Abstract
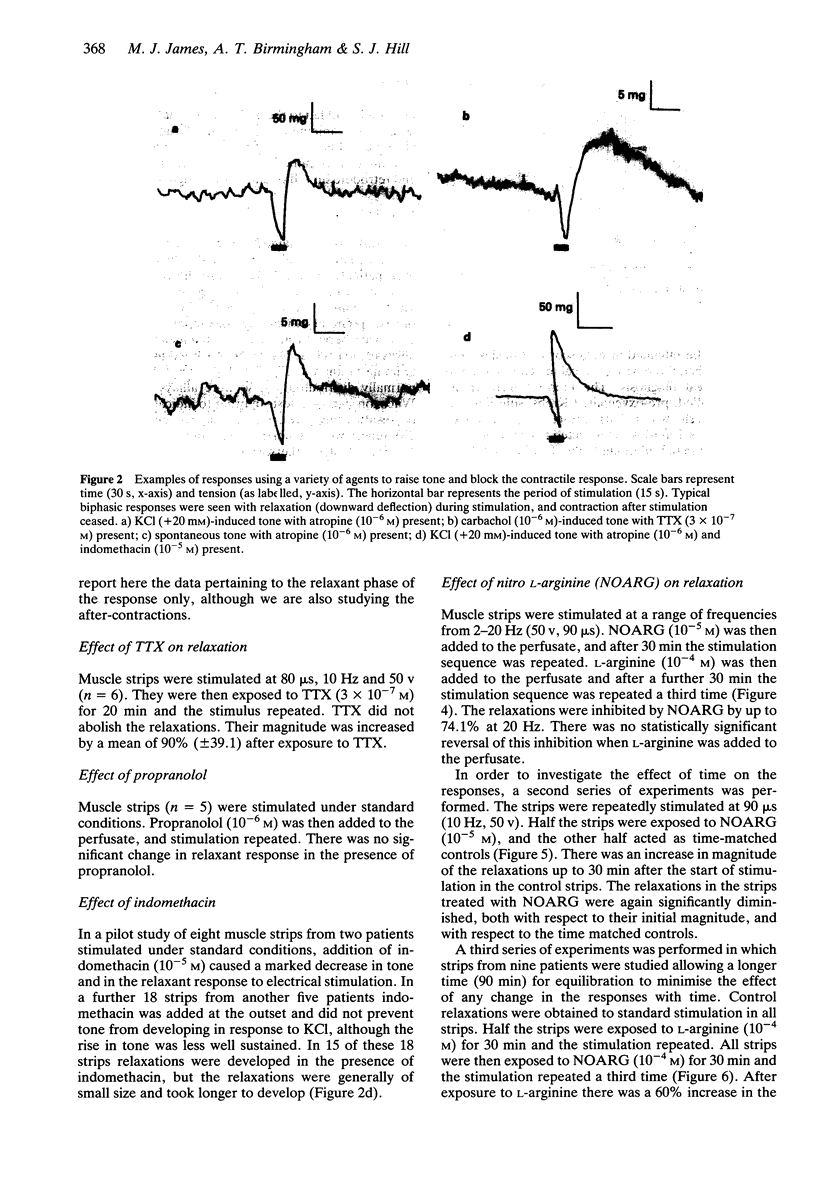
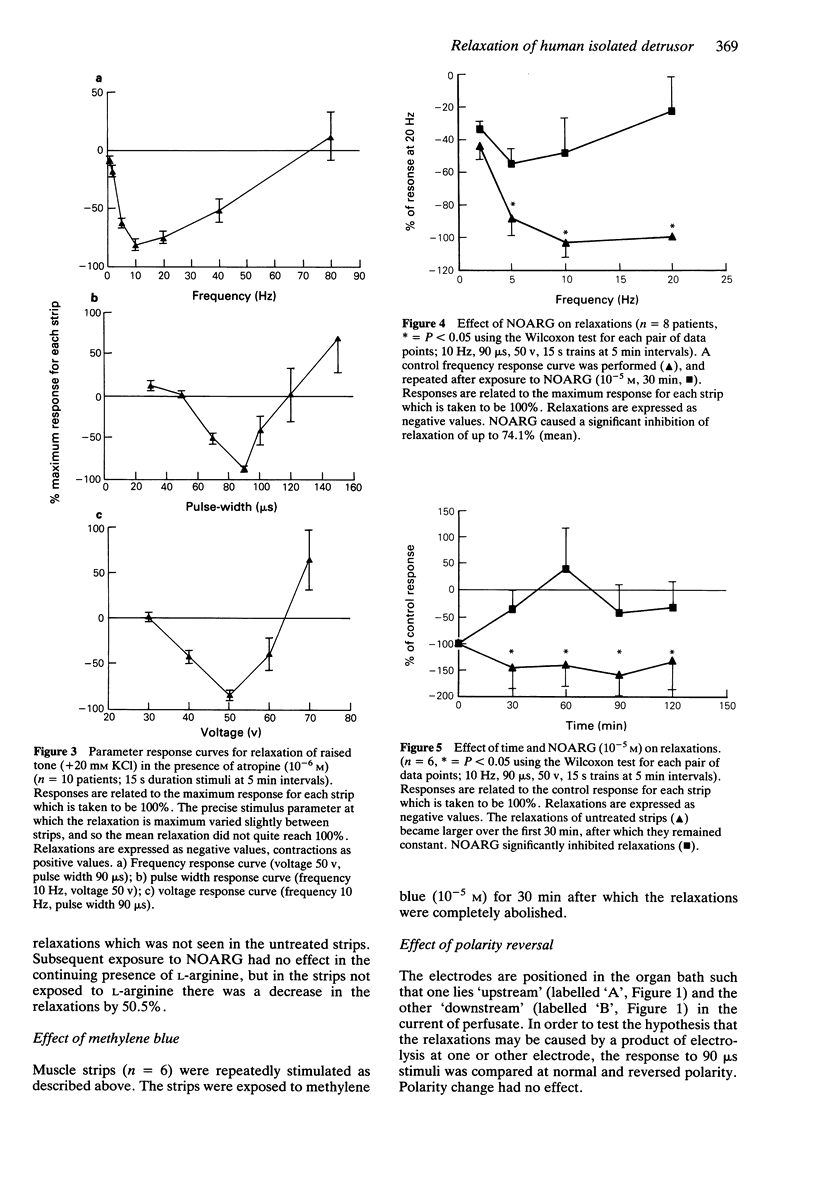
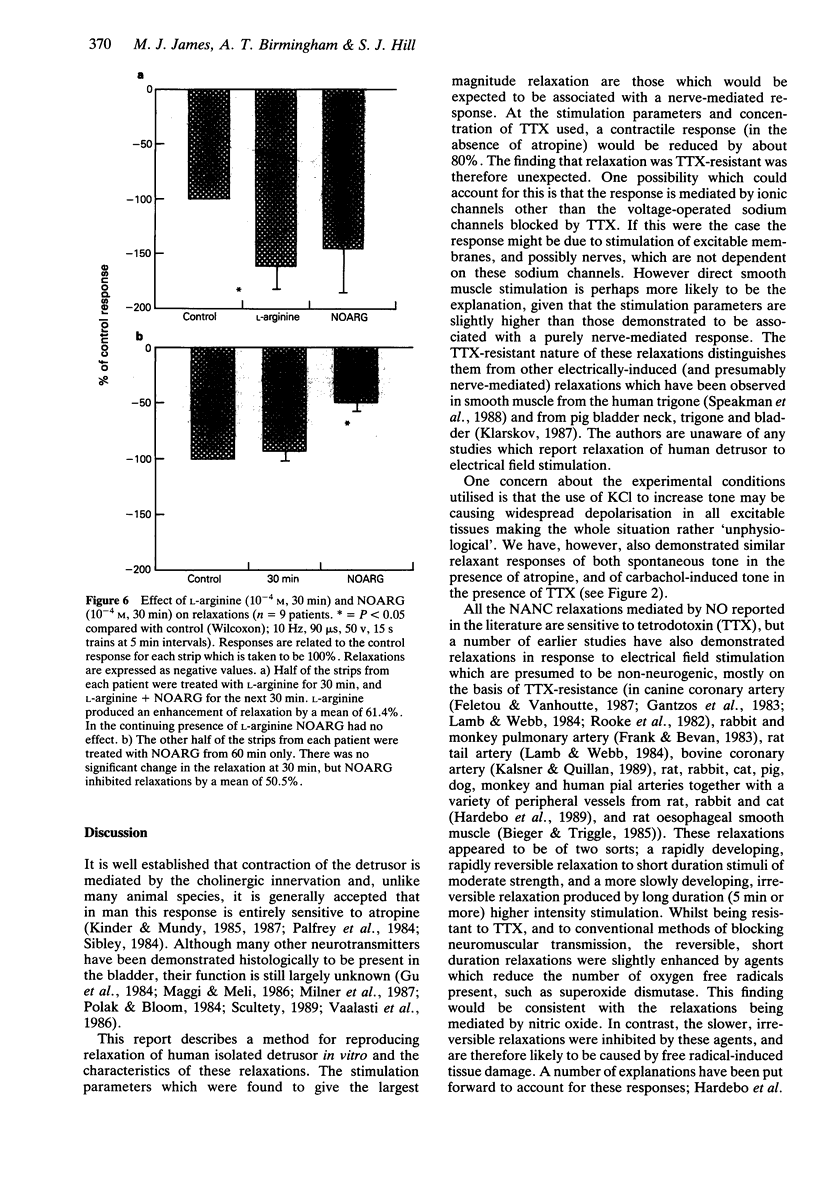
1. A method for reproducing relaxation of human isolated detrusor smooth muscle in vitro in response to electrical field stimulation is described. 2. The parameters of stimulation associated with relaxation were those which would be expected to give a largely nerve-mediated response: the relaxations were not reduced by tetrodotoxin (3 x 10(-7) M) and were therefore not dependent on voltage sensitive sodium channels. 3. The relaxations were decreased (mean 74.1%) by nitro L-arginine (NOARG, 10(-5) M). 4. Methylene blue (10(-5) M), an inhibitor of soluble guanylate cyclase, abolished the relaxations. 5. These results indicate that there may be a relaxation mechanism in the human bladder which is at least partly mediated via the production of nitric oxide.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieger D., Triggle C. Pharmacological properties of mechanical responses of the rat oesophageal muscularis mucosae to vagal and field stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;84(1):93–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feletou M., Vanhoutte P. M. Relaxation of canine coronary artery to electrical stimulation: limited role of free radicals. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 2):H884–H889. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.4.H884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. W., Bevan J. A. Electrical stimulation causes endothelium-dependent relaxation in lung vessels. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):H793–H798. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.244.6.H793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantzos R. D., Ebeigbe A. B., Webb R. C. Ca2+, histamine antagonists and relaxation to electrical impulses in dog coronary artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 May 6;89(3-4):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90508-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson A., Mirzazadeh S., Hobbs A. J., Moore P. K. L-NG-monomethyl arginine and L-NG-nitro arginine inhibit non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic relaxation of the mouse anococcygeus muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):602–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J., Blank M. A., Huang W. M., Islam K. N., McGregor G. P., Christofides N., Allen J. M., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Peptide-containing nerves in human urinary bladder. Urology. 