Abstract
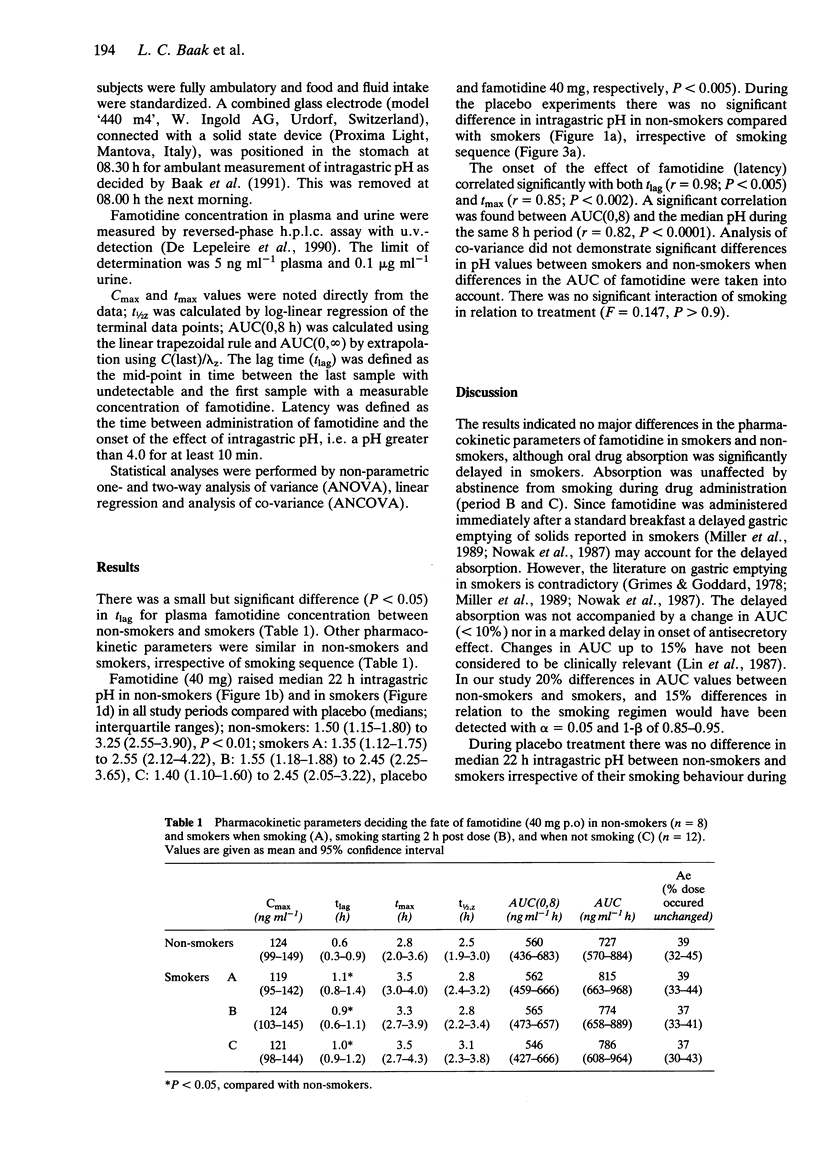
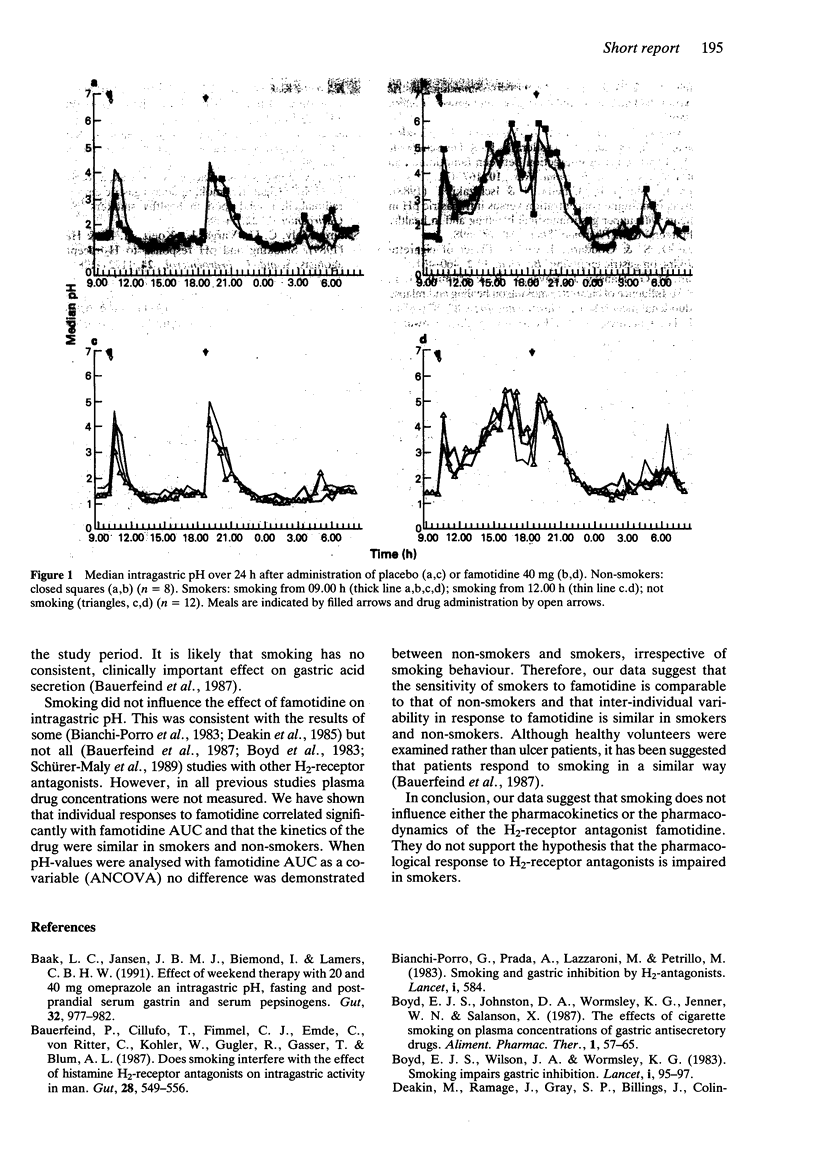
Twelve healthy habitual cigarette smokers and eight non-smokers participated in a double-blind placebo controlled study to determine the effect of smoking on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the H2-receptor antagonist famotidine. In smokers, cigarette smoking was standardised and started 1 h before (A), or 2 h after (B) drug administration, or was prohibited (C). Intragastric pH-levels (IGpH) were measured with an ambulatory pH-recorder. Famotidine (40 mg orally) significantly raised median 22 h IGpH in non-smokers and smokers in all study periods. The smoking sequence (A, B, C) did not significantly influence median 22 h IGpH in both placebo-treated and famotidine-treated smokers, and no significant difference in median 22 h IGpH was shown between smokers and non-smokers. Plasma drug concentrations were similar in the various experiments, although famotidine was detected earlier in plasma from non-smokers compared with smokers (P less than 0.05). Smoking did not interfere significantly with the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of famotidine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baak L. C., Jansen J. B., Biemond I., Lamers C. B. Weekend treatment with 20 and 40 mg omeprazole: effect on intragastric pH, fasting and postprandial serum gastrin, and serum pepsinogens. Gut. 1991 Sep;32(9):977–982. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.9.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauerfeind P., Cilluffo T., Fimmel C. J., Emde C., von Ritter C., Kohler W., Gugler R., Gasser T., Blum A. L. Does smoking interfere with the effect of histamine H2-receptor antagonists on intragastric acidity in man? Gut. 1987 May;28(5):549–556. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd E. J., Johnston D. A., Wormsley K. G., Jenner W. N., Salanson X. The effects of cigarette smoking on plasma concentrations of gastric antisecretory drugs. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1987 Feb;1(1):57–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1987.tb00607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd E. J., Wilson J. A., Wormsley K. G. Smoking impairs therapeutic gastric inhibition. Lancet. 1983 Jan 15;1(8316):95–97. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91742-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lepeleire I., Van Hecken A., Verbesselt R., Tjandra-Maga T. B., Buntinx A., Distlerath L., De Schepper P. J. Lack of interaction between famotidine and warfarin. