Abstract
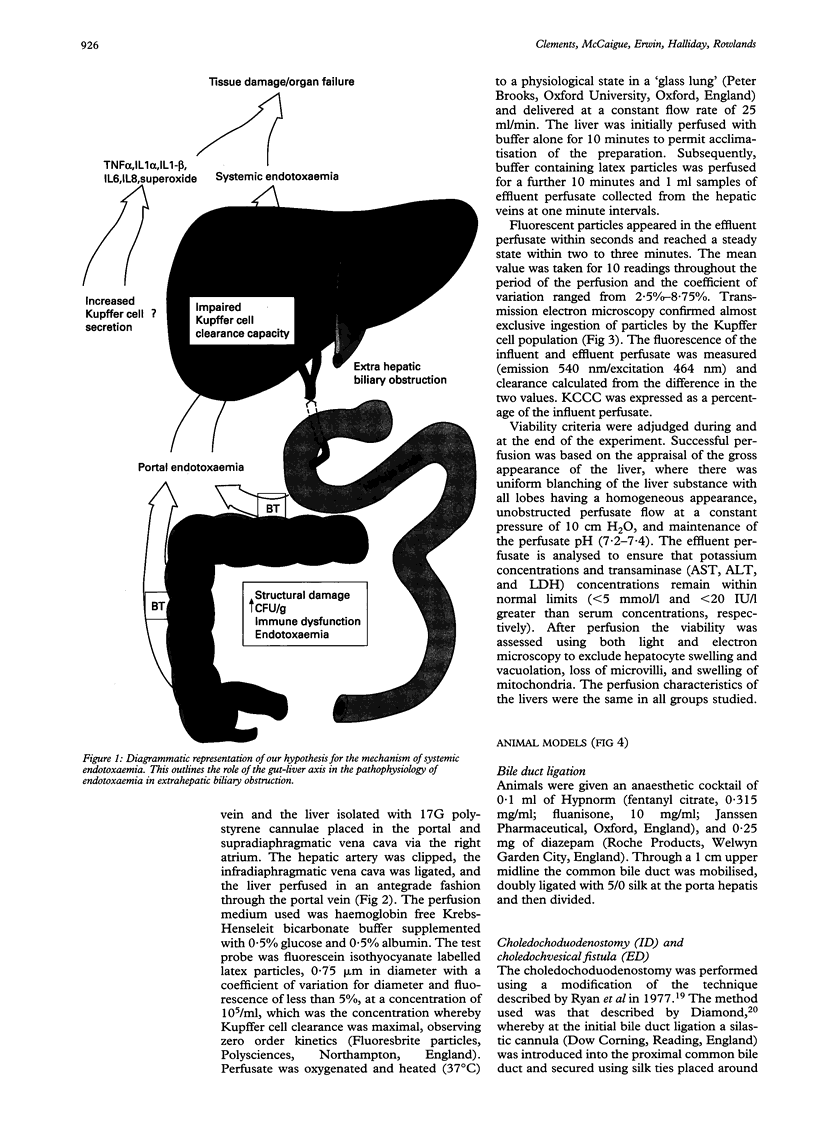
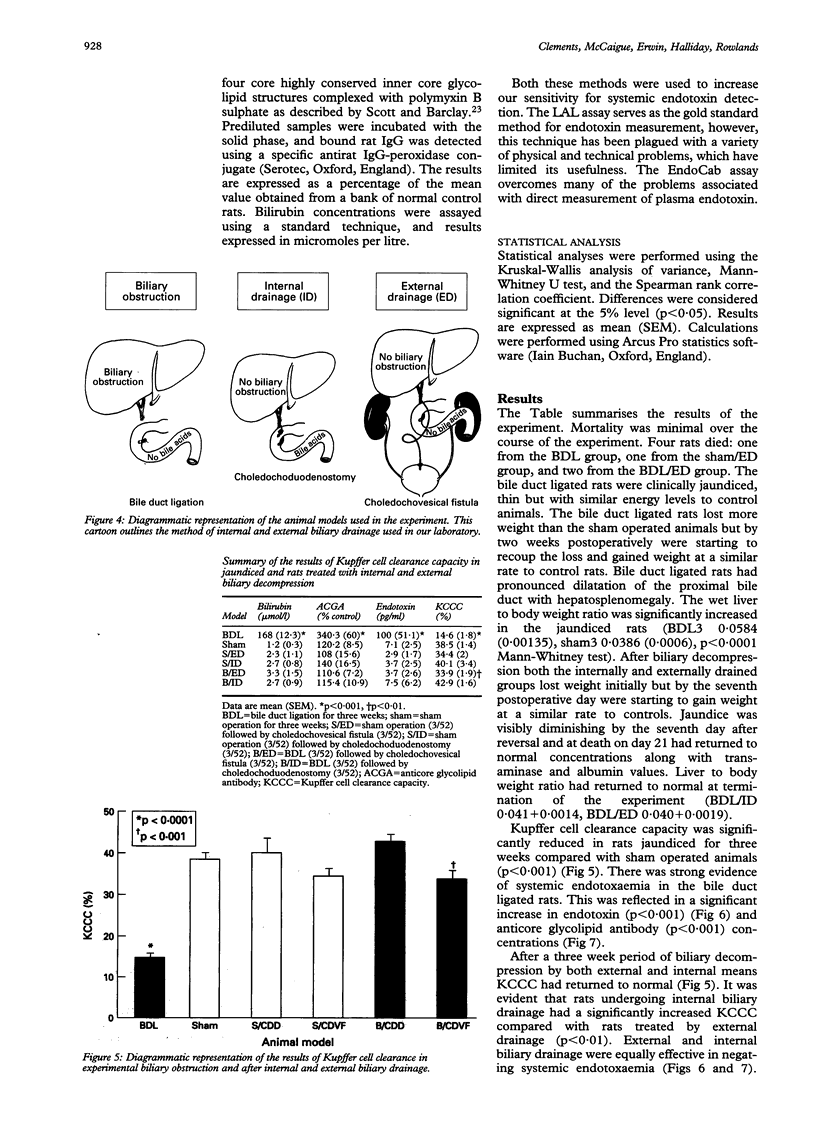
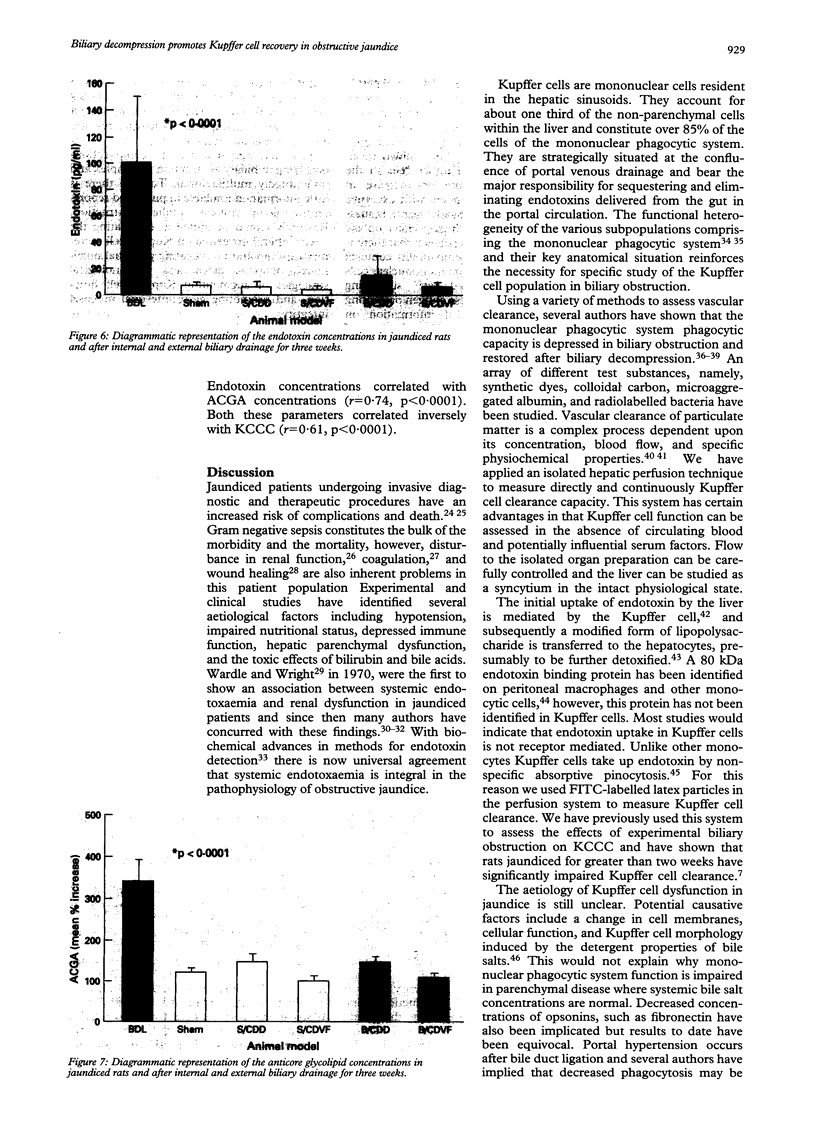
BACKGROUND: Jaundiced patients undergoing surgical procedures have an increased risk of Gram negative sepsis with potential morbidity and mortality. Depressed Kupffer cell clearance capacity (KCCC) predisposes jaundiced patients to endotoxaemia and its sequelae. Biliary decompression remains the main therapeutic strategy in obstructive jaundice. AIMS: This study investigates the efficacy of internal (ID) and external biliary drainage (ED) on KCCC in an experimental model of extrahepatic biliary obstruction. METHODS: Adult male Wistar rats (250-300 g) were assigned to one of six groups: sham operated, where the bile duct was mobilised but not divided; bile duct ligation (BDL) for three weeks, and sham operated or BDL for three weeks followed by a second laparotomy and further 21 days of ID or ED, by way of choledochoduodenostomy or choledochovesical fistula respectively. KCCC was measured using an isolated hepatic perfusion technique with FITC labelled latex particles (0.75 mu) as the test probe. Plasma was assayed for bilirubin, endotoxin, and anticore glycolipid antibody (ACGA) concentrations. RESULTS: Jaundiced rats had reduced KCCC (p < 0.001), increased concentrations of ACGA (p < 0.001), and endotoxin (p < 0.001) compared with controls. Biliary drainage for three weeks produced a recovery in KCCC and normalisation of endotoxin and ACGA concentrations, however, external drainage was less effective than ID (p < 0.01). CONCLUSIONS: These data support the hypothesis that endotoxaemia and its mediated effects are integral in the pathophysiology of jaundice. Furthermore, a short period of internal biliary drainage is a useful therapeutic strategy in restoring Kupffer cell function and negating systemic endotoxaemia and consequent complications in biliary obstruction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. P., Dixon J. M., Taylor T. V., Davies G. C. Surgical experience of deeply jaundiced patients with bile duct obstruction. Br J Surg. 1984 Mar;71(3):234–238. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakkevold K. E., Kambestad B. Morbidity and mortality after radical and palliative pancreatic cancer surgery. Risk factors influencing the short-term results. Ann Surg. 1993 Apr;217(4):356–368. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199304000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blamey S. L., Fearon K. C., Gilmour W. H., Osborne D. H., Carter D. C. Prediction of risk in biliary surgery. Br J Surg. 1983 Sep;70(9):535–538. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800700910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boender J., Nix G. A., de Ridder M. A., Dees J., Schütte H. E., van Buuren H. R., van Blankenstein M. Endoscopic sphincterotomy and biliary drainage in patients with cholangitis due to common bile duct stones. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995 Feb;90(2):233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradfield J. W. Control of spillover. The importance of Kupffer-cell function in clinical medicine. Lancet. 1974 Oct 12;2(7885):883–886. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Stone D. E., Beaman J., Gracey M. Effects of biliary diversion on intestinal microflora in the rat. J Med Microbiol. 1977 May;10(2):241–244. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-2-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursuker I., Goldman R. On the origin of macrophage heterogeneity: a hypothesis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Mar;33(3):207–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements B. W., Halliday I. M., Rowlands B. J. Measuring Kupffer cell clearance capacity (KCCC) using an isolated hepatic perfusion technique. Biochem Soc Trans. 1994 Feb;22(1):24S–24S. doi: 10.1042/bst022024s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements W. D., Halliday M. I., McCaigue M. D., Barclay R. G., Rowlands B. J. Effects of extrahepatic obstructive jaundice on Kupffer cell clearance capacity. Arch Surg. 1993 Feb;128(2):200–205. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1993.01420140077012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A. Infection in the compromised host. Surg Clin North Am. 1988 Feb;68(1):181–197. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)44439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A., Sittig K., Li M., Berg R., Specian R. D. Obstructive jaundice promotes bacterial translocation from the gut. Am J Surg. 1990 Jan;159(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)80610-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Dolan S., Rowlands B. J. An improved technique for choledochoduodenostomy in a rat model of obstructive jaundice. Lab Anim Sci. 1991 Jan;41(1):82–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Dolan S., Thompson R. L., Rowlands B. J. Development and reversal of endotoxemia and endotoxin-related death in obstructive jaundice. Surgery. 1990 Aug;108(2):370–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Rowlands B. J. Endotoxaemia in obstructive jaundice. HPB Surg. 1991 Jun;4(2):81–94. doi: 10.1155/1991/48672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding J. W., Andersson R., Stenram U., Lunderquist A., Bengmark S. Effect of biliary decompression on reticuloendothelial function in jaundiced rats. Br J Surg. 1992 Jul;79(7):648–652. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800790718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foutch P. G. A prospective assessment of results for needle-knife papillotomy and standard endoscopic sphincterotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995 Jan;41(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(95)70272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. S., Thomas P., Broitman S. A. Hepatic mechanisms for clearance and detoxification of bacterial endotoxins. J Nutr Biochem. 1990 Dec;1(12):620–628. doi: 10.1016/0955-2863(90)90020-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grande L., Garcia-Valdecasas J. C., Fuster J., Visa J., Pera C. Obstructive jaundice and wound healing. Br J Surg. 1990 Apr;77(4):440–442. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800770426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. W., Gouma D. J., Buurman W. A. Complications in obstructive jaundice: role of endotoxins. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1992;194:8–12. doi: 10.3109/00365529209096019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. W., Gouma D. J., Soeters P. B., Buurman W. A. Suppression of cellular immunity in obstructive jaundice is caused by endotoxins: a study with germ-free rats. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):478–485. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90841-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafström L., Holmberg S. B. Vascular clearance of particulate substances: function of the reticuloendothelial system or measurement of liver blood flow? Invited commentary. Eur J Surg. 1992 Mar;158(3):165–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems R., Ross B. D., Berry M. N., Krebs H. A. Gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):284–292. doi: 10.1042/bj1010284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman J. M., Jr, Rikkers L. F., Moody F. G. Sepsis in the management of complicated biliary disorders. Am J Surg. 1979 Dec;138(6):809–813. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. R., Allison M. E., Prentice C. R., Blumgart L. H. Endotoxemia, disturbance of coagulation, and obstructive jaundice. Am J Surg. 1982 Sep;144(3):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(82)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S., Yang R., Rodefeld M. J., Folkening W. J., Grosfeld J. L. Impaired hepatic bacterial clearance is reversed by surgical relief of obstructive jaundice. J Pediatr Surg. 1991 Apr;26(4):401–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(91)90986-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Chu K. M., Lo C. Y., Mok F. P., Fan S. T., Lo C. M., Wong J. Surgery for malignant obstructive jaundice: analysis of mortality. Surgery. 