Abstract
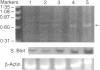
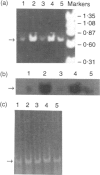
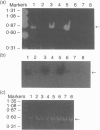
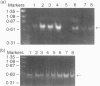
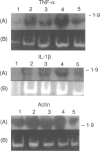
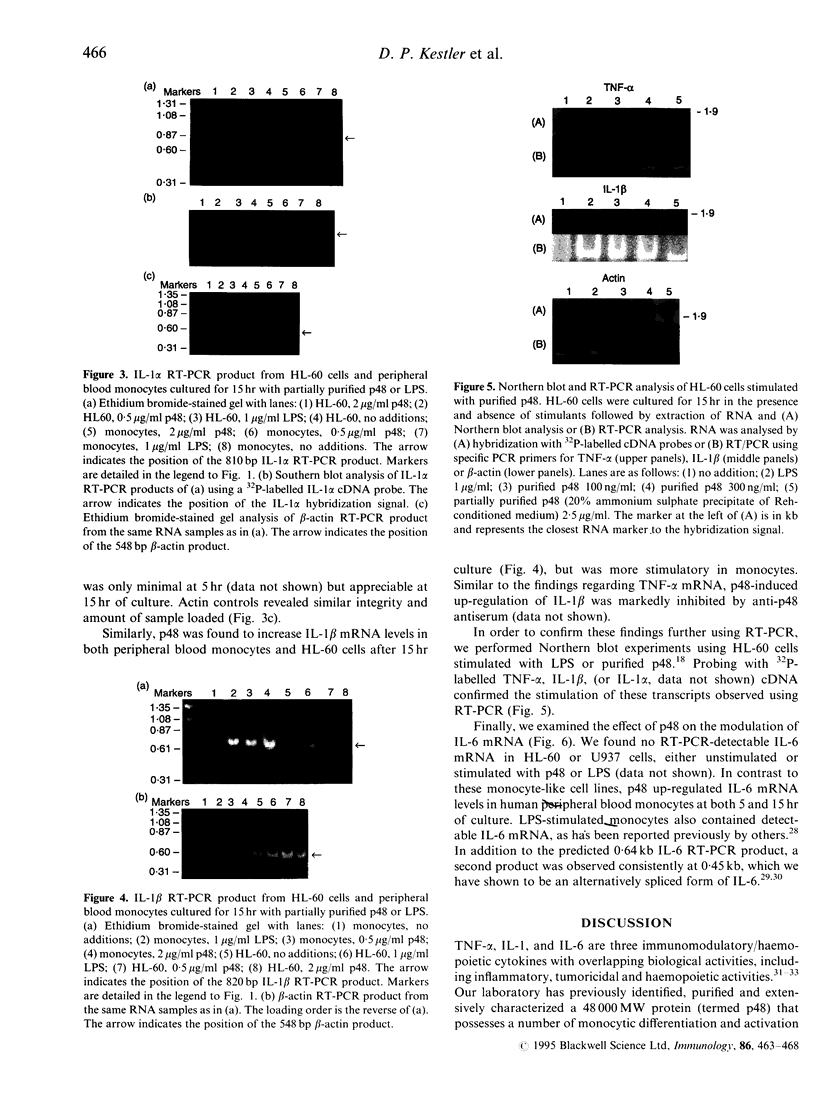
Polypeptide 48 is a 48,000 MW protein, originally isolated from conditioned media of some human leukaemic cell lines, that induces differentiation and cytolytic activity in HL-60 promyelocytic leukaemia cells and activates human peripheral blood monocytes to secrete interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). In the present study we examined the effects of p48 on the accumulation of a series of monokine transcripts, including TNF-alpha, IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta and IL-6, in human peripheral blood monocytes and the myeloid/monocyte cell lines HL-60 and U937. Using reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Northern blot analysis, p48 was found to induce accumulation of TNF-alpha, IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta mRNA in peripheral blood monocytes, HL-60 and U937 cells. IL-6 mRNA was found to be increased in p48-stimulated peripheral blood monocytes but not HL-60 or U937. Thus, the secretion of IL-1 and TNF-alpha by p48-stimulated monocytic cells was associated with up-regulation of cytokine mRNA, suggesting that p48 leads to increased transcription or mRNA stability in these cells. As U937 and HL-60 are likely to represent premonocyte stages of haemopoietic differentiation, it is possible that the effect of p48 on IL-6 mRNA, in contrast to its effect on TNF and IL-1, requires cells to be at a later differentiation step.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:1–78. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachwich P. R., Chensue S. W., Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates interleukin-1 and prostaglandin E2 production in resting macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):94–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90881-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beezhold D. H., Leftwich J. A., Hall R. E. P48 induces tumor necrosis factor and IL-1 secretion by human monocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3217–3221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan C., Nathan C. Modulation of macrophage function by transforming growth factor beta, interleukin-4, and interleukin-10. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 23;685:713–739. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb35934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C. A., Tam A. W., Nelson P. A., Engleman E. G., Suzuki N., Fry K. E., Larrick J. W. Message amplification phenotyping (MAPPing): a technique to simultaneously measure multiple mRNAs from small numbers of cells. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1096–1103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D., de Kossodo S., Vassalli P. Gamma interferon enhances macrophage transcription of the tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin 1, and urokinase genes, which are controlled by short-lived repressors. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2113–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descoteaux A., Matlashewski G. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor gene expression and protein synthesis in murine macrophages treated with recombinant tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):846–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar M. A., Schreiber R. D. The molecular cell biology of interferon-gamma and its receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:571–611. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber M. F., Gerrard T. L. Production of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) by human monocytes is differentially regulated by GM-CSF, TNF alpha, and IFN-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1992 Jul;142(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90297-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg U., Nilsson E. Recombinant lymphotoxin enhances the growth of normal, but not of chronic myeloid leukemic, human hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro. Leuk Res. 1989;13(11):953–957. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(89)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P., Ralph P. Human leukemic models of myelomonocytic development: a review of the HL-60 and U937 cell lines. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Apr;37(4):407–422. doi: 10.1002/jlb.37.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii Y., Muraguchi A., Suematsu S., Matsuda T., Yoshizaki K., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Regulation of BSF-2/IL-6 production by human mononuclear cells. Macrophage-dependent synthesis of BSF-2/IL-6 by T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1529–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyal D. A., Beezhold D. H., Hall R. E. Differentiation-inducing cytokine P48 exists in a membrane-associated form. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):893–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramnik I., Skamene E., Radzioch D. Assessment of lymphokine profiles in activated lymphocytes by semiquantitative PCR. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Jun 18;162(2):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90379-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leftwich J. A., Hall R. E. Initial characterization of a cytokine which induces differentiation and cytolytic activity in HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells: evidence that the cytokine is distinct from other known differentiation-active cytokines. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Jan;47(1):87–96. doi: 10.1002/jlb.47.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leftwich J. A., Hall R. E. Purification and further characterization of a non-tumor necrosis factor alpha or beta differentiation-inducing cytokine, P48. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 15;49(16):4459–4465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a cDNA encoding MyD88, a novel myeloid differentiation primary response gene induced by IL6. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):1095–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melby P. C., Darnell B. J., Tryon V. V. Quantitative measurement of human cytokine gene expression by polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Feb 26;159(1-2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90162-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The colony stimulating factors. Discovery, development, and clinical applications. Cancer. 1990 May 15;65(10):2185–2195. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900515)65:10<2185::aid-cncr2820651005>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Int J Cell Cloning. 1991 Mar;9(2):95–108. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530090201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Miyatake S., Schreurs J., De Vries J., Arai N., Yokota T., Arai K. Coordinate regulation of immune and inflammatory responses by T cell-derived lymphokines. FASEB J. 1988 Jun;2(9):2462–2473. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.9.2836253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Kharbanda S., Spriggs D., Kufe D. Effects of dexamethasone on induction of monocytic differentiation in human U-937 cells by dimethylsulfoxide. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Feb;142(2):261–267. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neta R., Sayers T. J., Oppenheim J. J. Relationship of TNF to interleukins. Immunol Ser. 1992;56:499–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orcel P., Bielakoff J., De Vernejoul M. C. Effects of transforming growth factor-beta on long-term human cord blood monocyte cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Feb;142(2):293–298. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn L. C., Guyre P. M., Fanger M. W. Functional comparison of the inductions of NADPH oxidase activity and Fc gamma RI in IFN gamma-treated U937 cells. Mol Immunol. 1990 Mar;27(3):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(90)90139-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamatani T., Kimura S., Hashimoto T., Onozaki K. Purification of guinea pig tumor necrosis factor (TNF): comparison of its antiproliferative and differentiative activities for myeloid leukemic cell lines with those of recombinant human TNF. J Biochem. 1989 Jan;105(1):55–60. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines in infectious disease. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989 Feb;1(3):454–461. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(88)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trechsel U., Evêquoz V., Fleisch H. Stimulation of interleukin 1 and 3 production by retinoic acid in vitro. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 1;230(2):339–344. doi: 10.1042/bj2300339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi Y., Gunji Y., Nakamura M., Hayakawa K., Maeda M., Osawa H., Nagayoshi K., Kasahara T., Suda T. Expression of c-kit mRNA and protein during the differentiation of human hematopoietic progenitor cells. Exp Hematol. 1993 Aug;21(9):1233–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Loosdrecht A. A., Beelen R. H., Ossenkoppele G. J., Broekhoven M. G., Langenhuijsen M. M. Cellular and cytokine dependent monocyte-mediated leukemic cell death: modulation by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Exp Hematol. 1993 Mar;21(3):461–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]