Abstract
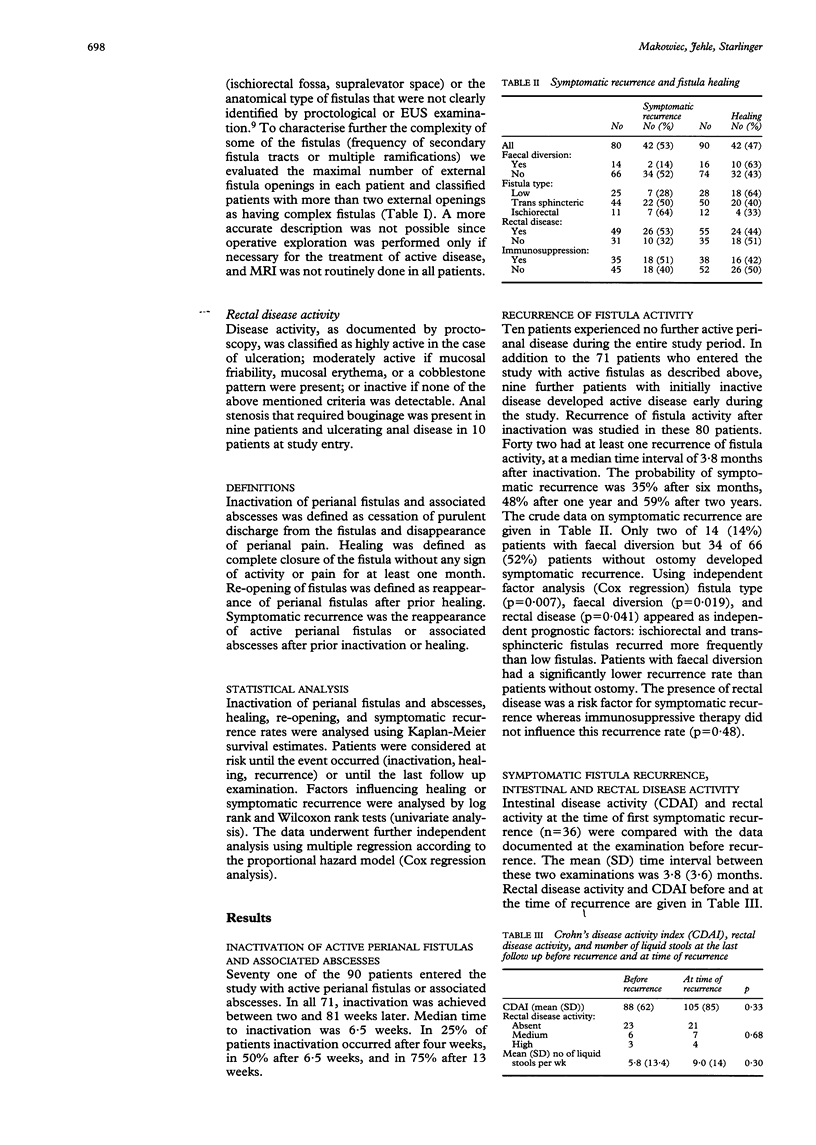
The clinical course of perianal fistulas and associated abscesses was evaluated prospectively in 90 patients with Crohn's disease. Fistula type, rectal disease, faecal diversion, and immunosuppression were examined as prognostic indicators for fistula healing and recurrence. Median follow up was 22 months. The outcome was evaluated with life table analysis. Prognostic factors were analysed by multiple regression. Inactivation was achieved in all patients. The risks of recurrent fistula activity were 48% at one year and 59% at two years. Fistulas were healed in 51% after two years but reopened in 44% within 18 months of healing. Faecal diversion and absence of rectal disease decreased recurrence rates (p = 0.019/0.04) and increased healing rates (p = 0.005/0.017). The outcome in patients with trans-sphincteric fistulas was better than that in those with ischiorectal fistulas but worse than in patients with subcutaneous fistulas (p = 0.015 for healing; p = 0.007 for recurrent fistula activity). After initial treatment about 20% of the patients were symptomatic and about 10% had painful events per six month period. Incontinence was rare and did not increase during the study period. Perianal fistulas and associated abscesses can be controlled safely by simple drainage of pus collections. Frequent reinfection and re-opening after healing of fistulas are characteristic. Fistula type, rectal disease, and stool contamination influence the clinical course. Only a few patients, however, have continuous symptoms from perianal fistulas.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander-Williams J., Buchmann P. Perianal Crohn's disease. World J Surg. 1980;4(2):203–208. doi: 10.1007/BF02393577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer I., Gordon P. H. Selected operative management of fistula-in-ano in Crohn's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994 Aug;37(8):760–765. doi: 10.1007/BF02050138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmann P., Keighley M. R., Allan R. N., Thompson H., Alexander-Williams J. Natural history of perianal Crohn's disease. Ten year follow-up: a plea for conservatism. Am J Surg. 1980 Nov;140(5):642–644. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francois Y., Descos L., Vignal J. Conservative treatment of low rectovaginal fistula in Crohn's disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1990 Feb;5(1):12–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00496142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry R. D., Shemesh E. I., Kodner I. J., Timmcke A. Techniques and results in the management of anal and perianal Crohn's disease. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1989 Jan;168(1):42–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. H., Kettlewell M. G., Lee E. C. The effect of split ileostomy on perianal Crohn's disease. Br J Surg. 1982 Oct;69(10):608–610. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800691017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellers G., Bergstrand O., Ewerth S., Holmström B. Occurrence and outcome after primary treatment of anal fistulae in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1980 Jun;21(6):525–527. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.6.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuman R., Bolin T., Sjödahl R., Tagesson C. The incidence and course of perianal complications and arthralgia after intestinal resection with restoration of continuity for Crohn's disease. Br J Surg. 1981 Aug;68(8):528–530. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800680803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones I. T., Fazio V. W., Jagelman D. G. The use of transanal rectal advancement flaps in the management of fistulas involving the anorectum. Dis Colon Rectum. 1987 Dec;30(12):919–923. doi: 10.1007/BF02554276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keighley M. R., Allan R. N. Current status and influence of operation on perianal Crohn's disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1986 Apr;1(2):104–107. doi: 10.1007/BF01648416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelbel G., Schmiedl U., Majer M. C., Weber P., Jenss H., Kueper K., Hess C. F. Diagnosis of fistulae and sinus tracts in patients with Crohn disease: value of MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989 May;152(5):999–1003. doi: 10.2214/ajr.152.5.