1992 Nov;112(5):891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillemoe K. D., Sauter P. K., Pitt H. A., Yeo C. J., Cameron J. L. Current status of surgical palliation of periampullary carcinoma. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1993 Jan;176(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Ulevitch R. J. The clearance, tissue distribution, and cellular localization of intravenously injected lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2133–2143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megison S. M., Dunn C. W., Horton J. W., Chao H. Effects of relief of biliary obstruction on mononuclear phagocyte system function and cell mediated immunity. Br J Surg. 1991 May;78(5):568–571. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann S. J. Kinetics of phagocytosis. II. Analysis of in vivo clearance with demonstration of competitive inhibition between similar and dissimilar foreign particles. Lab Invest. 1974 Aug;31(2):161–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson E. G. The effect of biliary obstruction on the distribution of the hepatic blood flow and reticuloendothelial system in dogs. Acta Chir Scand. 1972;138(2):159–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain J. A., Cahill C. J., Bailey M. E. Perioperative complications in obstructive jaundice: therapeutic considerations. Br J Surg. 1985 Dec;72(12):942–945. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800721203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain J. A. Reticulo-endothelial function in obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg. 1987 Dec;74(12):1091–1094. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800741207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt H. A., Cameron J. L., Postier R. G., Gadacz T. R. Factors affecting mortality in biliary tract surgery. Am J Surg. 1981 Jan;141(1):66–72. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughneen P. T., Gouma D. J., Kulkarni A. D., Fanslow W. F., Rowlands B. J. Impaired specific cell-mediated immunity in experimental biliary obstruction and its reversibility by internal biliary drainage. J Surg Res. 1986 Aug;41(2):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(86)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. J., Than T., Blumgart L. H. Choledochoduodenostomy in the rat with obstructive jaundice. J Surg Res. 1977 Nov;23(5):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(77)90069-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Conner C. E., Grogan J. B. The pathophysiology of biliary obstruction and its effect on phagocytic and immune function. J Surg Res. 1994 Aug;57(2):316–336. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1994.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. B., Barclay G. R. Endotoxin-polymyxin complexes in an improved enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for IgG antibodies in blood donor sera to gram-negative endotoxin core glycolipids. Vox Sang. 1987;52(4):272–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1987.tb04893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikora S. S., Kapoor R., Pradeep R., Kapoor V. K., Saxena R., Kaushik S. P. Palliative surgical treatment of malignant obstructive jaundice. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1994 Oct;20(5):580–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. H., P'eng F. K., Lui W. Y. Factors affecting morbidity and mortality in biliary tract surgery. World J Surg. 1992 May-Jun;16(3):536–540. doi: 10.1007/BF02104465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiguchi S., Koga A. Effects of bile acids and endotoxin on the function and morphology of cultured hamster Kupffer cells. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1988;54(5):303–311. doi: 10.1007/BF02899227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. L., Hoper M., Diamond T., Rowlands B. J. Development and reversibility of T lymphocyte dysfunction in experimental obstructive jaundice. Br J Surg. 1990 Nov;77(11):1229–1232. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800771112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth C. A., Thomas P. Liver endocytosis and Kupffer cells. Hepatology. 1992 Jul;16(1):255–266. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wait R. B., Kahng K. U. Renal failure complicating obstructive jaundice. Am J Surg. 1989 Feb;157(2):256–263. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(89)90540-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N., Wright N. A. Endotoxin and acute renal failure associated with obstructive jaundice. Br Med J. 1970 Nov 21;4(5733):472–474. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5733.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch R. P., van der Schelling G. P., Klinkenbijl J. H., Mulder P. G., van Blankenstein M., Jeekel J. Guidelines for the application of surgery and endoprostheses in the palliation of obstructive jaundice in advanced cancer of the pancreas. Ann Surg. 1994 Jan;219(1):18–24. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199401000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



