Abstract
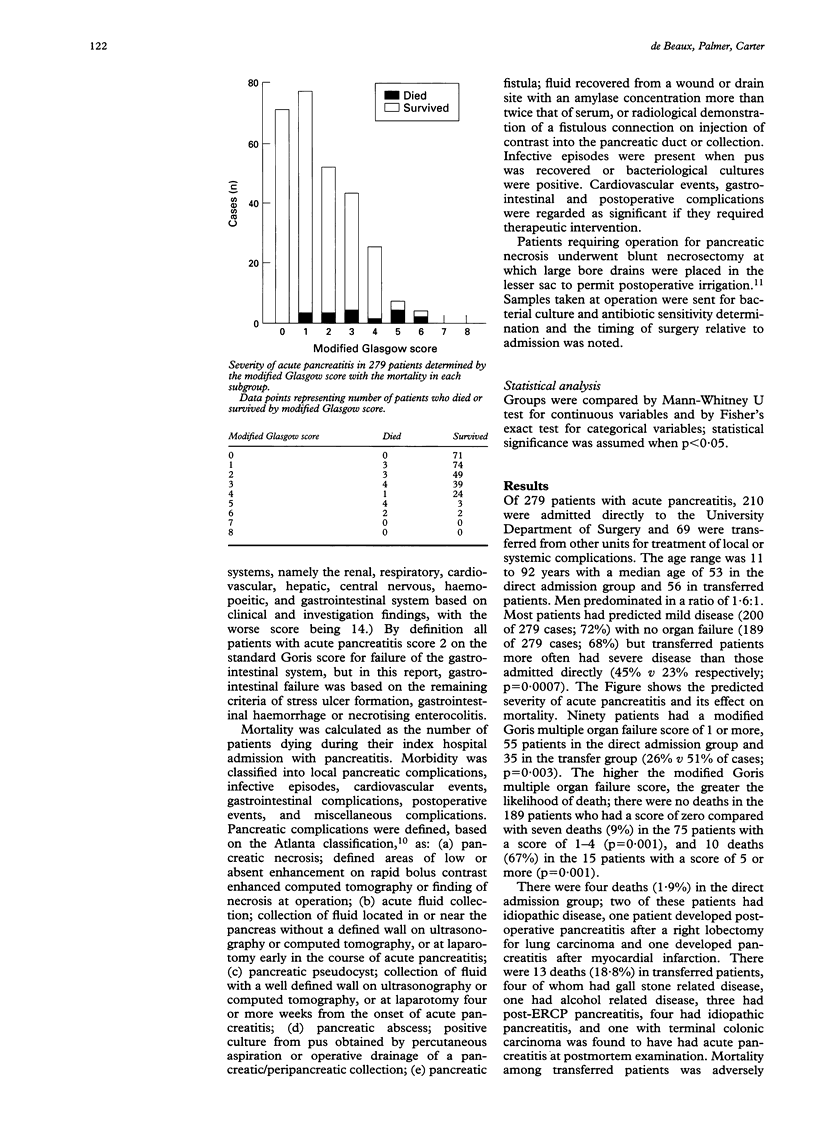
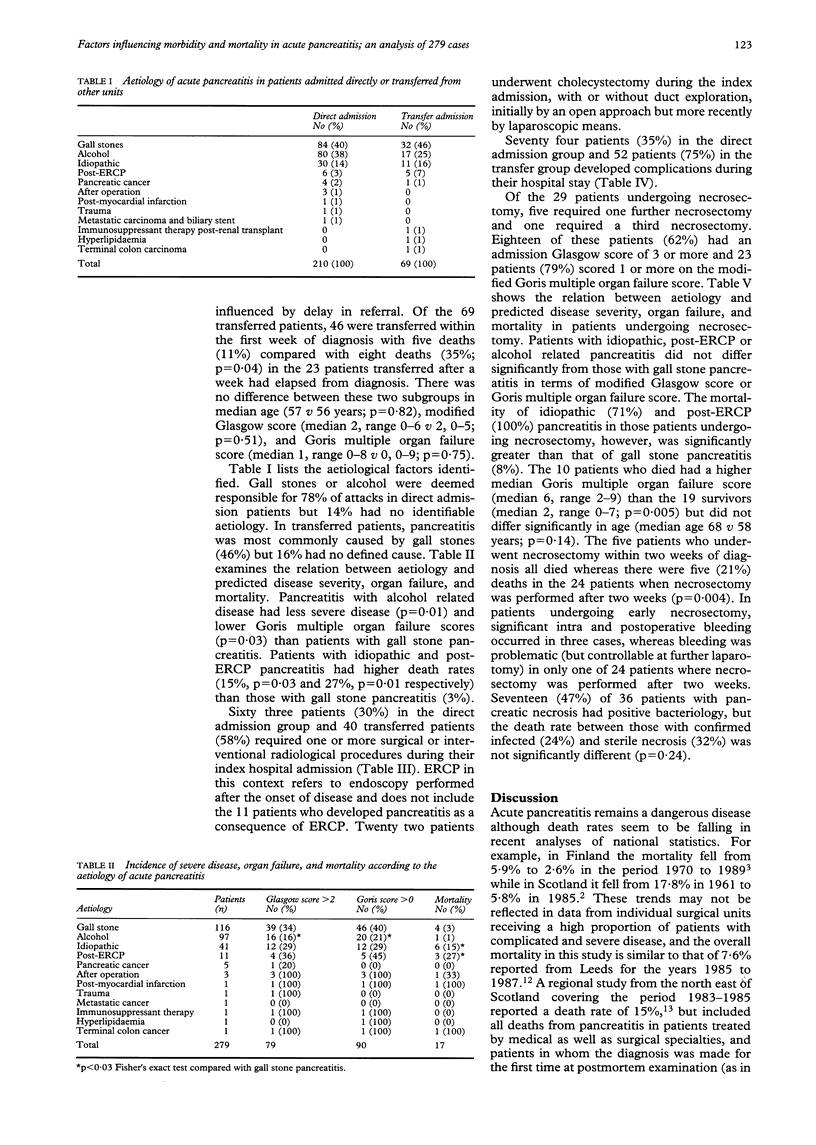
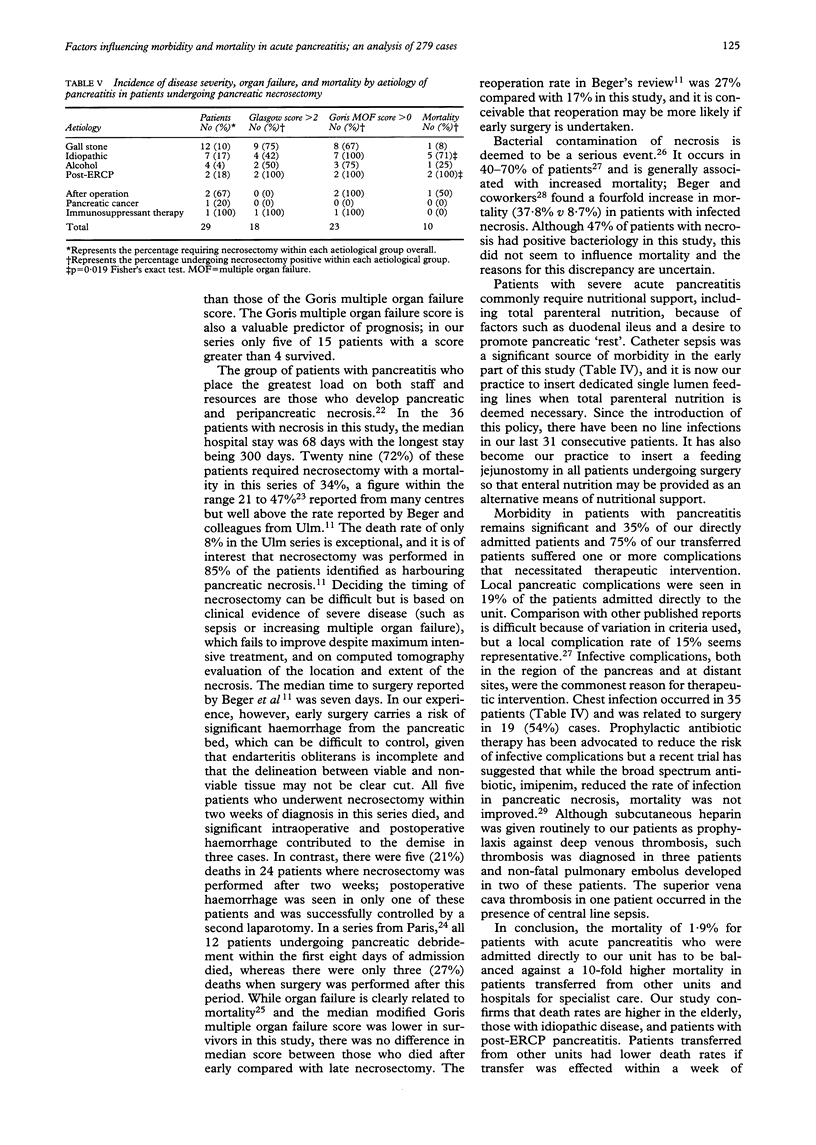
Of 279 patients admitted to a specialist unit with acute pancreatitis, 210 were admitted directly and 69 were transferred for treatment of local or systemic complications. Outcome was assessed in terms of mortality and morbidity and in relation to aetiology, predicted severity of disease (modified Glasgow score), organ failure (modified Goris multiple organ failure score), and need for surgical intervention. The death rate was 1.9% in patients admitted directly but was 18.8% in those transferred from other units. Mortality in gall stone related pancreatitis was 3% compared with 15% (p = 0.03) in pancreatitis of unknown aetiology and 27% (p = 0.01) in post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis. Mortality was related to age (mortality > 55 years old 11% v 2%; p = 0.003) and Goris score (score 0, mortality 0% v score 5-9, mortality 67%; p = 0.001). In patients transferred from other units, mortality was 11% in those transferred within a week of diagnosis and 35% when transfer was delayed (p = 0.04). Thirty six patients had pancreatic necrosis on dynamic computed tomography of whom 29 underwent pancreatic necrosectomy with a 34% mortality. Mortality was related to the modified Goris score (median score 2 in survivors v 6 in non-survivors; p = 0.005) and was higher when necrosectomy was performed within the first two weeks of admission (100% vs 21%; p = 0.004). In conclusion, mortality in acute pancreatitis is influenced by age, aetiology of the disease, and presence of organ failure. Patients transferred for specialist care have a 10-fold greater mortality than those admitted directly and mortality is greatest when transfer is delayed. Early necrosectomy carries a prohibitively high mortality.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bank S., Wise L., Gersten M. Risk factors in acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983 Oct;78(10):637–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beger H. G., Bittner R., Block S., Büchler M. Bacterial contamination of pancreatic necrosis. A prospective clinical study. Gastroenterology. 