Abstract
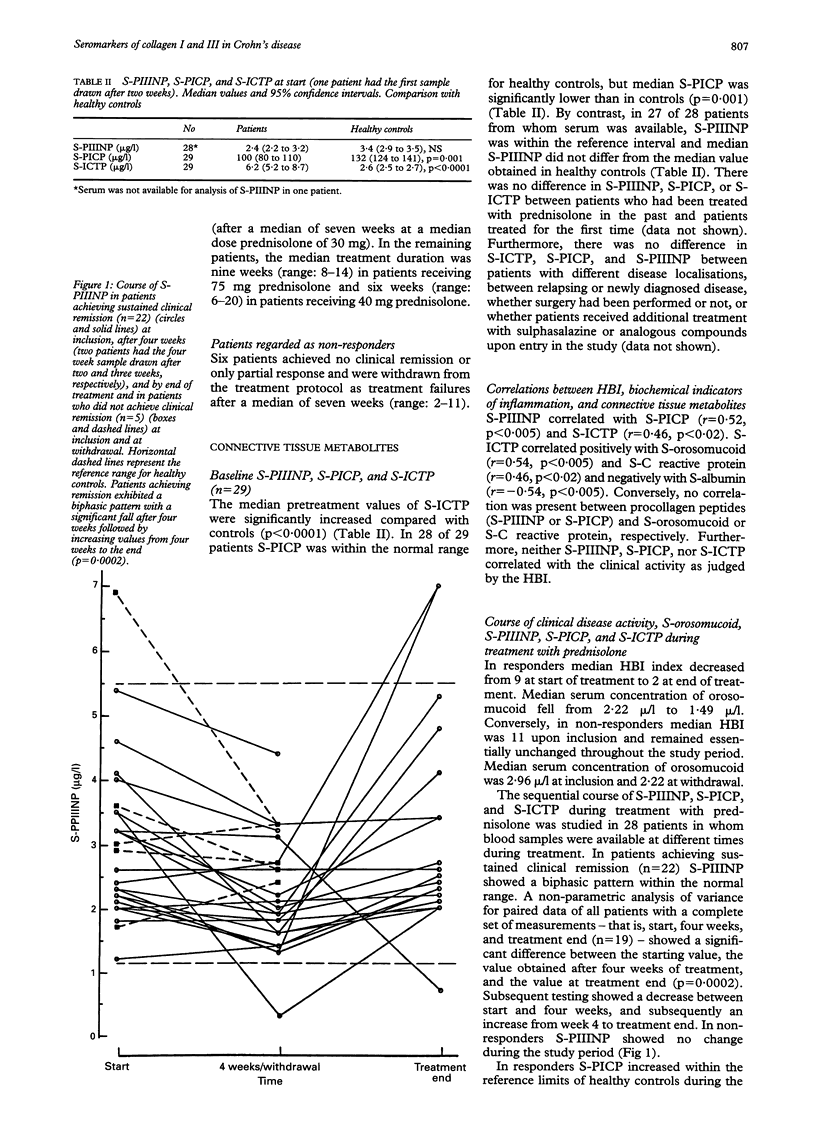
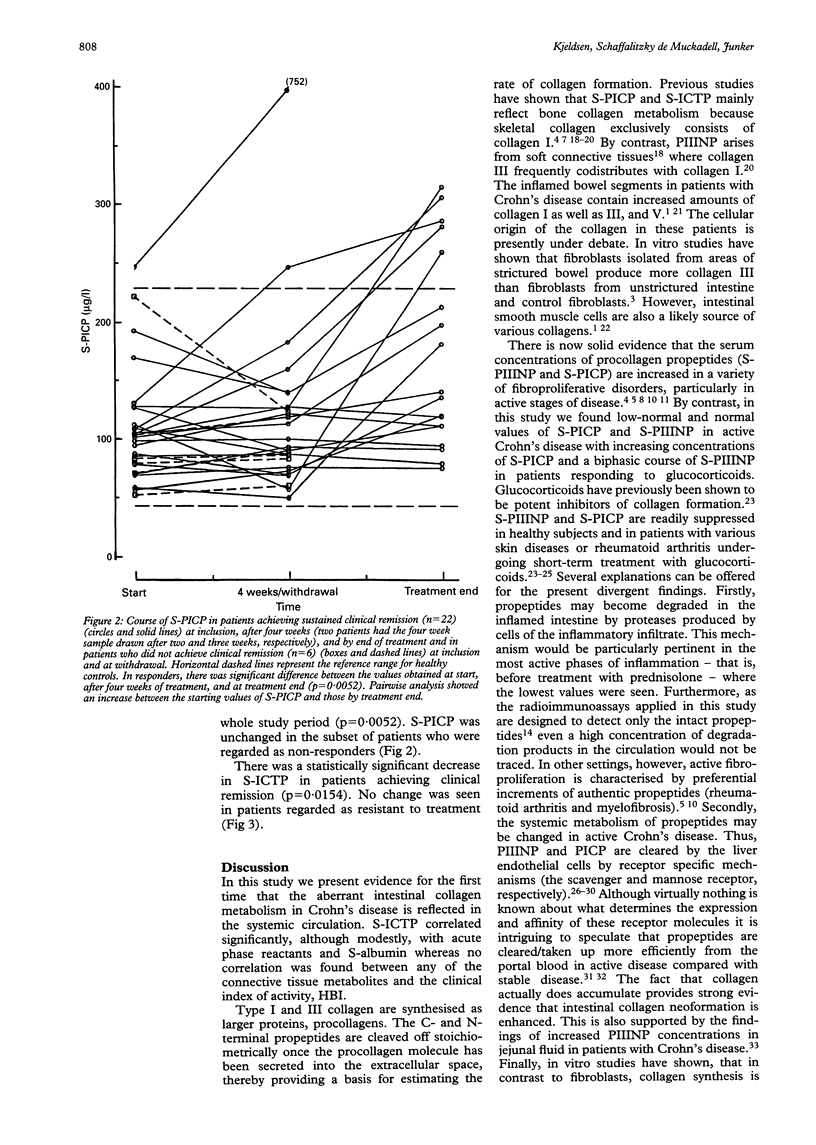
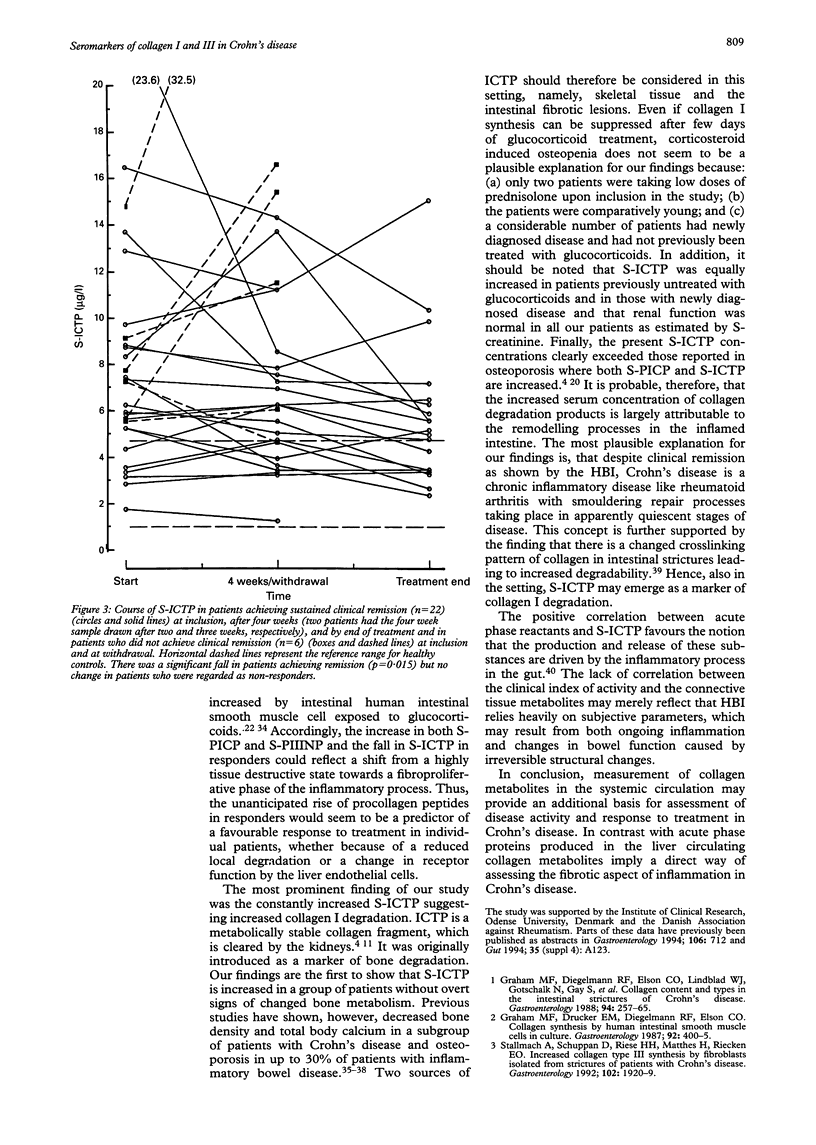
Crohn's disease is characterised by gradual development of intestinal fibrotic lesions containing large amounts of collagen type I, III, and V. Measurement of circulating connective tissue metabolites has emerged as a useful tool for assessment of fibroproliferative activity in various diseases. Serum concentrations of procollagen peptides, N-terminal propeptide of type III procollagen (PII-INP), and C-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen (PICP), reflect the synthesis rate of the parent collagens, while the C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (ICTP) reflects its degradation. S-PIIINP, S-PICP, and S-ICTP were measured by radioimmunoassays in 29 patients with active Crohn's disease. S-ICTP was significantly increased, median 6.2 micrograms/l (95% CI 5.2 to 8.7 micrograms/l) versus controls 2.6 micrograms/l (2.5 to 2.7 micrograms/l) (p < 0.0001), S-PICP reduced, 100 micrograms/l (80 to 110 micrograms/l) versus 132 micrograms/l (124 to 141 micrograms/l) (p = 0.001), and S-PIIINP did not differ from controls. Patients with sustained clinical remission during prednisolone therapy exhibited an increase in S-PICP (p = 0.0052). S-PIIINP changed significantly (p = 0.0002), however, exhibiting a biphasic pattern. S-ICTP decreased (p = 0.015) in treatment responders but remained above the upper normal limit even when clinical remission had been achieved. Non-responders showed no significant changes in any of the marker molecules of collagen synthesis or degradation. Correlations were found between S-PIIINP and S-PICP (p < 0.005) and S-ICTP (p < 0.02), and between S-ICTP and S-orosomucoid (p < 0.005) and S-C reactive protein (p < 0.02). By contrast, there was no relation between the connective tissue metabolites and Harvey Bradshaw Index. These data provide evidence that collagen I degradation is increased not only in active Crohn's disease, but also in patients entering clinical remission. The concurrent normal/low-normal values of markers of collagen formation may reflect a changed local or systemic elimination of the propeptides.