Abstract
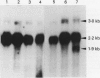
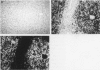
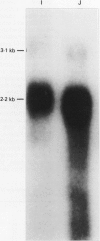
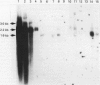
The human CYP3A subfamily is of interest due to its multiplicity, activity toward known carcinogens, and extrahepatic expression. In situ hybridisation analysis of formalin fixed, routinely processed biopsy specimens was used to localise CYP3A mRNA in human gastrointestinal tissues from several individuals. CYP3A mRNA is abundant in human liver and in mucosal epithelial cells of all segments of the human small intestine. RNA blot analyses showed that the mRNA species observed in most livers and in human small intestine represent CYP3A3/3A4 transcripts. This was confirmed at the protein level by immunoblot comparison of small intestine microsomes to in vitro expressed CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 proteins. In liver and small intestine, CYP3A mRNA is not uniformly distributed, with grain density highest in cells within the respective non-proliferative compartments. CYP3A mRNA was also observed in human oesophagus and colon. RNA blot analysis of multiple colons showed heterogeneity in the CYP3A mRNAs present. Two CYP3A mRNAs (CYP3A3/3A4 and CYP3A5) were detected in colon samples from several individuals. In addition to those localisation studies, the capacity of expressed CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 to activate the dietary heterocyclic amine MeIQ in the presence of alpha-naphthoflavone was shown. These results show that there is considerable heterogeneity in the expression of the CYP3A subfamily in human gastrointestinal tissues.
Full text
PDF

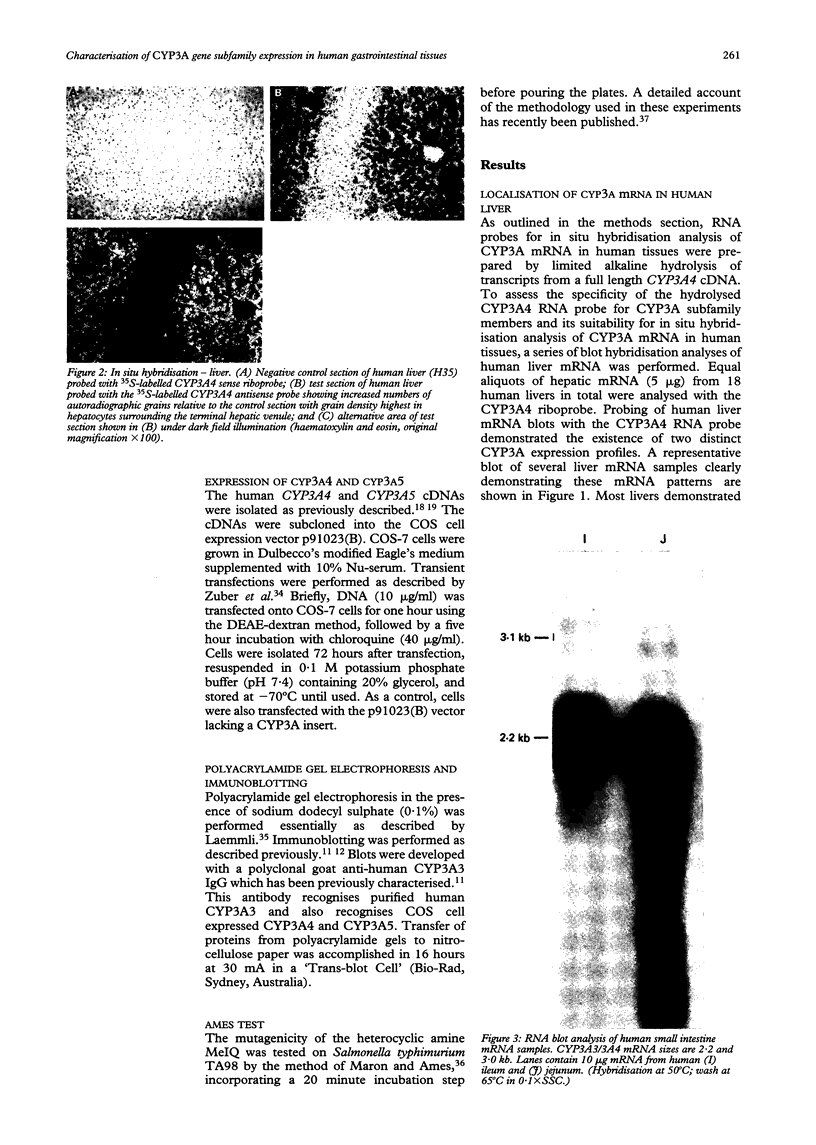






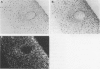
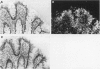
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama T., Yamano S., Guzelian P. S., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. Five of 12 forms of vaccinia virus-expressed human hepatic cytochrome P450 metabolically activate aflatoxin B1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4790–4793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron J., Redick J. A., Guengerich F. P. An immunohistochemical study on the localization and distributions of phenobarbital- and 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible cytochromes P-450 within the livers of untreated rats. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5931–5937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron J., Redick J. A., Guengerich F. P. Effects of 3-methylcholanthrene, beta-naphthoflavone, and phenobarbital on the 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible isozyme of cytochrome P-450 within centrilobular, midzonal, and periportal hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):953–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaune P. H., Umbenhauer D. R., Bork R. W., Lloyd R. S., Guengerich F. P. Isolation and sequence determination of a cDNA clone related to human cytochrome P-450 nifedipine oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8064–8068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bork R. W., Muto T., Beaune P. H., Srivastava P. K., Lloyd R. S., Guengerich F. P. Characterization of mRNA species related to human liver cytochrome P-450 nifedipine oxidase and the regulation of catalytic activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):910–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett M. D., Self A. J., van Oers C., Hall A. Identification of distinct cytoplasmic targets for ras/R-ras and rho regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):10–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. Molecular genetics of the P-450 superfamily. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;45(1):1–38. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90006-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Schmid B. J., Umeno M., Mcbride O. W., Hardwick J. P., Meyer U. A., Gelboin H. V., Idle J. R. Human P450PCN1: sequence, chromosome localization, and direct evidence through cDNA expression that P450PCN1 is nifedipine oxidase. DNA. 1988 Mar;7(2):79–86. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. The molecular biology of cytochrome P450s. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Dec;40(4):243–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassett C., Luchtel D. L., Omiecinski C. J. Hepatic expression of rat P450 mRNA assessed by in situ hybridization to oligomer probes. DNA. 1989 Jan-Feb;8(1):29–37. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingelman-Sundberg M., Johansson I., Penttilä K. E., Glaumann H., Lindros K. O. Centrilobular expression of ethanol-inducible cytochrome P-450 (IIE1) in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori M., Nishio K., Fujitani T., Ohi H., Kitada M., Mima S., Itahashi K., Kamataki T. Isolation of a new human fetal liver cytochrome P450 cDNA clone: evidence for expression of a limited number of forms of cytochrome P450 in human fetal livers. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Jul;272(1):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori M., Nishio K., Ohi H., Kitada M., Kamataki T. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA containing the entire coding region for human fetal liver cytochrome P-450. J Biochem. 1989 Feb;105(2):161–163. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maron D. M., Ames B. N. Revised methods for the Salmonella mutagenicity test. Mutat Res. 1983 May;113(3-4):173–215. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(83)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinnon R. A., Burgess W. M., Hall P. M., Abdul-Aziz Z., McManus M. E. Metabolism of food-derived heterocyclic amines in human and rabbit tissues by P4503A proteins in the presence of flavonoids. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7 Suppl):2108s–2113s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinnon R. A., Hall P. D., Quattrochi L. C., Tukey R. H., McManus M. E. Localization of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 messenger RNA in normal human liver and in hepatocellular carcinoma by in situ hybridization. Hepatology. 1991 Nov;14(5):848–856. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840140517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus M. E., Burgess W. M., Veronese M. E., Huggett A., Quattrochi L. C., Tukey R. H. Metabolism of 2-acetylaminofluorene and benzo(a)pyrene and activation of food-derived heterocyclic amine mutagens by human cytochromes P-450. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 1;50(11):3367–3376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus M. E., Burgess W., Snyderwine E., Stupans I. Specificity of rabbit cytochrome P-450 isozymes involved in the metabolic activation of the food derived mutagen 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f] quinoline. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 15;48(16):4513–4519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus M. E., Felton J. S., Knize M. G., Burgess W. M., Roberts-Thomson S., Pond S. M., Stupans I., Veronese M. E. Activation of the food-derived mutagen 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine by rabbit and human liver microsomes and purified forms of cytochrome P-450. Carcinogenesis. 1989 Feb;10(2):357–363. doi: 10.1093/carcin/10.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus M. E., Hall P. D., Stupans I., Brennan J., Burgess W., Robson R., Birkett D. J. Immunohistochemical localization and quantitation of NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase in human liver. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;32(1):189–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus M. E., McKinnon R. A. Measurement of cytochrome P450 activation of xenobiotics using the Ames Salmonella test. Methods Enzymol. 1991;206:501–509. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)06119-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molowa D. T., Schuetz E. G., Wrighton S. A., Watkins P. B., Kremers P., Mendez-Picon G., Parker G. A., Guzelian P. S. Complete cDNA sequence of a cytochrome P-450 inducible by glucocorticoids in human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5311–5315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray G. I., Barnes T. S., Sewell H. F., Ewen S. W., Melvin W. T., Burke M. D. The immunocytochemical localisation and distribution of cytochrome P-450 in normal human hepatic and extrahepatic tissues with a monoclonal antibody to human cytochrome P-450. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;25(4):465–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1988.tb03331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray G. I., Barnes T. S., Sewell H. F., Ewen S. W., Melvin W. T., Shaw P. M., Fowler J., Burke M. D. Cytochrome P-450 localization in normal human adult and foetal liver by immunocytochemistry using a monoclonal antibody against human cytochrome P-450. Histochem J. 1987 Oct-Nov;19(10-11):537–545. doi: 10.1007/BF01687361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Kamataki T., Waxman D. J., Guengerich F. P., Estabrook R. W., Feyereisen R., Gonzalez F. J., Coon M. J., Gunsalus I. C., Gotoh O. The P450 superfamily: update on new sequences, gene mapping, accession numbers, early trivial names of enzymes, and nomenclature. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Jan-Feb;12(1):1–51. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi K., Mishima A., Okuda K. Immunofluorescence of phenobarbital inducible cytochrome P-450 in the hepatic lobule of normal and phenobarbital-treated rats. Hepatology. 1982 Nov-Dec;2(6):849–855. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W. H., Boon C. E., Roelofs H. M., Wobbes T., Nagengast F. M., Kremers P. G. Expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes and P-170 glycoprotein in colorectal carcinoma and normal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1992 Aug;103(2):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90833-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W. H., Kremers P. G. Cytochromes P-450 in the intestinal mucosa of man. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 1;38(9):1535–1538. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz J. D., Molowa D. T., Guzelian P. S. Characterization of a cDNA encoding a new member of the glucocorticoid-responsive cytochromes P450 in human liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Nov 1;274(2):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Guengerich F. P. Evidence for cytochrome P-450NF, the nifedipine oxidase, being the principal enzyme involved in the bioactivation of aflatoxins in human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):462–465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Iwasaki M., Martin M. V., Guengerich F. P. Human liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 enzymes involved in the bioactivation of procarcinogens detected by umu gene response in Salmonella typhimurium TA 1535/pSK1002. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 15;49(12):3218–3228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Martin M. V., Pruess-Schwartz D., Marnett L. J., Guengerich F. P. Roles of individual human cytochrome P-450 enzymes in the bioactivation of benzo(a)pyrene, 7,8-dihydroxy-7,8-dihydrobenzo(a)pyrene, and other dihydrodiol derivatives of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Cancer Res. 1989 Nov 15;49(22):6304–6312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi M., Lasker J. M., Shimizu M., Rosman A. S., Lieber C. S. The intralobular distribution of ethanol-inducible P450IIE1 in rat and human liver. Hepatology. 1989 Oct;10(4):437–446. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Wrighton S. A., Schuetz E. G., Molowa D. T., Guzelian P. S. Identification of glucocorticoid-inducible cytochromes P-450 in the intestinal mucosa of rats and man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1029–1036. doi: 10.1172/JCI113156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton S. A., Brian W. R., Sari M. A., Iwasaki M., Guengerich F. P., Raucy J. L., Molowa D. T., Vandenbranden M. Studies on the expression and metabolic capabilities of human liver cytochrome P450IIIA5 (HLp3). Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;38(2):207–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrighton S. A., Ring B. J., Watkins P. B., VandenBranden M. Identification of a polymorphically expressed member of the human cytochrome P-450III family. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):97–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Expression of bovine 17 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 cDNA in nonsteroidogenic (COS 1) cells. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1258–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.3535074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waziers I., Cugnenc P. H., Yang C. S., Leroux J. P., Beaune P. H. Cytochrome P 450 isoenzymes, epoxide hydrolase and glutathione transferases in rat and human hepatic and extrahepatic tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Apr;253(1):387–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]