1984 Oct;24(4):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(84)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardebo J. E., Kåhrström J., Owman C. Characterization of dilatation induced by electrical field stimulation in mammalian cerebral and peripheral vessels. Q J Exp Physiol. 1989 Jul;74(4):475–491. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1989.sp003295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S., Quillan M. Nonneurogenic relaxation to field stimulation in coronary arteries. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Aug;250(2):461–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinder R. B., Mundy A. R. Atropine blockade of nerve-mediated stimulation of the human detrusor. Br J Urol. 1985 Aug;57(4):418–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1985.tb06301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinder R. B., Mundy A. R. Pathophysiology of idiopathic detrusor instability and detrusor hyper-reflexia. An in vitro study of human detrusor muscle. Br J Urol. 1987 Dec;60(6):509–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1987.tb05031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarskov P. Non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic inhibitory nerve responses of bladder outlet smooth muscle in vitro. Br J Urol. 1987 Oct;60(4):337–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1987.tb04980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klück P. The autonomic innervation of the human urinary bladder, bladder neck and urethra: a histochemical study. Anat Rec. 1980 Nov;198(3):439–447. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091980306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb F. S., Webb R. C. Vascular effects of free radicals generated by electrical stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):H709–H714. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1984.247.5.H709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Meli A. The role of neuropeptides in the regulation of the micturition reflex. J Auton Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;6(2):133–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1986.tb00640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner P., Crowe R., Burnstock G., Light J. K. Neuropeptide Y- and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-containing nerves in the intrinsic external urethral sphincter in the areflexic bladder compared to detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia in patients with spinal cord injury. J Urol. 1987 Oct;138(4):888–892. