Abstract
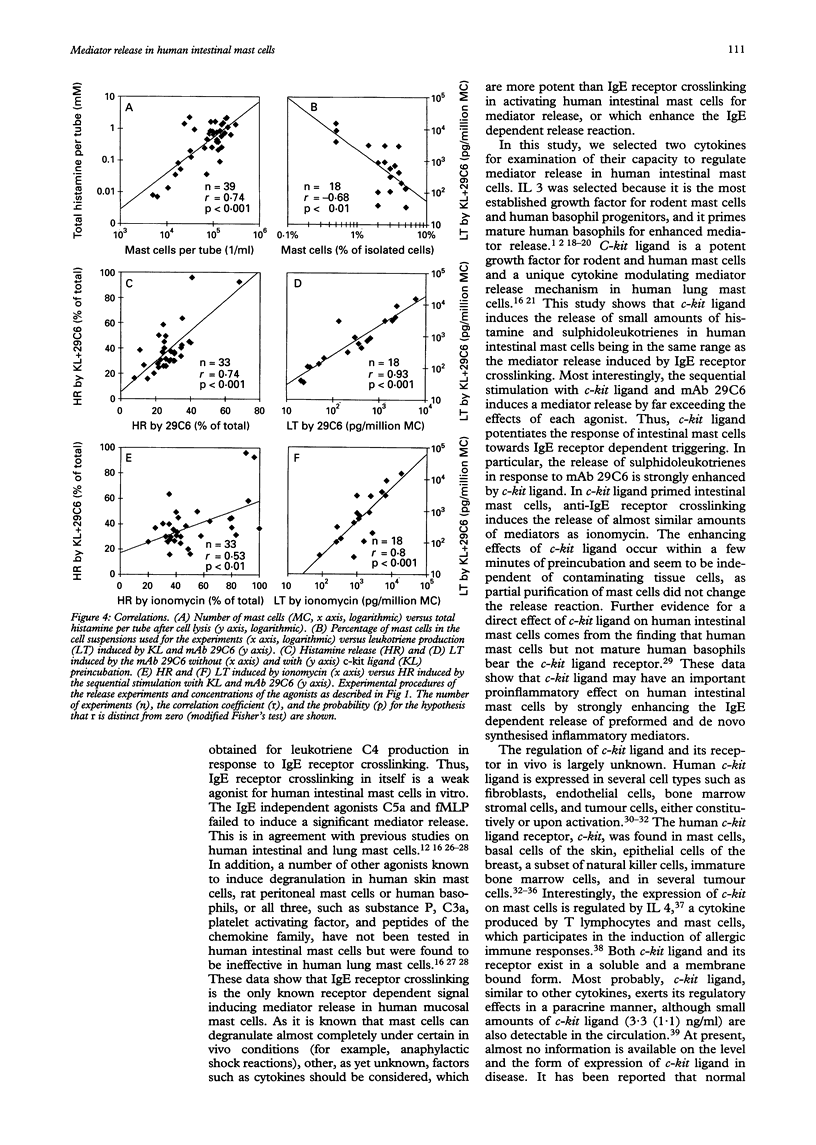
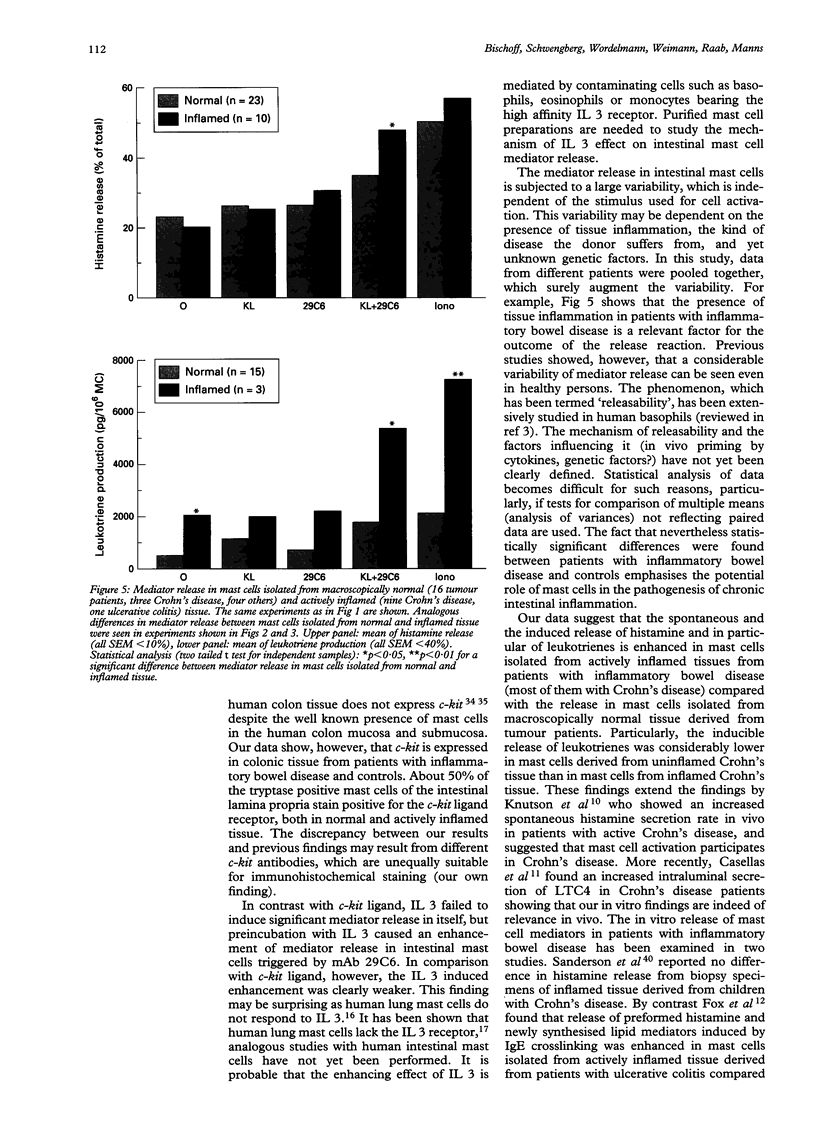
The regulation of mediator release in human intestinal mast cells is largely unknown. Apart from IgE receptor crosslinking no secretagogues have been described so far. This study examined the effect of two cytokines (c-kit ligand and interleukin 3) and other agonists on human intestinal mast cell function. Cells were isolated from surgery specimens of 47 patients undergoing intestinal resection because of tumours or inflammatory bowel disease. Cell suspensions contained 3.6% mast cells (mean of 50 experiments). After preincubation without or with c-kit ligand or interleukin 3, cells were stimulated by IgE receptor crosslinking, C5a or formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP). Histamine and sulphidoleukotriene release was measured in supernatants. The sequential stimulation of the cells with c-kit ligand and IgE receptor crosslinking induced the release of high amounts of histamine and leukotrienes, whereas each agonist by itself induced only marginal mediator release. Interleukin 3 induced no release by itself, but enhanced the IgE receptor dependent release, possibly by an indirect mechanism. No significant mediator release was seen in response to C5a and fMLP, even if the cells were pretreated with c-kit ligand. The mediator release, particularly that of leukotrienes, was higher in cells isolated from actively inflamed tissue from patients with inflammatory bowel disease compared with controls. In conclusion, it was found that, apart from IgE receptor crosslinking, c-kit ligand and interleukin 3 regulate mediator release in human intestinal mast cells. The enhancement of mediator release by cytokines may be of particular relevance in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases and food intolerance reactions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum C. A., Bhatia P., Miner P. B., Jr Increased colonic mucosal mast cells associated with severe watery diarrhea and microscopic colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1989 Sep;34(9):1462–1465. doi: 10.1007/BF01538086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff S. C., Brunner T., De Weck A. L., Dahinden C. A. Interleukin 5 modifies histamine release and leukotriene generation by human basophils in response to diverse agonists. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1577–1582. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff S. C., Dahinden C. A. Effect of nerve growth factor on the release of inflammatory mediators by mature human basophils. Blood. 1992 May 15;79(10):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff S. C., Dahinden C. A. c-kit ligand: a unique potentiator of mediator release by human lung mast cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):237–244. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradding P., Feather I. H., Howarth P. H., Mueller R., Roberts J. A., Britten K., Bews J. P., Hunt T. C., Okayama Y., Heusser C. H. Interleukin 4 is localized to and released by human mast cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Nov 1;176(5):1381–1386. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.5.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broudy V. C., Kovach N. L., Bennett L. G., Lin N., Jacobsen F. W., Kidd P. G. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells display high-affinity c-kit receptors and produce a soluble form of the c-kit receptor. Blood. 1994 Apr 15;83(8):2145–2152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherner J. A., Jensen R. T., Dubois A., O'Dorisio T. M., Gardner J. D., Metcalfe D. D. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in systemic mastocytosis. A prospective study. Gastroenterology. 1988 Sep;95(3):657–667. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(88)80012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Columbo M., Horowitz E. M., Botana L. M., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Bochner B. S., Gillis S., Zsebo K. M., Galli S. J., Lichtenstein L. M. The human recombinant c-kit receptor ligand, rhSCF, induces mediator release from human cutaneous mast cells and enhances IgE-dependent mediator release from both skin mast cells and peripheral blood basophils. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):599–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe S. E., Perdue M. H. Gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity: basic mechanisms of pathophysiology. Gastroenterology. 1992 Sep;103(3):1075–1095. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weck A. L., Dahinden C. A., Bischoff S. The multiple role of cytokines in IgE-mediated allergic reactions. Behring Inst Mitt. 1992 Apr;(91):100–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Else K. J., Finkelman F. D., Maliszewski C. R., Grencis R. K. Cytokine-mediated regulation of chronic intestinal helminth infection. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):347–351. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. C., Lazenby A. J., Moore W. C., Yardley J. H., Bayless T. M., Lichtenstein L. M. Enhancement of human intestinal mast cell mediator release in active ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jul;99(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91238-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. C., Lichtenstein L. M., Roche J. K. Intestinal mast cell responses in idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Histamine release from human intestinal mast cells in response to gut epithelial proteins. Dig Dis Sci. 1993 Jun;38(6):1105–1112. doi: 10.1007/BF01295728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto K., Imamura I., Granger D. N., Wada H., Sakata T., Tso P. Histamine and histidine decarboxylase are correlated with mucosal repair in rat small intestine after ischemia-reperfusion. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):126–133. doi: 10.1172/JCI115552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J. New concepts about the mast cell. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jan 28;328(4):257–265. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199301283280408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Zsebo K. M., Geissler E. N. The kit ligand, stem cell factor. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:1–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich M. C., Dooley D. C., Freed A. C., Band L., Hoatlin M. E., Keeble W. W., Peters S. T., Silvey K. V., Ey F. S., Kabat D. Constitutive expression of steel factor gene by human stromal cells. Blood. 