;79(4):563–568. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli S. A micromethod for free erythrocyte porphyrins: the FEP test. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Jun;81(6):932–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli S., Seaman C., Zullow D., Curran A., Davidow B. Threshold for lead damage to heme synthesis in urban children. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3335–3339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush D., Horvitz D. G., Seaver W. B., Alvir J. M., Garbowski G. C., Leighton J., Sloan N. L., Johnson S. S., Kulka R. A., Shanklin D. S. The National WIC Evaluation: evaluation of the Special Supplemental Food Program for Women, Infants, and Children. I. Background and introduction. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988 Aug;48(2 Suppl):389–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan A. S., Martinez G. A., Malec D. J. The effect of the WIC program on nutrient intake of infants, 1984. Med Anthropol. 1985 Spring;9(2):153–172. doi: 10.1080/01459740.1985.9965927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent J. D., Brown M. J., Freeman J. L., Bailey A., Goodman D., Freeman D. H., Jr Childhood lead poisoning in Massachusetts communities: its association with sociodemographic and housing characteristics. Am J Public Health. 1995 Apr;85(4):528–534. doi: 10.2105/ajph.85.4.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Branch G., Henry S. E., Magpuri P. R. Effectiveness of a nutrition program for mothers and their anemic children under 5 years of age. J Am Diet Assoc. 1986 Aug;86(8):1039–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Seoane P., Windom R., Pearson H. A. Disappearance of iron-deficiency anemia in a high-risk infant population given supplemental iron. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 7;313(19):1239–1240. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511073131936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. R., DECKER E., LICHTMAN H. C. Hematologic studies of children with lead poisoning. Pediatrics. 1958 Jan;21(1):40–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip R., Binkin N. J., Fleshood L., Trowbridge F. L. Declining prevalence of anemia among low-income children in the United States. JAMA. 1987 Sep 25;258(12):1619–1623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip R., Dallman P. R. Developmental changes in erythrocyte protoporphyrin: roles of iron deficiency and lead toxicity. J Pediatr. 1984 May;104(5):710–713. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80949-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip R., Schwartz S., Deinard A. S. Screening for iron deficiency with the erythrocyte protoporphyrin test. Pediatrics. 1983 Aug;72(2):214–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip R., Walsh K. M., Goldfarb M. G., Binkin N. J. Declining prevalence of anemia in childhood in a middle-class setting: a pediatric success story? Pediatrics. 1987 Sep;80(3):330–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