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Autio P., Risteli J., Kiistala U., Risteli L., Karvonen J., Oikarinen A. Serum markers of collagen synthesis and degradation in skin diseases. Altered levels in diseases with systemic manifestation and during systemic glucocorticoid treatment. Arch Dermatol Res. 1993;285(6):322–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00371831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentsen K. D., Henriksen J. H., Bendtsen F., Hørslev-Petersen K., Lorenzen I. Splanchnic and renal extraction of circulating type III procollagen aminoterminal propeptide in patients with normal liver function and in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1990 Jun;11(6):957–963. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentsen K. D., Henriksen J. H., Boesby S., Hørslev-Petersen K., Lorenzen I. Hepatic and renal extraction of circulating type III procollagen amino-terminal propeptide and hyaluronan in pig. J Hepatol. 1989 Sep;9(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg S., Brodin B., Hesselvik F., Laurent T. C., Maller R. Elevated levels of plasma hyaluronan in septicaemia. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1988 Dec;48(8):727–732. doi: 10.3109/00365518809088752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles P., Mosekilde L., Risteli L., Risteli J., Eriksen E. F. Assessment of bone remodeling using biochemical indicators of type I collagen synthesis and degradation: relation to calcium kinetics. Bone Miner. 1994 Feb;24(2):81–94. doi: 10.1016/s0169-6009(08)80147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombel J. F., Hällgren R., Engström-Laurent A., Rambaud J. C. Hyaluronic acid and type III procollagen peptide in jejunal perfusion fluid as markers of connective tissue turnover. Gastroenterology. 1989 Jan;96(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90765-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compston J. E., Judd D., Crawley E. O., Evans W. D., Evans C., Church H. A., Reid E. M., Rhodes J. Osteoporosis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1987 Apr;28(4):410–415. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.4.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elomaa I., Virkkunen P., Risteli L., Risteli J. Serum concentration of the cross-linked carboxyterminal telopeptide of type I collagen (ICTP) is a useful prognostic indicator in multiple myeloma. Br J Cancer. 1992 Aug;66(2):337–341. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen E. F., Charles P., Melsen F., Mosekilde L., Risteli L., Risteli J. Serum markers of type I collagen formation and degradation in metabolic bone disease: correlation with bone histomorphometry. J Bone Miner Res. 1993 Feb;8(2):127–132. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650080202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Cowen S., Hannan W. J., Ferguson A. Low bone mineral density in Crohn's disease, but not in ulcerative colitis, at diagnosis. Gastroenterology. 