Abstract
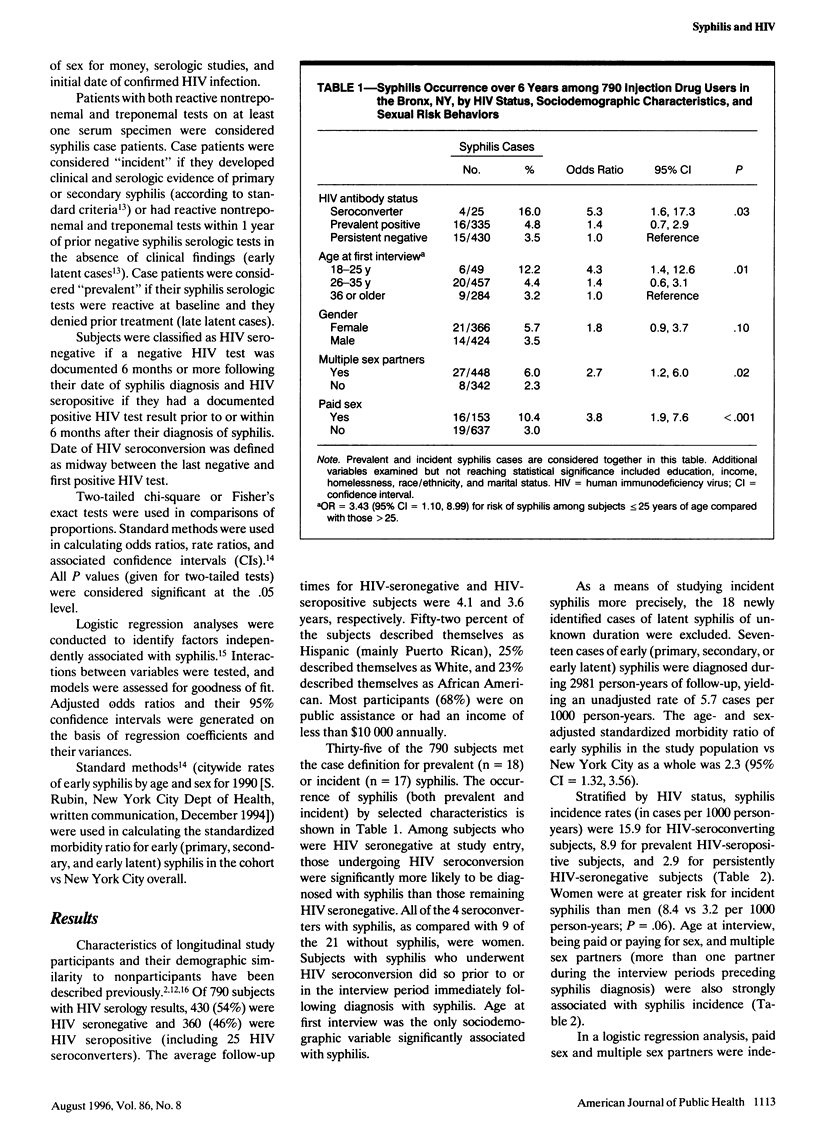
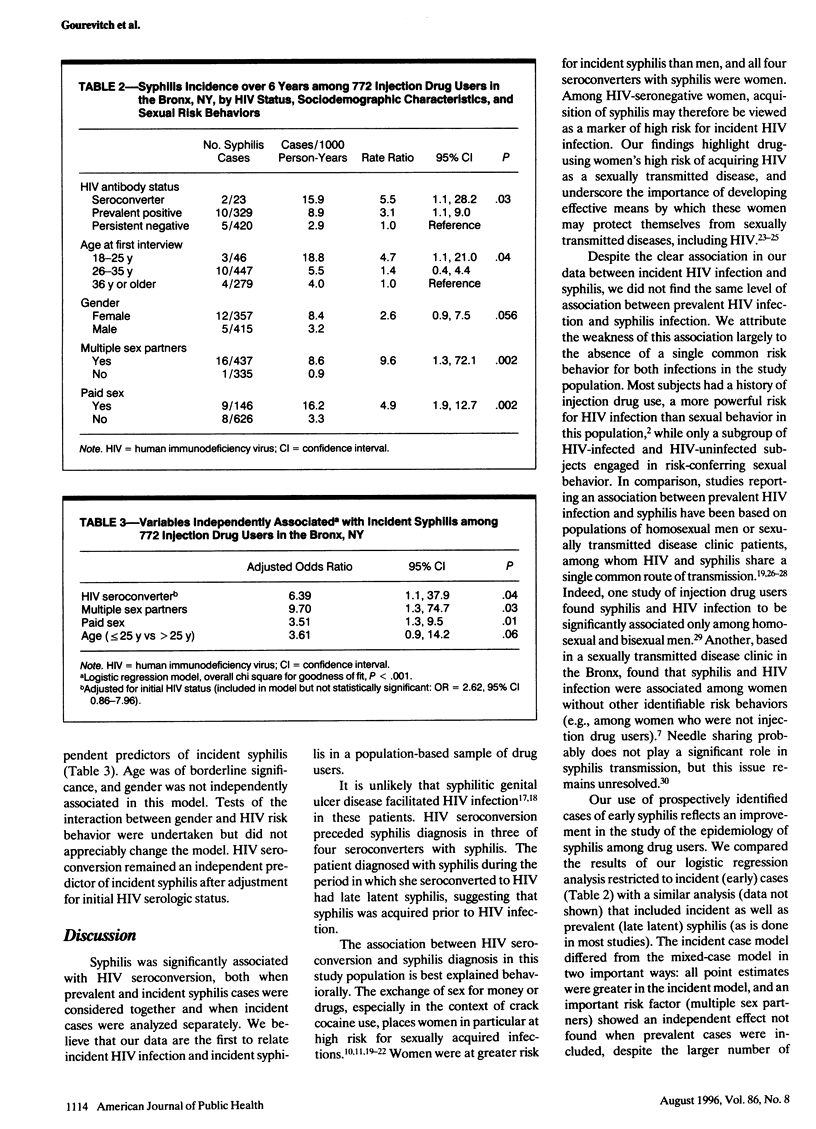
OBJECTIVES. The purpose of this study was to assess the relationship between syphilis and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in injection drug users. METHODS. A 6-year prospective study of 790 injection drug users receiving methadone maintenance treatment in the Bronx, NY, was conducted. RESULTS. Sixteen percent (4/25) of HIV-seroconverting patients, 4.8% (16/335) of prevalent HIV-seropositive patients, and 3.5% (15/430) of persistently HIV-seronegative patients was diagnosed with syphilis. Incidence rates for early syphilis (cases per 1000 person-years) were 15.9 for HIV-seroconverting patients, 8.9 for prevalent HIV-seropositive patients, and 2.9 for persistently HIV-seronegative patients. Early syphilis incidence was higher among women than men (8.4 vs 3.2 cases per 1000 person-years). Independent risks for early syphilis included multiple sex partners, HIV seroconversion, paid sex, and young age. All HIV seroconverters with syphilis were female. CONCLUSIONS. Diagnosis of syphilis in drug-using women reflects high-risk sexual activity and is associated with acquiring HIV infection. Interventions to reduce the risk of sexually acquired infections are urgently needed among female drug users.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astemborski J., Vlahov D., Warren D., Solomon L., Nelson K. E. The trading of sex for drugs or money and HIV seropositivity among female intravenous drug users. Am J Public Health. 1994 Mar;84(3):382–387. doi: 10.2105/ajph.84.3.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson M. A., Stoneburner R. L., Hildebrandt D. S., Ewing W. E., Telzak E. E., Jaffe H. W. Heterosexual transmission of HIV-1 associated with the use of smokable freebase cocaine (crack). AIDS. 1991 Sep;5(9):1121–1126. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199109000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson M. A., Stoneburner R. L., Lifson A. R., Hildebrandt D. S., Ewing W. E., Schultz S., Jaffe H. W. Risk factors for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in patients at a sexually transmitted disease clinic in New York City. Am J Epidemiol. 1990 Feb;131(2):208–220. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin B. R., Irwin K. L., Faruque S., McCoy C. B., Word C., Serrano Y., Inciardi J. A., Bowser B. P., Schilling R. F., Holmberg S. D. Intersecting epidemics--crack cocaine use and HIV infection among inner-city young adults. Multicenter Crack Cocaine and HIV Infection Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1994 Nov 24;331(21):1422–1427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199411243312106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley T. A., Hadler J. L., Gunn R. A. The syphilis epidemic in Connecticut: relationship to drug use and prostitution. Sex Transm Dis. 1990 Oct-Dec;17(4):163–168. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199010000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullilove R. E., Fullilove M. T., Bowser B. P., Gross S. A. Risk of sexually transmitted disease among black adolescent crack users in Oakland and San Francisco, Calif. JAMA. 1990 Feb 9;263(6):851–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollub E. L., Stein Z. A. Commentary: the new female condom--item 1 on a women's AIDS prevention agenda. Am J Public Health. 1993 Apr;83(4):498–500. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.4.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourevitch M. N., Selwyn P. A., Davenny K., Buono D., Schoenbaum E. E., Klein R. S., Friedland G. H. Effects of HIV infection on the serologic manifestations and response to treatment of syphilis in intravenous drug users. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Mar 1;118(5):350–355. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-118-5-199303010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. W., Choi K., Thomas P. A., Haverkos H. W., Auerbach D. M., Guinan M. E., Rogers M. F., Spira T. J., Darrow W. W., Kramer M. A. National case-control study of Kaposi's sarcoma and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in homosexual men: Part 1. Epidemiologic results. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Aug;99(2):145–151. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-2-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laga M., Manoka A., Kivuvu M., Malele B., Tuliza M., Nzila N., Goeman J., Behets F., Batter V., Alary M. Non-ulcerative sexually transmitted diseases as risk factors for HIV-1 transmission in women: results from a cohort study. AIDS. 1993 Jan;7(1):95–102. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199301000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx R., Aral S. O., Rolfs R. T., Sterk C. E., Kahn J. G. Crack, sex, and STD. Sex Transm Dis. 1991 Apr-Jun;18(2):92–101. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199118020-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger D. S., Woody G. E., McLellan A. T., O'Brien C. P., Druley P., Navaline H., DePhilippis D., Stolley P., Abrutyn E. Human immunodeficiency virus seroconversion among intravenous drug users in- and out-of-treatment: an 18-month prospective follow-up. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993 Sep;6(9):1049–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkoff H. L., McCalla S., Delke I., Stevens R., Salwen M., Feldman J. The relationship of cocaine use to syphilis and human immunodeficiency virus infections among inner city parturient women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Aug;163(2):521–526. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(90)91188-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss A. R., Osmond D., Bacchetti P., Chermann J. C., Barre-Sinoussi F., Carlson J. Risk factors for AIDS and HIV seropositivity in homosexual men. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Jun;125(6):1035–1047. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. E., Vlahov D., Cohn S., Odunmbaku M., Lindsay A., Antohony J. C., Hook E. W., 3rd Sexually transmitted diseases in a population of intravenous drug users: association with seropositivity to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):457–463. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten M. W., Jr, Zaidi A. A., Peterman T. A., Rolfs R. T., Witte J. J. High rate of HIV seroconversion among patients attending urban sexually transmitted disease clinics. AIDS. 1994 Apr;8(4):549–553. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199404000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plourde P. J., Pepin J., Agoki E., Ronald A. R., Ombette J., Tyndall M., Cheang M., Ndinya-Achola J. O., D'Costa L. J., Plummer F. A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 seroconversion in women with genital ulcers. J Infect Dis. 1994 Aug;170(2):313–317. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts M. The urgent need for a vaginal microbicide in the prevention of HIV transmission. Am J Public Health. 1994 Jun;84(6):890–891. doi: 10.2105/ajph.84.6.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C., Cannon R. O., Glasser D., Groseclose S. L., Brathwaite W. S., Fauci A. S., Hook E. W., 3rd The association of syphilis with risk of human immunodeficiency virus infection in patients attending sexually transmitted disease clinics. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Jun;150(6):1297–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfs R. T., Goldberg M., Sharrar R. G. Risk factors for syphilis: cocaine use and prostitution. Am J Public Health. 1990 Jul;80(7):853–857. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.7.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum E. E., Hartel D., Selwyn P. A., Klein R. S., Davenny K., Rogers M., Feiner C., Friedland G. Risk factors for human immunodeficiency virus infection in intravenous drug users. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 28;321(13):874–879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909283211306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn P. A., Alcabes P., Hartel D., Buono D., Schoenbaum E. E., Klein R. S., Davenny K., Friedland G. H. Clinical manifestations and predictors of disease progression in drug users with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 10;327(24):1697–1703. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212103272401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn P. A., Hartel D., Lewis V. A., Schoenbaum E. E., Vermund S. H., Klein R. S., Walker A. T., Friedland G. H. A prospective study of the risk of tuberculosis among intravenous drug users with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1989 Mar 2;320(9):545–550. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198903023200901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telzak E. E., Chiasson M. A., Bevier P. J., Stoneburner R. L., Castro K. G., Jaffe H. W. HIV-1 seroconversion in patients with and without genital ulcer disease. A prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Dec 15;119(12):1181–1186. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-119-12-199312150-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