1993 Aug 1;82(3):771–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Kyo S., Fujita M., Enomoto T., Kondoh G. Coexpression of the c-kit receptor and the stem cell factor in gynecological tumors. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 1;54(11):3049–3053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson L., Ahrenstedt O., Odlind B., Hällgren R. The jejunal secretion of histamine is increased in active Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1990 Apr;98(4):849–854. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90006-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurimoto Y., De Weck A. L., Dahinden C. A. The effect of interleukin 3 upon IgE-dependent and IgE-independent basophil degranulation and leukotriene generation. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):361–368. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley K. E., Bennett L. G., Wypych J., Yancik S. A., Liu X. D., Westcott K. R., Chang D. G., Smith K. A., Zsebo K. M. Soluble stem cell factor in human serum. Blood. 1993 Feb 1;81(3):656–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence I. D., Warner J. A., Cohan V. L., Hubbard W. C., Kagey-Sobotka A., Lichtenstein L. M. Purification and characterization of human skin mast cells. Evidence for human mast cell heterogeneity. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3062–3069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W. L., Bosman L., Boulos P. B., Lau H. Y., Pearce F. L. Mast cells from human colonic mucosa and submucosa/muscle: a comparison with human lung mast cells. Agents Actions. 1990 Apr;30(1-2):70–73. doi: 10.1007/BF01969001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longley B. J., Jr, Morganroth G. S., Tyrrell L., Ding T. G., Anderson D. M., Williams D. E., Halaban R. Altered metabolism of mast-cell growth factor (c-kit ligand) in cutaneous mastocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 6;328(18):1302–1307. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305063281803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowman M. A., Rees P. H., Benyon R. C., Church M. K. Human mast cell heterogeneity: histamine release from mast cells dispersed from skin, lung, adenoids, tonsils, and colon in response to IgE-dependent and nonimmunologic stimuli. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988 Mar;81(3):590–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N., Hinde J. Inflammatory component of celiac sprue mucosa. I. Mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):92–101. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90749-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matos M. E., Schnier G. S., Beecher M. S., Ashman L. K., William D. E., Caligiuri M. A. Expression of a functional c-kit receptor on a subset of natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):1079–1084. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda R., Takahashi T., Nakamura S., Sekido Y., Nishida K., Seto M., Seito T., Sugiura T., Ariyoshi Y., Takahashi T. Expression of the c-kit protein in human solid tumors and in corresponding fetal and adult normal tissues. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):339–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazlam M. Z., Hodgson H. J. Why measure C reactive protein? Gut. 1994 Jan;35(1):5–7. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe D. D. Mast cell mediators with emphasis on intestinal mast cells. Ann Allergy. 1984 Dec;53(6 Pt 2):563–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson H. A., Mendelson L., Rosen J. P. Fatal and near-fatal anaphylactic reactions to food in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med. 1992 Aug 6;327(6):380–384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199208063270603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson I. R., Leung K. B., Pearce F. L., Walker-Smith J. A. Lamina propria mast cells in biopsies from children with Crohn's disease. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Mar;39(3):279–283. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman E. S., Post T. J., Henson P. M., Giclas P. C. Differential effects of the complement peptides, C5a and C5a des Arg on human basophil and lung mast cell histamine release. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):918–923. doi: 10.1172/JCI113403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selbekk B. H. A comparison between in vitro jejunal mast cell degranulation and intragastric challenge in patients with suspected food intolerance. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Apr;20(3):299–303. doi: 10.3109/00365528509091654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillaber C., Strobl H., Bevec D., Ashman L. K., Butterfield J. H., Lechner K., Maurer D., Bettelheim P., Valent P. IL-4 regulates c-kit proto-oncogene product expression in human mast and myeloid progenitor cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4224–4228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Austen K. F. Recent advances in the cellular and molecular biology of mast cells. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyota M., Hinoda Y., Itoh F., Takaoka A., Imai K., Yachi A. Complementary DNA cloning and characterization of truncated form of c-kit in human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1994 Jan 1;54(1):272–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuura Y., Hiraki H., Watanabe K., Igarashi S., Shimamura K., Fukuda T., Suzuki T., Seito T. Preferential localization of c-kit product in tissue mast cells, basal cells of skin, epithelial cells of breast, small cell lung carcinoma and seminoma/dysgerminoma in human: immunohistochemical study on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Virchows Arch. 1994;424(2):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00193492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent P., Besemer J., Sillaber C., Butterfield J. H., Eher R., Majdic O., Kishi K., Klepetko W., Eckersberger F., Lechner K. Failure to detect IL-3-binding sites on human mast cells. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3432–3437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent P., Majdic O., Maurer D., Bodger M., Muhm M., Bettelheim P. Further characterization of surface membrane structures expressed on human basophils and mast cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;91(2):198–203. doi: 10.1159/000235115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