1994 Oct;107(4):1031–1039. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham M. F., Diegelmann R. F., Elson C. O., Lindblad W. J., Gotschalk N., Gay S., Gay R. Collagen content and types in the intestinal strictures of Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1988 Feb;94(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham M. F., Drucker D. E., Diegelmann R. F., Elson C. O. Collagen synthesis by human intestinal smooth muscle cells in culture. Gastroenterology. 1987 Feb;92(2):400–405. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram J., Bollerslev J., Nielsen H. K., Junker P. Increased serum concentrations of type I procollagen C-terminal propeptide and osteocalcin during a short course of calcitriol administration to adult male volunteers. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1991 Dec;125(6):609–613. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1250609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakala M., Risteli L., Manelius J., Nieminen P., Risteli J. Increased type I collagen degradation correlates with disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Dec;52(12):866–869. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.12.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Bradshaw J. M. A simple index of Crohn's-disease activity. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):514–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbalch H., Junker P., Hørslev-Petersen K., Lisse I., Bentsen K. D. Procollagen type III aminoterminal peptide in serum in idiopathic myelofibrosis and allied conditions: relation to disease activity and effect of chemotherapy. Am J Hematol. 1990 Jan;33(1):18–26. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830330105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Muñoz I., de la Torre M. P., Pedraza M. A., Sánchez-Alcázar J. A., Muñoz-Yagüe M. T., Solis-Herruzo J. A. Toxic oil stimulates collagen synthesis acting at a pretranslational level in cultured fat-storing cells. Gastroenterology. 1994 Mar;106(3):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90704-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hørslev-Petersen K., Bentsen K. D., Engström-Laurent A., Junker P., Halberg P., Lorenzen I. Serum amino terminal type III procollagen peptide and serum hyaluronan in rheumatoid arthritis: relation to clinical and serological parameters of inflammation during 8 and 24 months' treatment with levamisole, penicillamine, or azathioprine. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Feb;47(2):116–126. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.2.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hørslev-Petersen K., Bentsen K. D., Junker P., Lorenzen I. Serum amino-terminal type III procollagen peptide in rheumatoid arthritis. Relationship to disease activity, treatment, and development of joint erosions. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 May;29(5):592–599. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen L. T., Henriksen J. H., Olesen H. P., Risteli J., Lorenzen I. Lymphatic clearance of synovial fluid in conscious pigs: the aminoterminal propeptide of type III procollagen. Eur J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;23(12):778–784. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1993.tb00731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen L. T., Olesen H. P., Risteli J., Lorenzen I. External thoracic duct-venous shunt in conscious pigs for long term studies of connective tissue metabolites in lymph. Lab Anim Sci. 1990 Nov;40(6):620–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I. The phenomenon of the acute phase response. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow H., Ewe K., Brandes J. W., Goebell H., Ehms H., Sommer H., Jesdinsky H. European Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study (ECCDS): results of drug treatment. Gastroenterology. 1984 Feb;86(2):249–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthes H., Herbst H., Schuppan D., Stallmach A., Milani S., Stein H., Riecken E. O. Cellular localization of procollagen gene transcripts in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90087-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazlam M. Z., Hodgson H. J. Interrelations between interleukin-6, interleukin-1 beta, plasma C-reactive protein values, and in vitro C-reactive protein generation in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1994 Jan;35(1):77–83. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melkko J., Hellevik T., Risteli L., Risteli J., Smedsrød B. Clearance of NH2-terminal propeptides of types I and III procollagen is a physiological function of the scavenger receptor in liver endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):405–412. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melkko J., Niemi S., Risteli L., Risteli J. Radioimmunoassay of the carboxyterminal propeptide of human type I procollagen. Clin Chem. 1990 Jul;36(7):1328–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motley R. J., Clements D., Evans W. D., Crawley E. O., Evans C., Rhodes J., Compston J. E. A four-year longitudinal study of bone loss in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Bone Miner. 