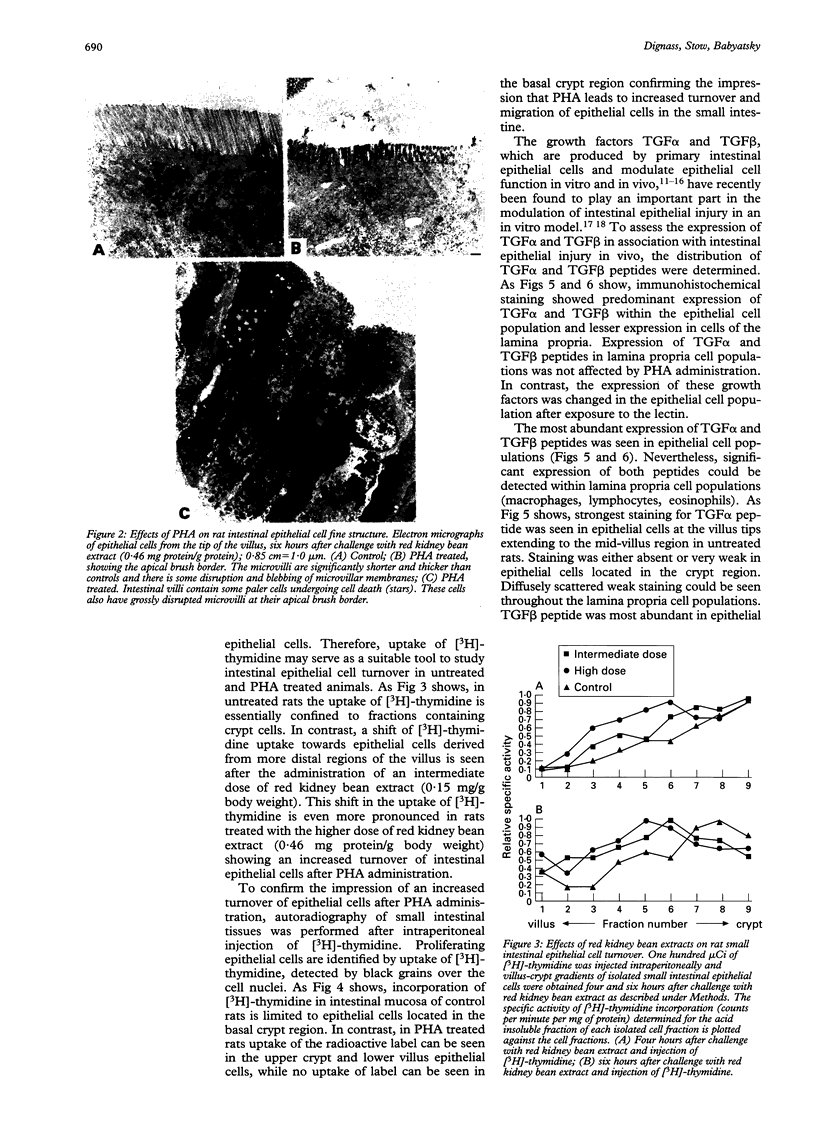
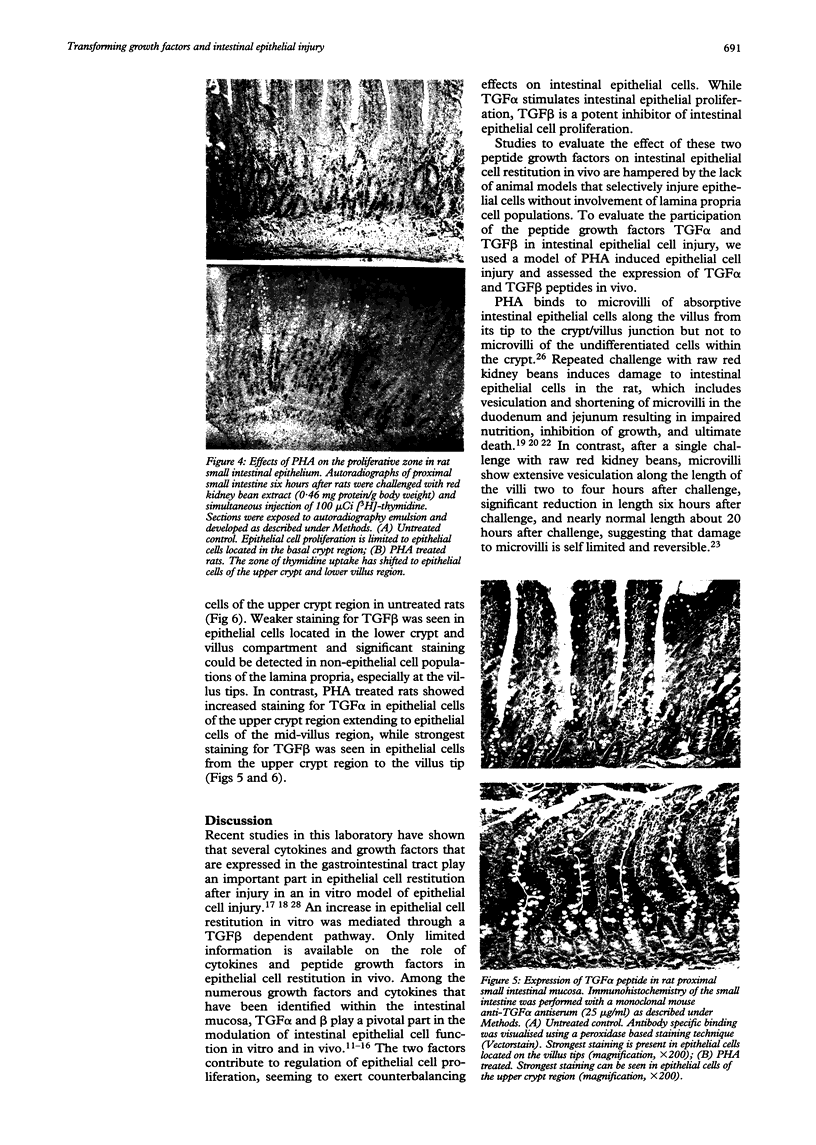
Abstract
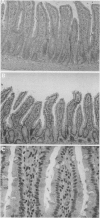
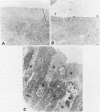
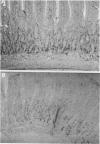
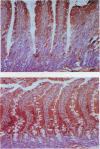
BACKGROUND--Previous studies have shown the importance of transforming growth factors alpha and beta (TGF alpha and TGF beta) in modulating epithelial cell restitution after injury in vitro. AIM--To investigate the role of the growth factors TGF alpha and TGF beta after acute epithelial injury in vivo. METHODS--An in vivo model of phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) induced acute epithelial injury in rat small intestine was used. Epithelial cell turnover was assessed by autoradiography and liquid scintillation counting of thymidine uptake. Expression of TGF alpha and TGF beta was assessed by immunohistochemistry. RESULTS--An expansion of the proliferative compartment and increased turnover of intestinal epithelial cells was seen in rats with PHA induced intestinal epithelial injury. Expression of TGF alpha and TGF beta peptides was shown in both the epithelial cell and lamina propria compartment. Different patterns of TGF alpha and TGF beta expression were seen, however, within the epithelium of rats with acute intestinal injury compared with untreated controls, while the expression of these peptides within the lamina propria was not changed. CONCLUSIONS--These findings suggest that acute intestinal epithelial cell injury in vivo is associated with compensatory changes in expression of TGF alpha and TGF beta in the epithelial cell compartment, while the lamina propria does not seem to be significantly affected.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banwell J. G., Boldt D. H., Meyers J., Weber F. L., Jr Phytohemagglutinin derived from red kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): a cause for intestinal malabsorption associated with bacterial overgrowth in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1983 Mar;84(3):506–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard J. A., Beauchamp R. D., Coffey R. J., Moses H. L. Regulation of intestinal epithelial cell growth by transforming growth factor type beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1578–1582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard J. A., Polk W. H., Moses H. L., Coffey R. J. Production of transforming growth factor-alpha by normal rat small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):C994–1000. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.6.C994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciacci C., Lind S. E., Podolsky D. K. Transforming growth factor beta regulation of migration in wounded rat intestinal epithelial monolayers. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jul;105(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignass A. U., Podolsky D. K. Cytokine modulation of intestinal epithelial cell restitution: central role of transforming growth factor beta. Gastroenterology. 1993 Nov;105(5):1323–1332. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90136-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignass A. U., Tsunekawa S., Podolsky D. K. Fibroblast growth factors modulate intestinal epithelial cell growth and migration. Gastroenterology. 