Abstract
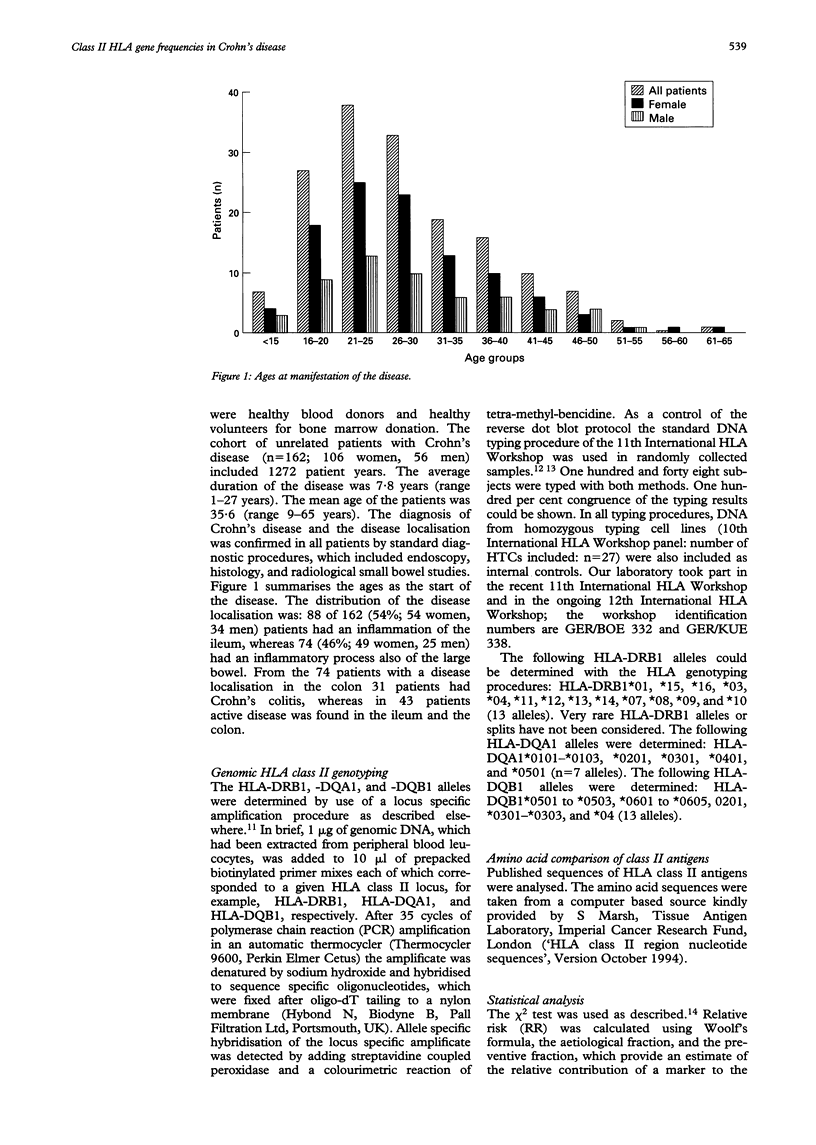
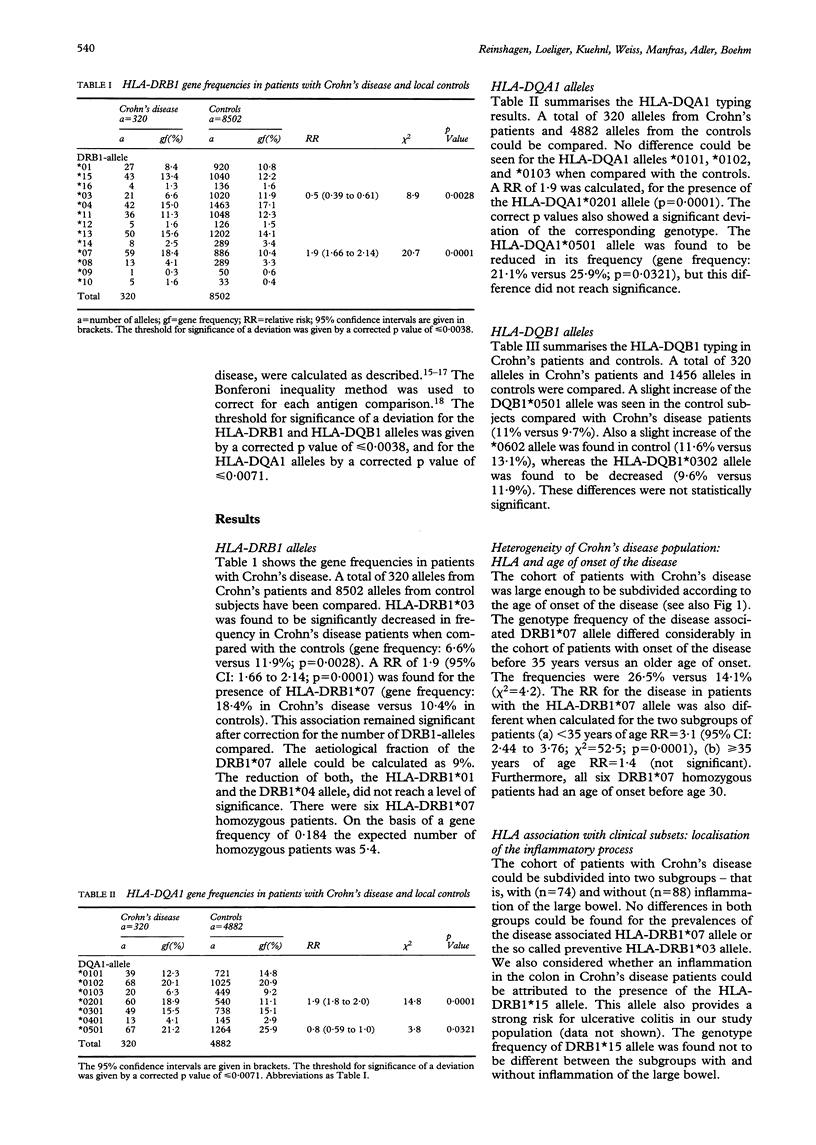
BACKGROUND--Ulcerative colitis is the only known inflammatory bowel disease associated with particular HLA alleles. Whereas the association with the HLA-DRB1*15 allele has been described in several independent studies for ulcerative colitis, no contribution of HLA alleles to susceptibility in Crohn's disease has yet been shown. AIM--This study was designed to study the strength of association of HLA class II alleles as risk markers for Crohn's disease in a homogenous population in Germany. PATIENTS--A total of 4251 randomly selected control subjects, and 162 unrelated subjects with Crohn's disease were studied. Subjects were studied for their HLA-DRB1, HLA-DQA1, and HLA-DQB1 alleles. METHOD--HLA DNA typing was performed after locus specific amplification with the polymerase chain reaction and reverse dot blot hybridisation. RESULTS--The HLA-DRB1*07 was the only HLA class II allele found to be significantly associated with Crohn's disease (relative risk (RR) = 1.9, 95% CI: 1.66 to 2.14; p = 0.0001). This association remained significant after correction for the number of DRB1 alleles compared. In patients with disease onset before 35 years the RR for the disease in HLA-DRB1*07 positive subjects was found to be higher (RR = 3.1, 95% CI: 2.44 to 3.76). The HLA-DRB1*03 was significantly decreased in frequency in Crohn's disease (RR = 0.5, 95% CI: 0.39 to 0.61; p = 0.0028). CONCLUSION--The HLA-DRB1*07 allele provides risk for the disease especially in patients with younger ages of onset. These data also provide indirect evidence for an immunogenetically based heterogeneity of the disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACHESON E. D. An association between ulcerative colitis, regional enteritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. Q J Med. 1960 Oct;29:489–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achord J. L., Gunn C. H., Jr, Jackson J. F. Regional enteritis and HLA concordance in multiple siblings. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Apr;27(4):330–332. doi: 10.1007/BF01296752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruso C., Oliva L., Palmeri P., Cottone M. B cell alloantigens in Sicilian patients with Crohn's disease. Tissue Antigens. 1983 Feb;21(2):170–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1983.tb00387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicz R. M., Urban R. G., Gorga J. C., Vignali D. A., Lane W. S., Strominger J. L. Specificity and promiscuity among naturally processed peptides bound to HLA-DR alleles. J Exp Med. 1993 Jul 1;178(1):27–47. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport M. P., Quinn C. L., Chicz R. M., Green B. N., Willis A. C., Lane W. S., Bell J. I., Hill A. V. Naturally processed peptides from two disease-resistance-associated HLA-DR13 alleles show related sequence motifs and the effects of the dimorphism at position 86 of the HLA-DR beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6567–6571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich H., Bugawan T., Begovich A. B., Scharf S., Griffith R., Saiki R., Higuchi R., Walsh P. S. HLA-DR, DQ and DP typing using PCR amplification and immobilized probes. Eur J Immunogenet. 