Abstract
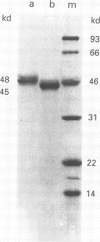
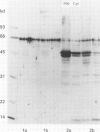
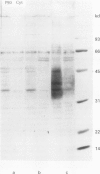
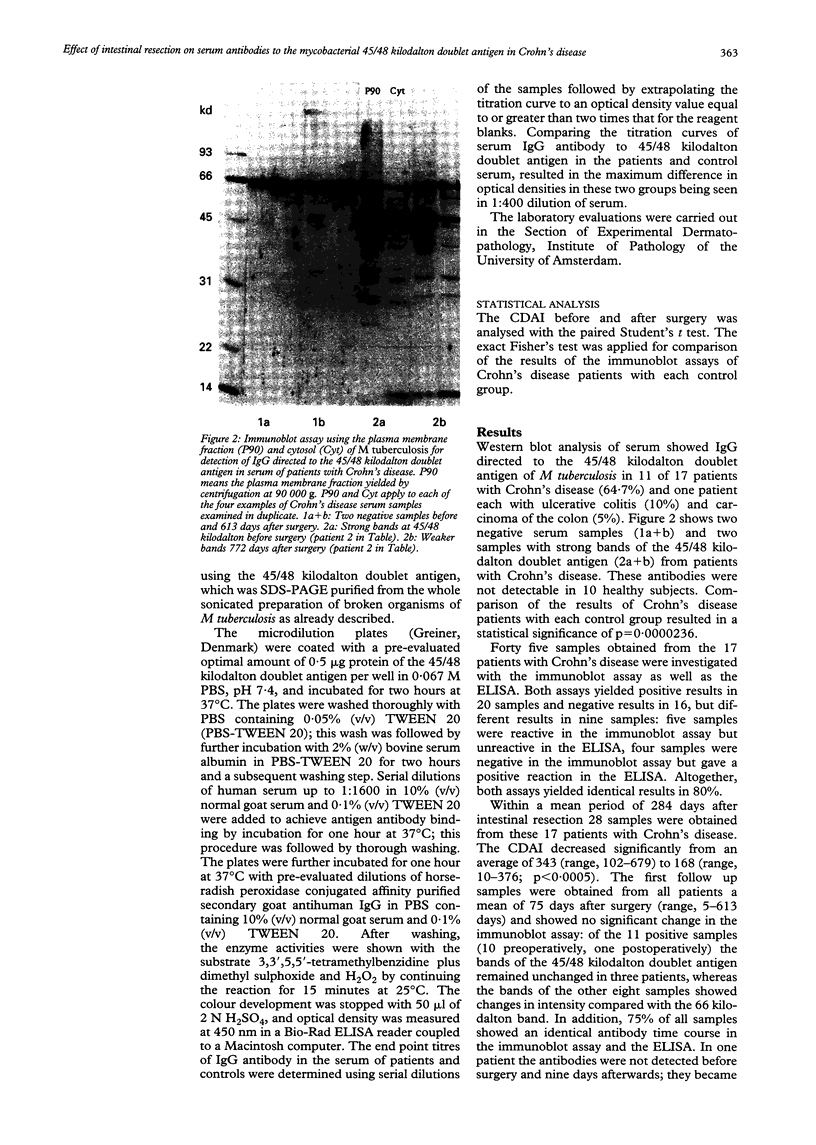
Interest in the role of mycobacterial infection in Crohn's disease has been revived by the cultural detection of Mycobacterium paratuberculosis in patients with Crohn's disease. This hypothesis was examined serologically using assays with high specificity for Crohn's disease. The effect of intestinal resection on serum antibodies specific for Crohn's disease was investigated with an immunoblot assay and an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay using the 45/48 kilodalton doublet antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antibodies were detected in 64.7% of patients with Crohn's disease (n = 17), 10% of patients with ulcerative colitis (n = 10), 5% of patients with carcinoma of the colon (n = 20), and none of 10 healthy subjects with the immunoblot assay. Statistical comparison of the Crohn's disease patients with each control group resulted in p = 0.0000236. Immunoglobulin G was essentially unchanged 75 days (mean) after surgery. After more than 180 days, however, the antibody response was reduced in all of five patients studied, and was no longer demonstrable in two of them (40%). Simultaneously, the Crohn's disease activity index (CDAI) decreased. Both the high specificity of this assay for Crohn's disease and the diminished antibody response after intestinal resection in parallel with decreased CDAI support a mycobacterial aetiology of Crohn's disease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best W. R., Becktel J. M., Singleton J. W., Kern F., Jr Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Miller R. A., Lacher J., Singleton J. W. Patients with active Crohn's disease have elevated serum antibodies to antigens of seven enteric bacterial pathogens. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):888–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho S. N., Brennan P. J., Yoshimura H. H., Korelitz B. I., Graham D. Y. Mycobacterial aetiology of Crohn's disease: serologic study using common mycobacterial antigens and a species-specific glycolipid antigen from Mycobacterium paratuberculosis. Gut. 1986 Nov;27(11):1353–1356. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.11.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das P. K., Ibrahim A. A., Binkhuysen F., Thi Hué P., Qui T. H., Rangarajan R., Ruitenberg E. J. The use of subcellular components of BCG for studying host-Mycobacterium interaction in relation to leprosy. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1982 Jul-Aug;133D(1):41–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das P. K., Rambukkana A., Baas J. G., Groothuis D. G., Halperin M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for distinguishing serological responses of lepromatous and tuberculoid leprosies to the 29/33-kilodalton doublet and 64-kilodalton antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):379–382. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.379-382.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott P. R., Lennard-Jones J. E., Burnham W. R., White S., Stanford J. L. Further data on skin testing with mycobacterial antigens in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet. 1980 Aug 30;2(8192):483–484. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91922-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsaghier A., Prantera C., Moreno C., Ivanyi J. Antibodies to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis-specific protein antigens in Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Dec;90(3):503–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funakoshi O. [Mycobacteria as a possible cause of Crohn's disease]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1988 Jul;85(7):1340–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange J. M., Gibson J., Nassau E., Kardjito T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): a study of antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the IgG, IgA and IgM classes in tuberculosis, sarcoidosis and Crohn's disease. Tubercle. 1980 Sep;61(3):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(80)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Brown W. R., Brennan P. J., Blaser M. J. Serum antibodies to mycobacterial antigens in active Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jun;94(6):1404–1411. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90679-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N., Mayberry J. F., Rhodes J., Neale L., Munro J., Wensinck F., Lawson G. H., Rowland A. C., Berkhoff G. A., Barthold S. W. Agglutinins to bacteria in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1980 May;21(5):376–380. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.5.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden J. J., Houdayer C. No evidence for antibodies to mycobacterial A60 antigen in Crohn's disease sera by enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay (ELISA). J Med Microbiol. 1988 Apr;25(4):295–298. doi: 10.1099/00222615-25-4-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morganroth J., Watson D. W. Sensitivity to atypical mycobacterial antigens in patients with Crohn's disease. Am J Dig Dis. 1970 Jul;15(7):653–657. doi: 10.1007/BF02236026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambukkana A., Das P. K., Chand A., Baas J. G., Groothuis D. G., Kolk A. H. Subcellular distribution of monoclonal antibody defined epitopes on immunodominant Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins in the 30-kDa region: identification and localization of 29/33-kDa doublet proteins on mycobacterial cell wall. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Jun;33(6):763–775. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb02551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson J. D., Moss M. T., Tizard M. L., Hermon-Taylor J. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis DNA in Crohn's disease tissue. Gut. 1992 Jul;33(7):890–896. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.7.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stainsby K. J., Lowes J. R., Allan R. N., Ibbotson J. P. Antibodies to Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and nine species of environmental mycobacteria in Crohn's disease and control subjects. Gut. 1993 Mar;34(3):371–374. doi: 10.1136/gut.34.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Wilks M., Coates P. J., Farthing M. J., Walker-Smith J. A., Tabaqchali S. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis and Crohn's disease. Gut. 1991 Jan;32(1):43–45. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer W. R., Jr, Coutu J. A., Chiodini R. J., Van Kruiningen H. J., Merkal R. S. Possible role of mycobacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. II. Mycobacterial antibodies in Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1984 Dec;29(12):1080–1085. doi: 10.1007/BF01317079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer W. R., Jr, Fixa B., Komarkova O., Charland C., Field C. E. Skin test reactivity in inflammatory bowel disease in the United States and Czechoslovakia. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 Apr;23(4):337–340. doi: 10.1007/BF01072417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]