Abstract
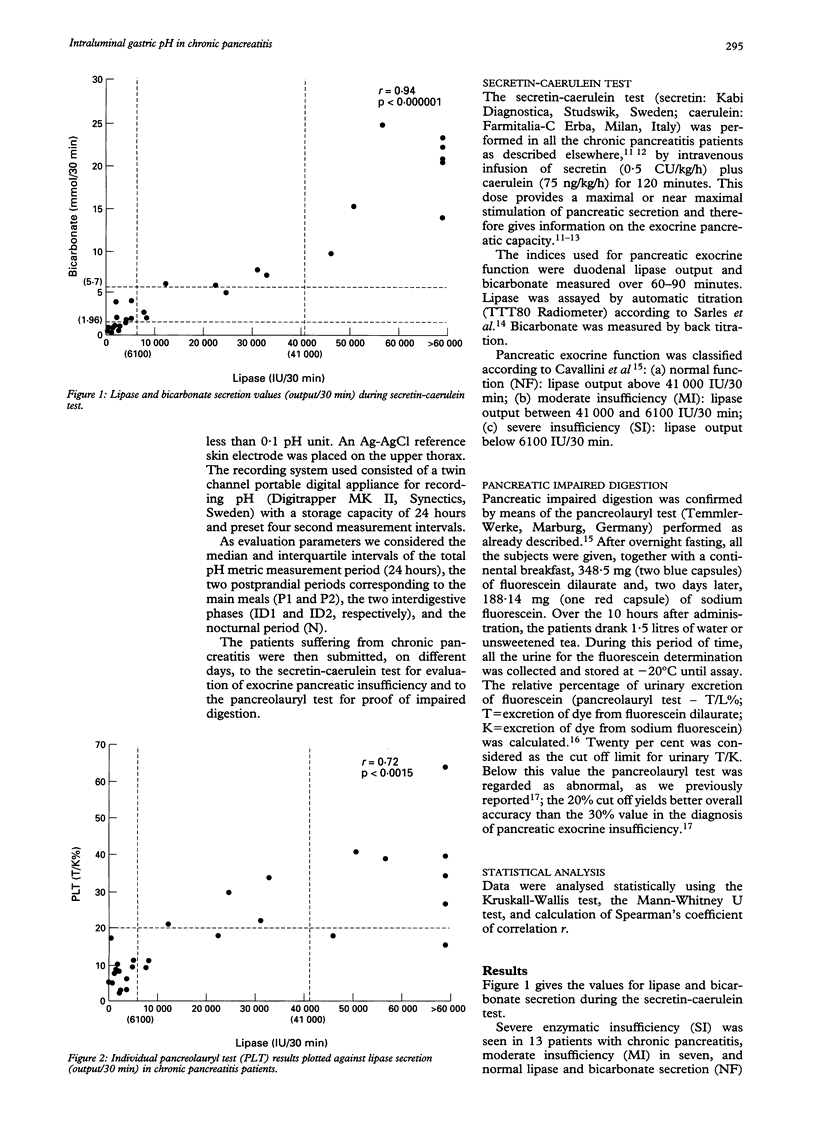
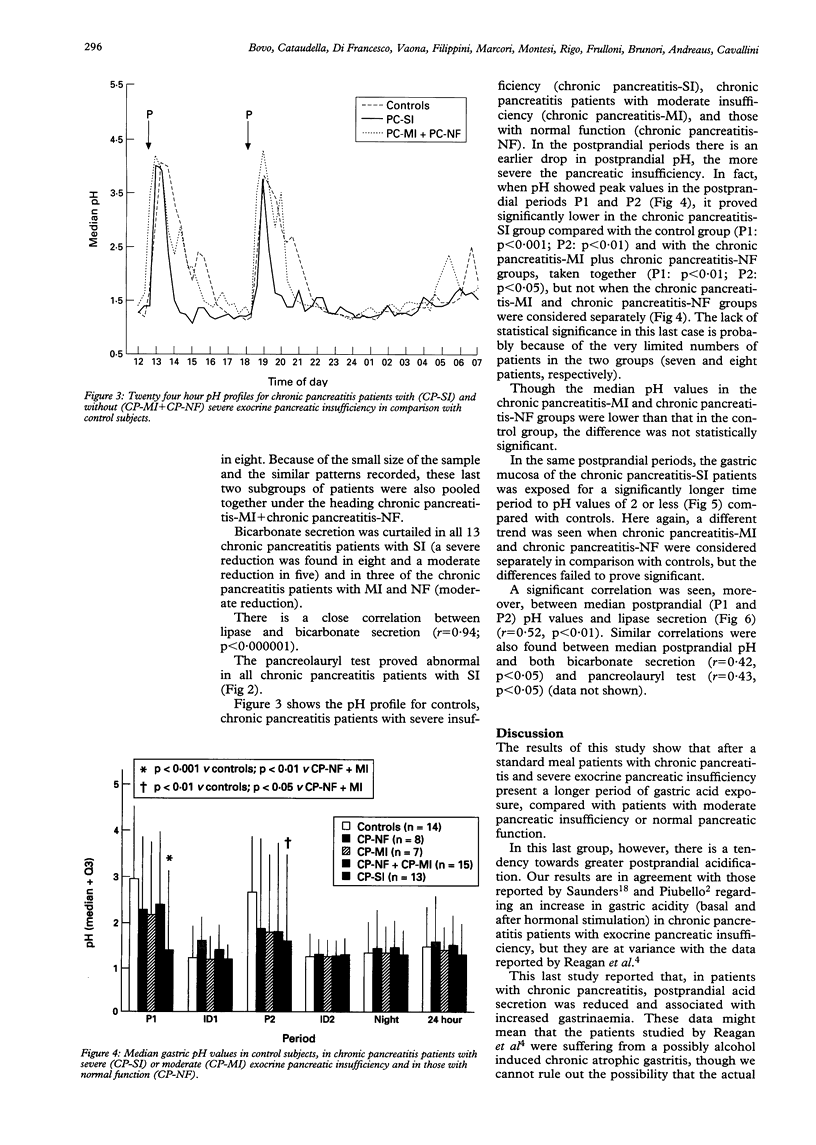
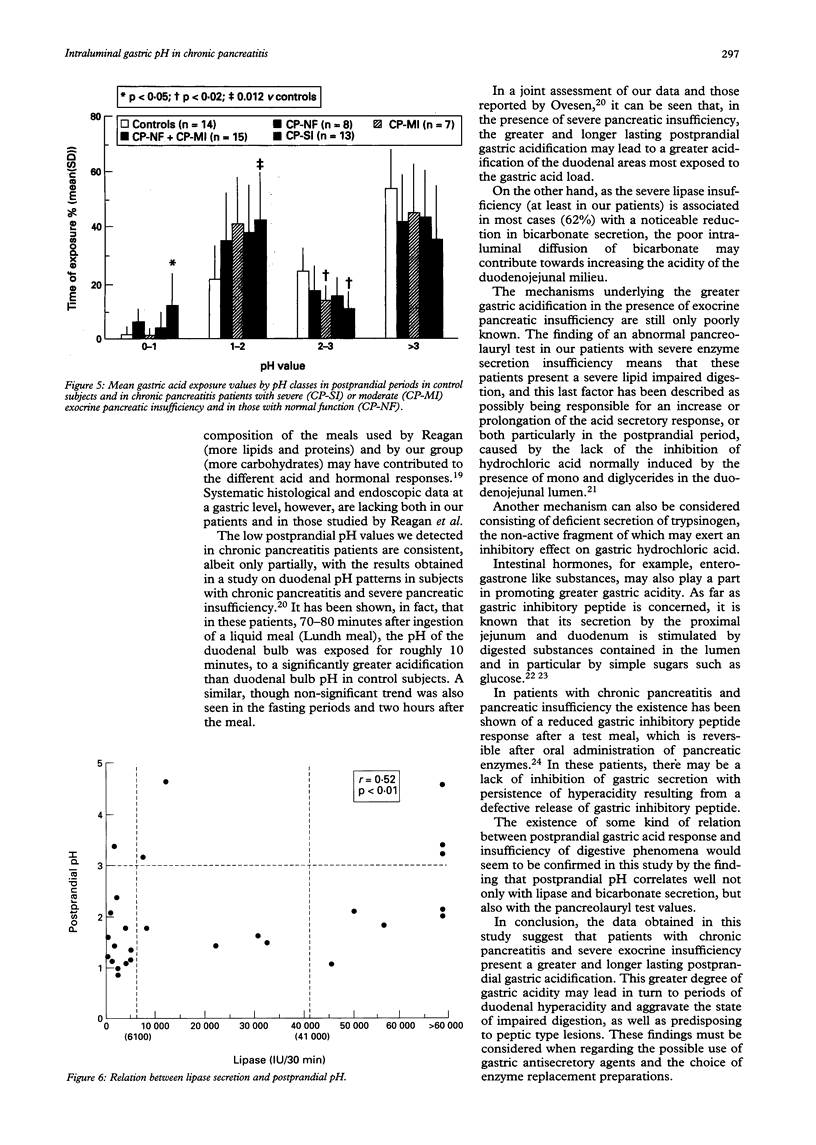
The aim of this study was to assess the circadian variations of intragastric pH in 28 inpatients with chronic pancreatitis (mean (SD) age 46.8 (12.4) years) and in 14 controls (45.4 (9.8)). pH Metry was performed using a monocrystalline antimony electrode placed in the body of the stomach under fluoroscopic control and connected up to a recorder (MKII Digitrapper, Synectics). The evaluation parameters, expressed as median and interquartile range, were: total period, postprandial periods (P1 and P2), interdigestive, and nocturnal phases. Patients with chronic pancreatitis were subdivided into three groups on the basis of severity of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (secretin-caerulein test: lipase output at 60-90 min)--that is, those with severe insufficiency (chronic pancreatitis-SI: 13 patients, lipase output < 10% normal values and pancreolauryl test < 20%), those with only mild insufficiency (chronic pancreatitis-MI: seven patients), and those with normal secretion (chronic pancreatitis-NF: eight patients). The chronic pancreatitis-SI patients present significantly greater gastric acidification in the postprandial periods compared with controls (P1: p < 0.001; P2: p < 0.01), and with chronic pancreatitis-MI plus chronic pancreatitis-NF subjects (P1: p < 0.01; P2: p < 0.05), taken together. In conclusion, gastric acidity, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, and impaired digestion are closely related during the course of chronic pancreatitis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cavallini G., Piubello W., Brocco G., Micciolo R., Chech G., Angelini G., Benini L., Riela A., Dalle Molle L., Vantini I. Serum PABA and fluorescein in the course of Bz-Ty-PABA and pancreolauryl test as an index of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Jul;30(7):655–663. doi: 10.1007/BF01308415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallini G., Piubello W., Brocco G., Vantini I., Angelini G., Benini L., Chech G., Marchiaro G., Dobrilla G., Bonoldi C. Reliability of the Bz-Ty-PABA and the pancreolauryl test in the assessment of exocrine pancreatic function. Digestion. 