Abstract
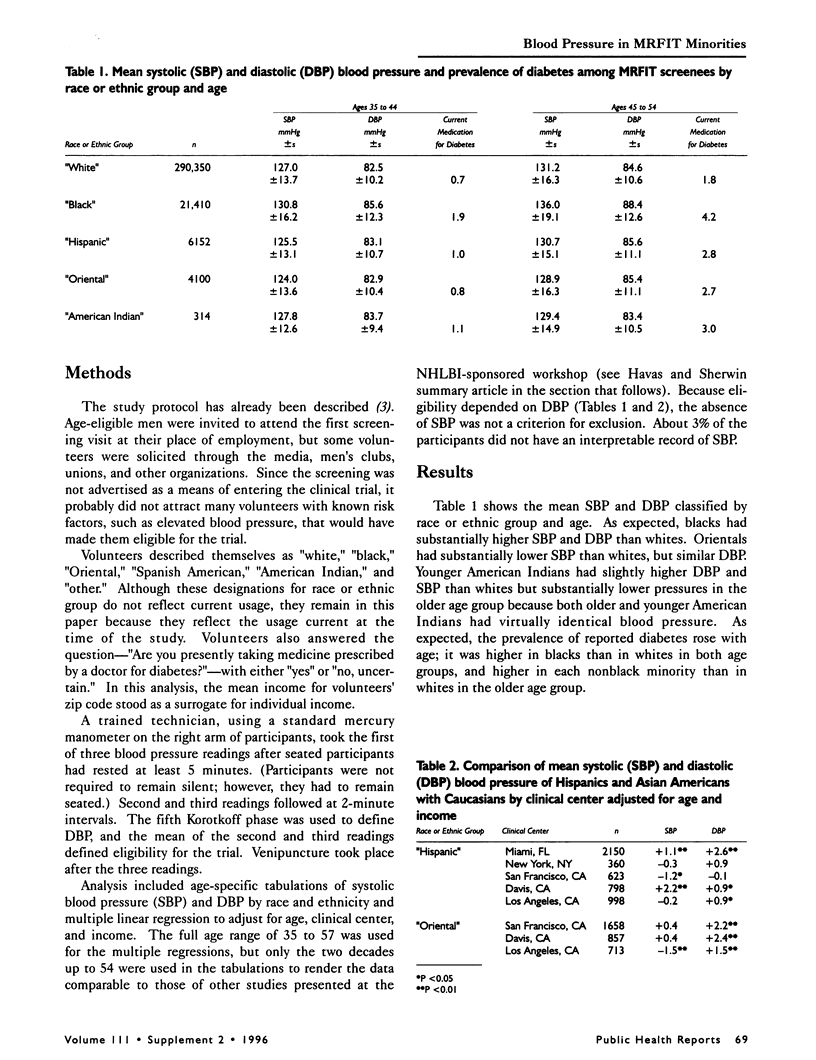
THE AUTHORS PRESENT DATA FROM 361, 662 MEN ages 35 to 57, screened from 1973 to 1976 for possible participation in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT). Volunteers identified themselves as "white," "black," "Oriental," "Spanish American," "American Indian," or "other." They also noted if they were taking medication for diabetes. A trained technician measured blood pressure after participants had rested for 5 minutes, using the fifth Korotkoff sound to define diastolic pressure and averaging the second and third of three readings. Differences among the groups included the following: blacks had consistently higher systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP and DBP) than other groups; Orientals had slightly lower pressure than other nonblack groups; American Indians had somewhat higher pressure than other nonblack groups at ages 35 to 44 but lower at ages 45 to 54; Hispanics in Miami and Davis, California, had significantly higher SBP and DBP than whites in the same area; Orientals in California had significantly higher DBP (but not SBP) than whites in California.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Sherwin R. W., Wentworth D. N., Cutler J. A., Hulley S. B., Kuller L. H., Stamler J. Serum cholesterol levels and cancer mortality in 361,662 men screened for the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. JAMA. 1987 Feb 20;257(7):943–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R., Kaelber C. T., Kezdi P., Kjelsberg M. O., Thomas H. E., Jr The multiple risk factor intervention trial (MRFIT) II. The development of the protocol. Prev Med. 1981 Jul;10(4):402–425. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(81)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J., Stamler R., Neaton J. D. Blood pressure, systolic and diastolic, and cardiovascular risks. US population data. Arch Intern Med. 1993 Mar 8;153(5):598–615. doi: 10.1001/archinte.153.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