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 1990;10(3):167–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deakin M., Ramage J., Gray S. P., Billings J., Colin-Jones D., Williams J. G. Smoking, gastric secretion, and inhibition by H2 receptor antagonists. Lancet. 1985 May 4;1(8436):1049–1049. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91654-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echizen H., Shoda R., Umeda N., Ishizaki T. Plasma famotidine concentration versus intragastric pH in patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding and in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Dec;44(6):690–698. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1988.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes D. S., Goddard J. Effect of cigarette smoking on gastric emptying. Br Med J. 1978 Aug 12;2(6135):460–461. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6135.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman M. G., Hansky J., Eaves E. R., Schmidt G. T. Influence of cigarette smoking on healing and relapse in duodenal ulcer disease. Gastroenterology. 1983 Oct;85(4):871–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. H., Chremos A. N., Kanovsky S. M., Schwartz S., Yeh K. C., Kann J. Effects of antacids and food on absorption of famotidine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;24(4):551–553. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Palmer K. R., Smith B., Ferrington C., Merrick M. V. Smoking delays gastric emptying of solids. Gut. 1989 Jan;30(1):50–53. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak A., Jonderko K., Kaczor R., Nowak S., Skrzypek D. Cigarette smoking delays gastric emptying of a radiolabelled solid food in healthy smokers. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987 Jan;22(1):54–58. doi: 10.3109/00365528708991856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürer-Maly C. C., Varga L., Koelz H. R., Halter F. Smoking and pH response to H2-receptor antagonists. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1989 Dec;24(10):1172–1178. doi: 10.3109/00365528909090783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoking and gastric inhibition by H2 antagonists. Lancet. 1983 Mar 12;1(8324):584–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