1994 May;106(5):1254–1262. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feil W., Wenzl E., Vattay P., Starlinger M., Sogukoglu T., Schiessel R. Repair of rabbit duodenal mucosa after acid injury in vivo and in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jun;92(6):1973–1986. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90632-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kik M. J., Koninkx J. F., van den Muysenberg A., Hendriksen F. Pathological effects of Phaseolus vulgaris isolectins on pig jejunal mucosa in organ culture. Gut. 1991 Aug;32(8):886–892. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.8.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Pusztai A., Clarke E. M. Immunocytochemical localization of ingested kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) lectins in rat gut. Histochem J. 1980 Mar;12(2):201–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01024550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Pusztai A., Clarke E. M. Kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) lectin-induced lesions in rat small intestine. 3. Ultrastructural studies. J Comp Pathol. 1982 Jul;92(3):357–373. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(82)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Pusztai A., Clarke E. M. Kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) lectin-induced lesions in the small intestine: 1. Light microscope studies. J Comp Pathol. 1980 Oct;90(4):585–595. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(80)90107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Pusztai A., Grant G., Slater D. Immunogold localization of ingested kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) lectins in epithelial cells of the rat small intestine. Histochem J. 1986 Aug;18(8):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF01675333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koninkx J. F., Hendriks H. G., van Rossum J. M., van den Ingh T. S., Mouwen J. M. Interaction of legume lectins with the cellular metabolism of differentiated Caco-2 cells. Gastroenterology. 1992 May;102(5):1516–1523. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91709-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokowa M., Lynch K., Podolsky D. K. Effects of growth factors on an intestinal epithelial cell line: transforming growth factor beta inhibits proliferation and stimulates differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):775–782. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91481-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPKIN M., SHERLOCK P., BELL B. CELL PROLIFERATION KINETICS IN THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT OF MAN. II. CELL RENEWAL IN STOMACH, ILEUM, COLON, AND RECTUM. Gastroenterology. 1963 Dec;45:721–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt R. D., Felsted R. L., Bachur N. R. Biological and biochemical properties of Phaseolus vulgaris isolectins. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2961–2966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzsonn V., Olsen W. A. In vivo responses of rat intestinal epithelium to intraluminal dietary lectins. Gastroenterology. 