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)43409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey E. L., Fry C. H., Shuttleworth K. E. A new in vitro microsuperfusion technique for investigation of human detrusor muscle. Br J Urol. 1984 Dec;56(6):635–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1984.tb06134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickard R. S., Powell P. H., Zar M. A. The effect of inhibitors of nitric oxide biosynthesis and cyclic GMP formation on nerve-evoked relaxation of human cavernosal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):755–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Localisation and measurement of VIP in the genitourinary system of man and animals. Peptides. 1984 Mar-Apr;5(2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooke T., Cohen R. A., Verbeuren T. J., Vanhoutte P. M. Non-neurogenic inhibitory effect of electrical impulses in isolated canine coronary arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 May 21;80(2-3):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scultéty S. Neuropeptides in urology. Int Urol Nephrol. 1989;21(1):39–45. doi: 10.1007/BF02549900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shikano K., Long C. J., Ohlstein E. H., Berkowitz B. A. Comparative pharmacology of endothelium-derived relaxing factor and nitric oxide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):873–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley G. N. A comparison of spontaneous and nerve-mediated activity in bladder muscle from man, pig and rabbit. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:431–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speakman M. J., Walmsley D., Brading A. F. An in vitro pharmacological study of the human trigone--a site of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neurotransmission. Br J Urol. 1988 Apr;61(4):304–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1988.tb13963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker J. F., Brave S. R., Charalambous L., Hobbs A. J., Gibson A. L-NG-nitro arginine inhibits non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic relaxations of guinea-pig isolated tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):663–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14072.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaalasti A., Tainio H., Pelto-Huikko M., Hervonen A. Light and electron microscope demonstration of VIP- and enkephalin-immunoreactive nerves in the human male genitourinary tract. Anat Rec. 1986 May;215(1):21–27. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092150104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Murad F. Biochemical mechanisms underlying vascular smooth muscle relaxation: the guanylate cyclase-cyclic GMP system. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1988;12 (Suppl 5):S115–S118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