1991 Feb-Apr;18(1-2):33–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1991.tb00005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. The epidemiologic approach to studies of association between HLA and disease. I. The basic measures, concepts and estimation procedures. Tissue Antigens. 1982 Apr;19(4):245–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1982.tb01449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. The epidemiologic approach to studies of association between HLA and disease. II. Estimation of absolute risks, etiologic and preventive fraction. Tissue Antigens. 1982 Apr;19(4):259–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1982.tb01450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALDANE J. B. The estimation and significance of the logarithm of a ratio of frequencies. Ann Hum Genet. 1956 May;20(4):309–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibbotson J. P., Lowes J. R. Potential role of superantigen induced activation of cell mediated immune mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1995 Jan;36(1):1–4. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühnl P., Sibrowski W., Böhm B. O., Bender S. W., Kalmar G., Löliger C. HLA antigen frequencies in familial Crohn's disease (CD). Beitr Infusionsther. 1990;26:283–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A. S., Biemond I., Kuiper G., Weterman I. T., van Leeuwen A., Schreuder I., van Rood J. J. HLA antigen distribution and HLA haplotype segregation in Crohn's disease. Tissue Antigens. 1980 Jul;16(1):56–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1980.tb00287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rammensee H. G., Friede T., Stevanoviíc S. MHC ligands and peptide motifs: first listing. Immunogenetics. 1995;41(4):178–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00172063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrumpf E., Fausa O., Førre O., Dobloug J. H., Ritland S., Thorsby E. HLA antigens and immunoregulatory T cells in ulcerative colitis associated with hepatobiliary disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1982 Mar;17(2):187–191. doi: 10.3109/00365528209182038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. E., Siegelbaum S. P., Fazio T. L., Hubbell C., Henry J. B. Regional enteritis: evidence for genetic transmission by HLA typing. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Sep;93(3):424–427. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-3-424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. S., Gangl A., Polterauer P., Menzel E. J., Mayr W. R. HLA antigens in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jan;82(1):34–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern L. J., Wiley D. C. Antigenic peptide binding by class I and class II histocompatibility proteins. Structure. 1994 Apr 15;2(4):245–251. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Wang S. J., Yang H. Y., Redford A., Magalong D., Tyan D., McElree C. K., Pressman S. R., Shanahan F., Targan S. R. Distinct associations of HLA class II genes with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1993 Mar;104(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