1993 Nov;23(2):95–104. doi: 10.1016/s0169-6009(08)80046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikarinen A., Autio P., Vuori J., Vänänen K., Risteli L., Kiistala U., Risteli J. Systemic glucocorticoid treatment decreases serum concentrations of carboxyterminal propeptide of type I procollagen and aminoterminal propeptide of type III procollagen. Br J Dermatol. 1992 Feb;126(2):172–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1992.tb07816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Elomaa I., Niemi S., Novamo A., Risteli L. Radioimmunoassay for the pyridinoline cross-linked carboxy-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen: a new serum marker of bone collagen degradation. Clin Chem. 1993 Apr;39(4):635–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Niemi S., Trivedi P., Mäentausta O., Mowat A. P., Risteli L. Rapid equilibrium radioimmunoassay for the amino-terminal propeptide of human type III procollagen. Clin Chem. 1988 Apr;34(4):715–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli L., Risteli J. Biochemical markers of bone metabolism. Ann Med. 1993 Aug;25(4):385–393. doi: 10.3109/07853899309147301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryde S. J., Clements D., Evans W. D., Motley R., Morgan W. D., Evans C., Rhodes J., Compston J. E. Total body calcium in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a longitudinal study. Clin Sci (Lond) 1991 Apr;80(4):319–324. doi: 10.1042/cs0800319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrød B., Melkko J., Risteli L., Risteli J. Circulating C-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen is cleared mainly via the mannose receptor in liver endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):345–350. doi: 10.1042/bj2710345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrød B., Pertoft H., Gustafson S., Laurent T. C. Scavenger functions of the liver endothelial cell. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):313–327. doi: 10.1042/bj2660313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallmach A., Schuppan D., Riese H. H., Matthes H., Riecken E. O. Increased collagen type III synthesis by fibroblasts isolated from strictures of patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jun;102(6):1920–1929. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90314-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


