Abstract
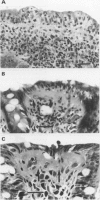
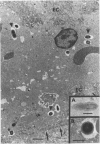
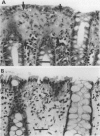
The colorectal biopsy specimens from 30 patients with chronic watery diarrhoea but normal endoscopic and radiographic findings were studied by light microscopy, morphometry, immunohistochemistry, and two patients with electron microscopy. The histological changes in the colorectum were originally diagnosed in six patients as lymphocytic colitis and in 24 patients as collagenous colitis. The analysis of the specimens for this study could delineate three distinct groups of microscopic colitis: lymphocytic colitis (six patients), collagenous colitis without lymphocytic attack on the surface epithelium (seven patients), and a mixed form presenting with both thickening of the collagen plate and increased number of intraepithelial lymphocytes (17 patients). No transformation was seen from one type to another during follow up of six patients for four to seven years. Increased numbers of active pericryptal myofibroblasts were found with the electron microscope in one patient with mixed microscopic colitis showing also myofibroblasts entrapped within the collagen layer. Hitherto undescribed flat mucosa of the ileum was found in one patient with lymphocytic colitis and both flat mucosa and thickening of the collagen plate in the ileum were seen in one patient with the mixed form of the disease. In another patient with mixed microscopic colitis, normalisation of the colorectal morphology occurred after temporary loop ileostomy, followed by the reappearance of both diarrhoea, inflammation, and thickening of the collagen plate after the ileostomy was reversed. No association was found between non-steroid anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) consumption and collagenous or mixed microscopic colitis. The primary cause of microscopic colitis is probably an immunological reaction to luminal antigen/s, perhaps of ileal origin. The engagement of the pericryptal myofibroblasts in the disease process might result in the development of the various forms of microscopic colitis. An inverse relation between intraepithelial lymphocyte count and collagen thickness may indicate that microscopic colitis is a spectral disease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armes J., Gee D. C., Macrae F. A., Schroeder W., Bhathal P. S. Collagenous colitis: jejunal and colorectal pathology. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Sep;45(9):784–787. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.9.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogomoletz W. V., Adnet J. J., Birembaut P., Feydy P., Dupont P. Collagenous colitis: an unrecognised entity. Gut. 1980 Feb;21(2):164–168. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen E. G., Farren C., Connolly C. E., McCarthy C. F. Collagenous colitis and coeliac disease. Gut. 1987 Mar;28(3):364–364. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.3.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadiot G., Flourie B., Galian A., Lavergne A., Modigliani R. Maladie coeliaque et colite collagène. Une association fortuite? Presse Med. 1990 Oct 27;19(35):1621–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flejou J. F., Grimaud J. A., Molas G., Baviera E., Potet F. Collagenous colitis. Ultrastructural study and collagen immunotyping of four cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1984 Dec;108(12):977–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello F. M., Bayless T. M., Jessurun J., Hamilton S. R., Yardley J. H. Collagenous colitis: physiologic and histopathologic studies in seven patients. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Jan;106(1):46–49. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-1-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giardiello F. M., Lazenby A. J., Bayless T. M., Levine E. J., Bias W. B., Ladenson P. W., Hutcheon D. F., Derevjanik N. L., Yardley J. H. Lymphocytic (microscopic) colitis. Clinicopathologic study of 18 patients and comparison to collagenous colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Nov;34(11):1730–1738. doi: 10.1007/BF01540051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grouls V., Vogel J., Sorger M. Collagenous colitis. Endoscopy. 1982 Jan;14(1):31–33. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1021570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton I., Sanders S., Hopwood D., Bouchier I. A. Collagenous colitis associated with small intestinal villous atrophy. Gut. 1986 Nov;27(11):1394–1398. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.11.1394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessurun J., Yardley J. H., Giardiello F. M., Hamilton S. R., Bayless T. M. Chronic colitis with thickening of the subepithelial collagen layer (collagenous colitis): histopathologic findings in 15 patients. Hum Pathol. 1987 Aug;18(8):839–848. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessurun J., Yardley J. H., Lee E. L., Vendrell D. D., Schiller L. R., Fordtran J. S. Microscopic and collagenous colitis: different names for the same condition? Gastroenterology. 1986 Dec;91(6):1583–1584. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingham J. G., Levison D. A., Ball J. A., Dawson A. M. Microscopic colitis-a cause of chronic watery diarrhoea. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Dec 4;285(6355):1601–1604. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6355.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingham J. G., Levison D. A., Morson B. C., Dawson A. M. Collagenous colitis. Gut. 1986 May;27(5):570–577. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.5.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingham J. G. Microscopic colitis. Gut. 1991 Mar;32(3):234–235. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.3.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazenby A. J., Yardley J. H., Giardiello F. M., Bayless T. M. Pitfalls in the diagnosis of collagenous colitis: experience with 75 cases from a registry of collagenous colitis at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. Hum Pathol. 1990 Sep;21(9):905–910. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazenby A. J., Yardley J. H., Giardiello F. M., Jessurun J., Bayless T. M. Lymphocytic ("microscopic") colitis: a comparative histopathologic study with particular reference to collagenous colitis. Hum Pathol. 1989 Jan;20(1):18–28. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(89)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström C. G. 'Collagenous colitis' with watery diarrhoea--a new entity? Pathol Eur. 1976;11(1):87–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Mahony S., Nawroz I. M., Ferguson A. Coeliac disease and collagenous colitis. Postgrad Med J. 1990 Mar;66(773):238–241. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.66.773.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieterse A. S., Hecker R., Rowland R. Collagenous colitis: a distinctive and potentially reversible disorder. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Mar;35(3):338–340. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.3.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read N. W., Krejs G. J., Read M. G., Santa Ana C. A., Morawski S. G., Fordtran J. S. Chronic diarrhea of unknown origin. Gastroenterology. 1980 Feb;78(2):264–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P. E., Owen D. A., Ramey C. W., Dunn W. L., Clay M. G., Jones E. A. Histochemical procedures for the simultaneous visualization of sialic acid, its side chain O-acyl variants and O-sulphate ester. Histochem J. 1985 Jan;17(1):113–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01003408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell R. H., Tanaka M., Mazzoleni G. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as a possible cause of collagenous colitis: a case-control study. Gut. 1992 May;33(5):683–686. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.5.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylwestrowicz T., Kelly J. K., Hwang W. S., Shaffer E. A. Collagenous colitis and microscopic colitis: the watery diarrhea-colitis syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Jul;84(7):763–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Mazzoleni G., Riddell R. H. Distribution of collagenous colitis: utility of flexible sigmoidoscopy. Gut. 1992 Jan;33(1):65–70. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teglbjaerg P. S., Thaysen E. H. Collagenous colitis: an ultrastructural study of a case. Gastroenterology. 1982 Mar;82(3):561–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teglbjaerg P. S., Thaysen E. H., Jensen H. H. Development of collagenous colitis in sequential biopsy specimens. Gastroenterology. 1984 Sep;87(3):703–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Bodmer H. Antigen recognition by class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:601–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widgren S., Jlidi R., Cox J. N. Collagenous colitis: histologic, morphometric, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. Report of 21 cases. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1988;413(4):287–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00783020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolber R., Owen D., Freeman H. Colonic lymphocytosis in patients with celiac sprue. Hum Pathol. 1990 Nov;21(11):1092–1096. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90144-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley J. H., Lazenby A. J., Giardiello F. M., Bayless T. M. Collagenous, "microscopic," lymphocytic, and other gentler and more subtle forms of colitis. Hum Pathol. 1990 Nov;21(11):1089–1091. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90143-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]