Abstract
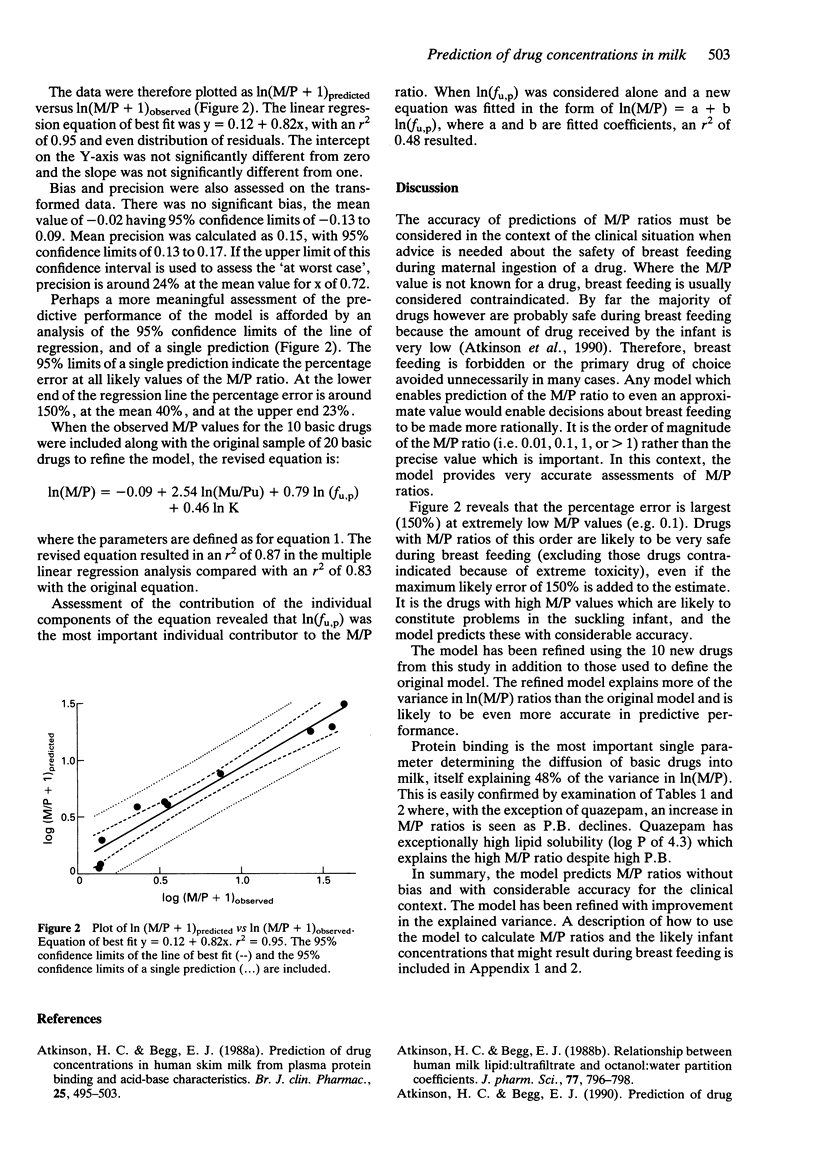
1. Milk:plasma (M/P) drug concentration ratios predicted by a model utilizing pKa, plasma protein binding and octanol:water partition coefficients have been compared with actual M/P values for 10 basic drugs. 2. There was a close relationship between predicted and observed M/P ratios with a coefficient of determination r2 of 0.97. However, there was a proportional error. 3. The data were transformed by taking logs of predicted and observed (M/P + 1) values. Regression analysis resulted in an r2 of 0.95, an intercept on the Y-axis not significantly different from zero and a slope not significantly different from one. 4. The 95% confidence interval around a single prediction revealed an error between 150% for the lowest and 23% for the highest M/P ratios. The error is therefore lowest for the drugs likely to have the greatest transfer into milk. 5. There was no significant bias in the predictions. 6. The model was refined by multiple linear regression analysis utilising the observed M/P ratios for the 10 basic drugs in addition to those of the original drugs. The revised equation resulted in an improvement in the explained variance. 7. Protein binding was the most important single predictor. 8. The results confirm that M/P ratios for basic drugs can be predicted accurately from their physicochemical characteristics.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson H. C., Begg E. J. Prediction of drug concentrations in human skim milk from plasma protein binding and acid-base characteristics. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;25(4):495–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson H. C., Begg E. J. Prediction of drug distribution into human milk from physicochemical characteristics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1990 Feb;18(2):151–167. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199018020-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson H. C., Begg E. J. Relationship between human milk lipid-ultrafiltrate and octanol-water partition coefficients. J Pharm Sci. 1988 Sep;77(9):796–798. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600770916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edstein M. D., Veenendaal J. R., Hyslop R. Excretion of mefloquine in human breast milk. Chemotherapy. 1988;34(3):165–169. doi: 10.1159/000238566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ette E. I., Essien E. E., Ogonor J. I., Brown-Awala E. A. Chloroquine in human milk. J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;27(7):499–502. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1987.tb03056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Arendt R. M., Abernethy D. R., Giles H. G., Sellers E. M., Shader R. I. In vitro quantitation of benzodiazepine lipophilicity: relation to in vivo distribution. Br J Anaesth. 1983 Oct;55(10):985–989. doi: 10.1093/bja/55.10.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett L. P., Wojnar-Horton R. E., Dusci L. J., Ilett K. F., Roberts M. J. Excretion of sotalol in breast milk. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;29(2):277–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann D., Lunell N. O., Friedrich G., Rane A. Excretion of tiapamil in breast milk. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;26(2):183–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert J. M., Gural R. P., Symchowicz S., Zampaglione N. Excretion of quazepam into human breast milk. J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;24(10):457–462. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1984.tb01819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowaluk E. A., Roberts M. S., Blackburn H. D., Polack A. E. Interactions between drugs and polyvinyl chloride infusion bags. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1981 Sep;38(9):1308–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüllmann H., Wehling M. The binding of drugs to different polar lipids in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Dec 1;28(23):3409–3415. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittard W. B., 3rd, Glazier H. Procainamide excretion in human milk. J Pediatr. 1983 Apr;102(4):631–633. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons G., Francoual C., Guillet P., Moran C., Hermann P., Bianchetti G., Thiercelin J. F., Thenot J. P., Olive G. Zolpidem excretion in breast milk. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;37(3):245–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00679778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons G., Schoerlin M. P., Tam Y. K., Moran C., Pfefen J. P., Francoual C., Pedarriosse A. M., Chavinie J., Olive G. Moclobemide excretion in human breast milk. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;29(1):27–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiner L. B., Beal S. L. Some suggestions for measuring predictive performance. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1981 Aug;9(4):503–512. doi: 10.1007/BF01060893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunstall M. E., Campbell D. M., Dawson B. M., Jostell K. G. Chlormethiazole treatment and breast feeding. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1979 Oct;86(10):793–798. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1979.tb10695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner X., Jouglard J., Moulin M., Miller A. M., Petitjean J., Pisapia A. Coadministration of flecainide acetate and sotalol during pregnancy: lack of teratogenic effects, passage across the placenta, and excretion in human breast milk. Am Heart J. 1990 Mar;119(3 Pt 1):700–702. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(05)80306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Brown R. D., Hinson J. L., Dailey J. W. Pharmacokinetic pitfalls in the estimation of the breast milk/plasma ratio for drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:667–689. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