1983;27(3):129–137. doi: 10.1159/000198942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domschke S., Bloom S. R., Adrian T. E., Lux G., Domschke W. Chronic pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus: plasma and gastroduodenal mucosal profiles of regulatory peptides (gastrin, motilin, secretin, cholecystokinin, gastric inhibitory polypeptide, somatostatin, VIP, substance P, pancreatic polypeptide, glucagon, enteroglucagon, neurotensin). Hepatogastroenterology. 1988 Oct;35(5):229–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert R., Creutzfeldt W. Reversal of impaired GIP and insulin secretion in patients with pancreatogenic steatorrhea following enzyme substitution. Diabetologia. 1980 Sep;19(3):198–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00275269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fimmel C. J., Etienne A., Cilluffo T., von Ritter C., Gasser T., Rey J. P., Caradonna-Moscatelli P., Sabbatini F., Pace F., Bühler H. W. Long-term ambulatory gastric pH monitoring: validation of a new method and effect of H2-antagonists. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jun;88(6):1842–1851. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaffarnik H., Meyer-Bertenrath J. G. Zur Methodik und klinischen Bedeutung eines neuen Pankreaslipase-Tests mit Fluoresceindilaurinsäureester. Klin Wochenschr. 1969 Feb 15;47(4):221–223. doi: 10.1007/BF01725679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R., Longstreth G. F., Summerskill W. H., Go V. L. Measurement of gastric functions during digestion of ordinary solid meals in man. Gastroenterology. 1976 Feb;70(2):203–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfertheiner P., Sarr M. G., Nelson D. K., DiMagno E. P. Role of the duodenum in postprandial release of pancreatic and gastrointestinal hormones. Pancreas. 1994 Jan;9(1):13–19. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199401000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masoero G., Rossanino A., de la Pierre M. Twenty-four-hour intragastric acidity. An update. Dig Dis. 1990;8(6):346–353. doi: 10.1159/000171267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mela G. S., Savarino V., Vigneri S. Optimizing the information obtained from continuous 24-hour gastric pH monitoring. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992 Aug;87(8):961–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piubello W., Vantini I., Scuro L. A., Novelli P., Benini L., Brocco G., Cavallini G. Gastric secretion, gastroduodenal histological changes, and serum gastrin in chronic alcoholic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1982 Feb;77(2):105–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan P. T., Malagelada J. R., Dimagno E. P., Go V. L. Postprandial gastric function in pancreatic insufficiency. Gut. 1979 Mar;20(3):249–254. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.3.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribet A., Tournut R., Duffaut M., Vaysse N. Use of caerulein with submaximal doses of secretin as a test of pancreatic function in man. Gut. 1976 Jun;17(6):431–434. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.6.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARLES H., TAULIER J., FIGARELLA C. DOSAGE DE LA LIPASE DANS LE SUC DUOD'ENAL. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1963 Aug-Sep;8:706–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. H., Cargill J. M., Wormsley K. G. Gastric secretion of acid in patients with pancreatic disease. Digestion. 1978 Jul-Aug;17(4):365–369. doi: 10.1159/000198129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savarino V., Mela G. S. Comparison of gastric aspiration and continuous pH monitoring with antimony electrode: methodological remarks. Dig Dis. 1990;8 (Suppl 1):23–30. doi: 10.1159/000171276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormsley K. G. Tests of pancreatic secretion. Clin Gastroenterol. 1978 May;7(2):529–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