1986 Aug;91(2):433–438. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90579-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beger H. G., Büchler M., Bittner R., Block S., Nevalainen T., Roscher R. Necrosectomy and postoperative local lavage in necrotizing pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1988 Mar;75(3):207–212. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blamey S. L., Imrie C. W., O'Neill J., Gilmour W. H., Carter D. C. Prognostic factors in acute pancreatitis. Gut. 1984 Dec;25(12):1340–1346. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.12.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley E. L., 3rd A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta, Ga, September 11 through 13, 1992. Arch Surg. 1993 May;128(5):586–590. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1993.01420170122019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browder W., Patterson M. D., Thompson J. L., Walters D. N. Acute pancreatitis of unknown etiology in the elderly. Ann Surg. 1993 May;217(5):469–475. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199305010-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. C. Acute pancreatitis: the value of life. Br J Surg. 1993 Dec;80(12):1499–1500. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800801202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corfield A. P., Cooper M. J., Williamson R. C. Acute pancreatitis: a lethal disease of increasing incidence. Gut. 1985 Jul;26(7):724–729. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.7.724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Egidio A., Schein M. Surgical strategies in the treatment of pancreatic necrosis and infection. Br J Surg. 1991 Feb;78(2):133–137. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan S. T., Choi T. K., Lai C. S., Wong J. Influence of age on the mortality from acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1988 May;75(5):463–466. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800750520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan S. T., Choi T. K., Lai E. C., Wong J. Prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis: an alternative approach. Gut. 1989 Nov;30(11):1591–1595. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.11.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton-Lee D., Imrie C. W. Pancreatic necrosis: assessment of outcome related to quality of life and cost of management. Br J Surg. 1993 Dec;80(12):1579–1582. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800801228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-del Castillo C., Rattner D. W., Warshaw A. L. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 1993 Aug 21;342(8869):475–479. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91598-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foitzik T., Bassi D. G., Schmidt J., Lewandrowski K. B., Fernandez-del Castillo C., Rattner D. W., Warshaw A. L. Intravenous contrast medium accentuates the severity of acute necrotizing pancreatitis in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jan;106(1):207–214. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(94)95457-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funnell I. C., Bornman P. C., Weakley S. P., Terblanche J., Marks I. N. Obesity: an important prognostic factor in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1993 Apr;80(4):484–486. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris R. J., te Boekhorst T. P., Nuytinck J. K., Gimbrère J. S. Multiple-organ failure. Generalized autodestructive inflammation? Arch Surg. 1985 Oct;120(10):1109–1115. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1985.01390340007001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaakkola M., Nordback I. Pancreatitis in Finland between 1970 and 1989. Gut. 1993 Sep;34(9):1255–1260. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.9.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larvin M., McMahon M. J. APACHE-II score for assessment and monitoring of acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 1989 Jul 22;2(8656):201–205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Nicholls J. F., Park H. Z. Biliary sludge as a cause of acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Feb 27;326(9):589–593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199202273260902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malangoni M. A., Richardson J. D., Shallcross J. C., Seiler J. G., Polk H. C., Jr Factors contributing to fatal outcome after treatment of pancreatic abscess. Ann Surg. 1986 Jun;203(6):605–613. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198606000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrilla Paricio P., García Olmo D., Pellicer Franco E., Prieto González A., Carrasco González L., Bermejo López J. Gallbladder cholesterolosis: an aetiological factor in acute pancreatitis of uncertain origin. Br J Surg. 1990 Jul;77(7):735–736. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800770706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smadja C., Bismuth H. Pancreatic debridement in acute necrotizing pancreatitis: an obsolete procedure? Br J Surg. 1986 May;73(5):408–410. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800730532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson S. R., Hendry W. S., McFarlane G. A., Davidson A. I. Epidemiology and outcome of acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1987 May;74(5):398–401. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran D. D., Cuesta M. A. Evaluation of severity in patients with acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992 May;87(5):604–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdison A. L., Karanjia N. D. Pancreatic infection complicating acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1993 Feb;80(2):148–154. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Imrie C. W. Changing patterns of incidence and mortality from acute pancreatitis in Scotland, 1961-1985. Br J Surg. 1990 Jul;77(7):731–734. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800770705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Imrie C. W. Deaths from acute pancreatitis: why do we miss the diagnosis so frequently? Int J Pancreatol. 1988 May;3(4):273–281. doi: 10.1007/BF02788456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


