Abstract
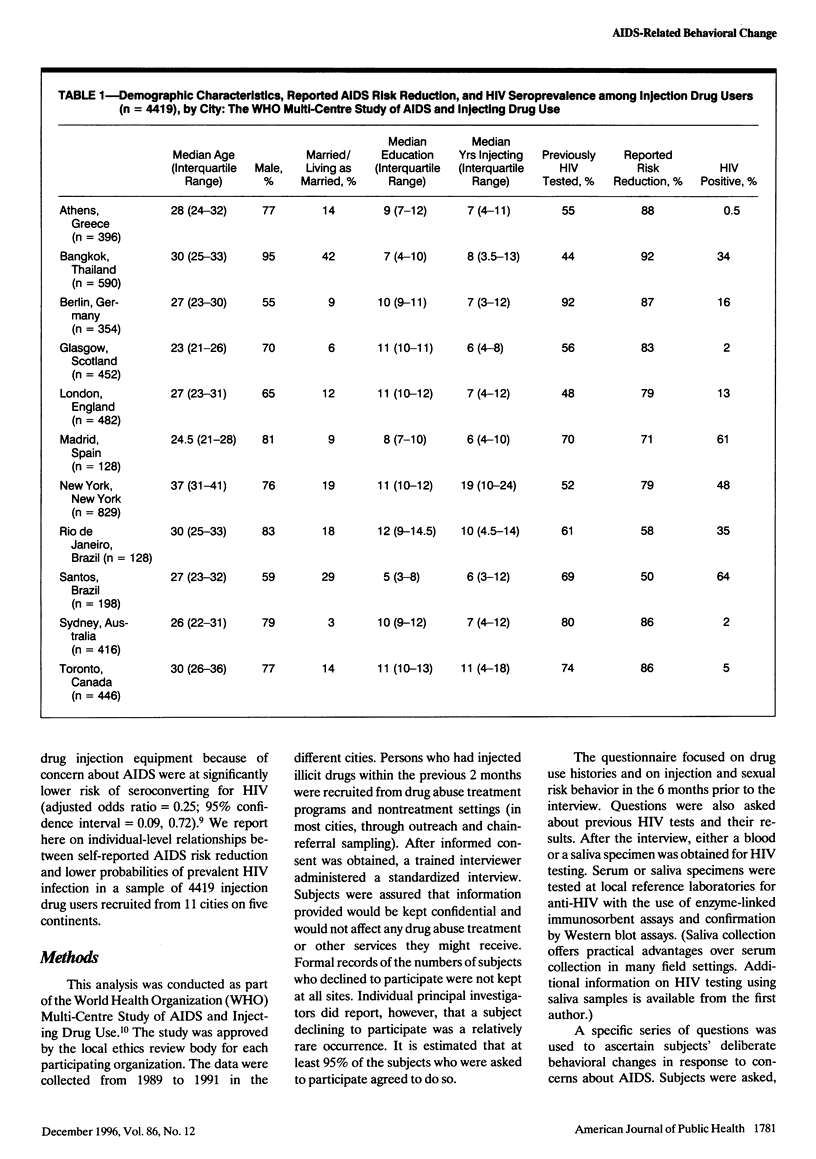
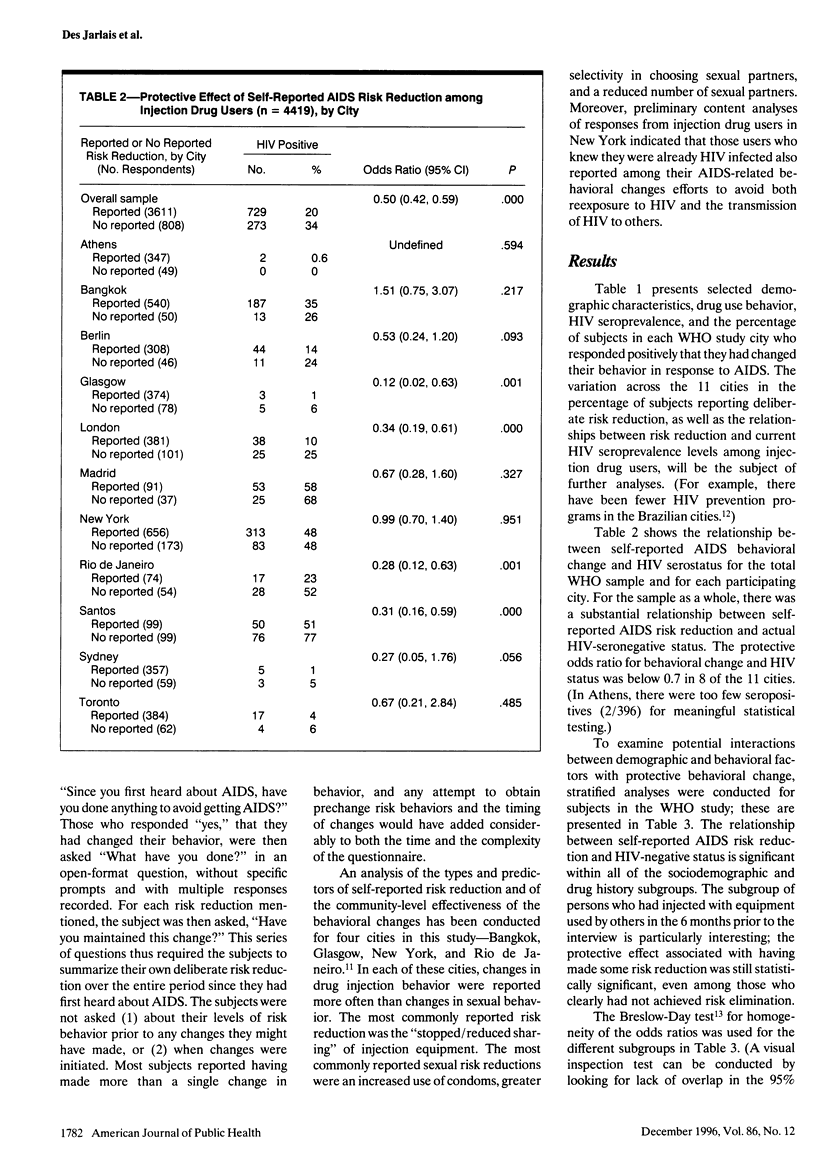
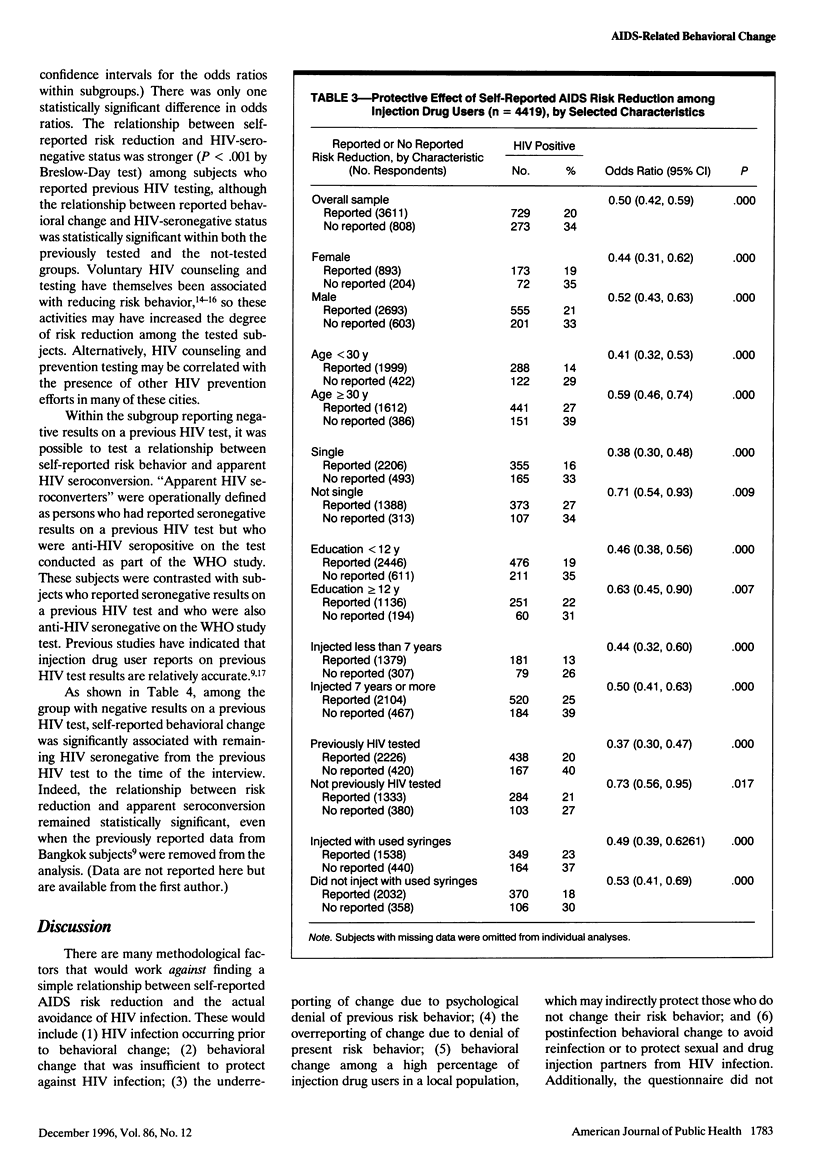
OBJECTIVE: This study assessed the relationship between self-reported acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) behavioral change and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) serostatus among injection drug users. METHODS: The study sample involved 4419 injection drug users recruited from drug abuse treatment and nontreatment settings in 11 cities in North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. The World Health Organization multisite risk behavior questionnaire was used, and either blood or saliva samples for HIV testing were obtained. Subjects were asked, "Since you first heard about AIDS, have you done anything to avoid getting AIDS?" RESULTS: The protective odds ratio for behavioral change against being infected with HIV was 0.50 (95% confidence interval = 0.42, 0.59). While there was important variation across sites, the relationship remained consistent across both demographic and drug use history subgroups. CONCLUSIONS: Injection drug users are capable of modifying their HIV risk behaviors and reporting accurately on behavioral changes. These behavioral changes are associated with their avoidance of HIV infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casadonte P. P., Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R., Rotrosen J. P. Psychological and behavioral impact among intravenous drug users of learning HIV test results. Int J Addict. 