1982 May;82(5 Pt 1):838–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Carlson S., Madara J. L. Rapid barrier restitution in an in vitro model of intestinal epithelial injury. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):237–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. P., Wallace J. L. The roles of ethanol and of acid in the production of gastric mucosal erosions in rats. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;38(1):23–38. doi: 10.1007/BF02892800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusrat A., Delp C., Madara J. L. Intestinal epithelial restitution. Characterization of a cell culture model and mapping of cytoskeletal elements in migrating cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1501–1511. doi: 10.1172/JCI115741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potten C. S., Kellett M., Roberts S. A., Rew D. A., Wilson G. D. Measurement of in vivo proliferation in human colorectal mucosa using bromodeoxyuridine. Gut. 1992 Jan;33(1):71–78. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi M. A., Mancini Filho J., Lajolo F. M. Jejunal ultrastructural changes induced by kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) lectins in rats. Br J Exp Pathol. 1984 Feb;65(1):117–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutten M. J., Ito S. Morphology and electrophysiology of guinea pig gastric mucosal repair in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):G171–G182. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.2.G171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjölander A., Magnusson K. E., Latkovic S. Morphological changes of rat small intestine after short-time exposure to concanavalin A or wheat germ agglutinin. Cell Struct Funct. 1986 Sep;11(3):285–293. doi: 10.1247/csf.11.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. M., Nasim M. M., Gullick W. J., Alison M. R. Immunoreactivity of transforming growth factor alpha in the normal adult gastrointestinal tract. Gut. 1992 May;33(5):628–631. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.5.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller D. A., Thomas N. W., Self T. J. Epithelial restitution in the large intestine of the rat following insult with bile salts. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1988;414(1):77–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00749741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman M. D., Allan C. H., Trier J. S., Hagen S. J. Repair of microvilli in the rat small intestine after damage with lectins contained in the red kidney bean. Gastroenterology. 1989 Nov;97(5):1193–1204. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Intestinal epithelial cell surface membrane glycoprotein synthesis. I. An indicator of cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui W., Ji Z. Q., Kuniyasu H., Ayhan A., Yokozaki H., Ito H., Tahara E. Expression of transforming growth factor alpha in human tissues: immunohistochemical study and northern blot analysis. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1992;421(6):513–519. doi: 10.1007/BF01606881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]