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korelitz B. I., Present D. H. Favorable effect of 6-mercaptopurine on fistulae of Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Jan;30(1):58–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01318372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levien D. H., Surrell J., Mazier W. P. Surgical treatment of anorectal fistula in patients with Crohn's disease. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1989 Aug;169(2):133–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makowiec F., Jehle E. C., Becker H. D., Starlinger M. Clinical course after transanal advancement flap repair of perianal fistula in patients with Crohn's disease. Br J Surg. 1995 May;82(5):603–606. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800820509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. G., Gathright J. B., Jr, Ray J. E., Ferrari B. T., Hicks T. C., Timmcke A. E. Surgical management of anorectal fistulas in Crohn's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1989 Jun;32(6):492–496. doi: 10.1007/BF02554504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordgren S., Fasth S., Hultén L. Anal fistulas in Crohn's disease: incidence and outcome of surgical treatment. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1992 Dec;7(4):214–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00341224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks A. G., Gordon P. H., Hardcastle J. D. A classification of fistula-in-ano. Br J Surg. 1976 Jan;63(1):1–12. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800630102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard T. J., Schoetz D. J., Jr, Roberts P. L., Murray J. J., Coller J. A., Veidenheimer M. C. Perirectal abscess in Crohn's disease. Drainage and outcome. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990 Nov;33(11):933–937. doi: 10.1007/BF02139102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott N. A., Nair A., Hughes L. E. Anovaginal and rectovaginal fistula in patients with Crohn's disease. Br J Surg. 1992 Dec;79(12):1379–1380. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800791247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher M. E., Bauer J. J., Gorphine S., Gelernt I. Low Hartmann's procedure for severe anorectal Crohn's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1992 Oct;35(10):975–980. doi: 10.1007/BF02253501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohn N., Korelitz B. I., Weinstein M. A. Anorectal Crohn's disease: definitive surgery for fistulas and recurrent abscesses. Am J Surg. 1980 Mar;139(3):394–397. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Outryve M. J., Pelckmans P. A., Michielsen P. P., Van Maercke Y. M. Value of transrectal ultrasonography in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Nov;101(5):1171–1177. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90064-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Hughes L. E. Abdominoperineal resection for severe perianal Crohn's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990 May;33(5):402–407. doi: 10.1007/BF02156267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Rothenberger D. A., Nemer F. D., Goldberg S. M. Fistula-in-ano in Crohn's disease. Results of aggressive surgical treatment. Dis Colon Rectum. 1991 May;34(5):378–384. doi: 10.1007/BF02053687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff B. G., Culp C. E., Beart R. W., Jr, Ilstrup D. M., Ready R. L. Anorectal Crohn's disease. A long-term perspective. Dis Colon Rectum. 1985 Oct;28(10):709–711. doi: 10.1007/BF02560279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen L. M., Lubbers E. J. Perianal fistulas in patients with Crohn's disease. Arch Surg. 1986 Oct;121(10):1187–1190. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1986.01400100099019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