1990 Apr;25(4):409–426. doi: 10.3109/10826089009053168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Choopanya K., Vanichseni S., Plangsringarm K., Sonchai W., Carballo M., Friedmann P., Friedman S. R. AIDS risk reduction and reduced HIV seroconversion among injection drug users in Bangkok. Am J Public Health. 1994 Mar;84(3):452–455. doi: 10.2105/ajph.84.3.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R., Choopanya K., Vanichseni S., Ward T. P. International epidemiology of HIV and AIDS among injecting drug users. AIDS. 1992 Oct;6(10):1053–1068. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199210000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R., Friedmann P., Wenston J., Sotheran J. L., Choopanya K., Vanichseni S., Raktham S., Goldberg D., Frischer M. HIV/AIDS-related behavior change among injecting drug users in different national settings. AIDS. 1995 Jun;9(6):611–617. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199506000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R., Novick D. M., Sotheran J. L., Thomas P., Yancovitz S. R., Mildvan D., Weber J., Kreek M. J., Maslansky R. HIV-1 infection among intravenous drug users in Manhattan, New York City, from 1977 through 1987. JAMA. 1989 Feb 17;261(7):1008–1012. doi: 10.1001/jama.261.7.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. R., Des Jarlais D. C. HIV among drug injectors: the epidemic and the response. AIDS Care. 1991;3(3):239–250. doi: 10.1080/09540129108253069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan H., Des Jarlais D. C., Purchase D., Friedman S. R., Reid T., Bell T. A. An interview study of participants in the Tacoma, Washington, syringe exchange. Addiction. 1993 Dec;88(12):1691–1697. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1993.tb02044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker J., Stoddard A. M., McCarthy E. The validity of self-reported HIV antibody test results. Am J Public Health. 1992 Apr;82(4):567–569. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.4.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimson G. V. Reconstruction of subregional diffusion of HIV infection among injecting drug users in Southeast Asia: implications for early intervention. AIDS. 1994 Nov;8(11):1630–1632. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199411000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanichseni S., Choopanya K., Des Jarlais D. C., Plangsringarm K., Sonchai W., Carballo M., Friedmann P., Friedman S. R. HIV testing and sexual behavior among intravenous drug users in Bangkok, Thailand. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(11):1119–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahov D., Anthony J. C., Celentano D., Solomon L., Chowdhury N. Trends of HIV-1 risk reduction among initiates into intravenous drug use 1982-1987. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1991;17(1):39–48. doi: 10.3109/00952999108992808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N. H., Vanichseni S., Akarasewi P., Wasi C., Choopanya K. Was the 1988 HIV epidemic among Bangkok's injecting drug users a common source outbreak? AIDS. 1994 Apr;8(4):529–532. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199404000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


