Abstract
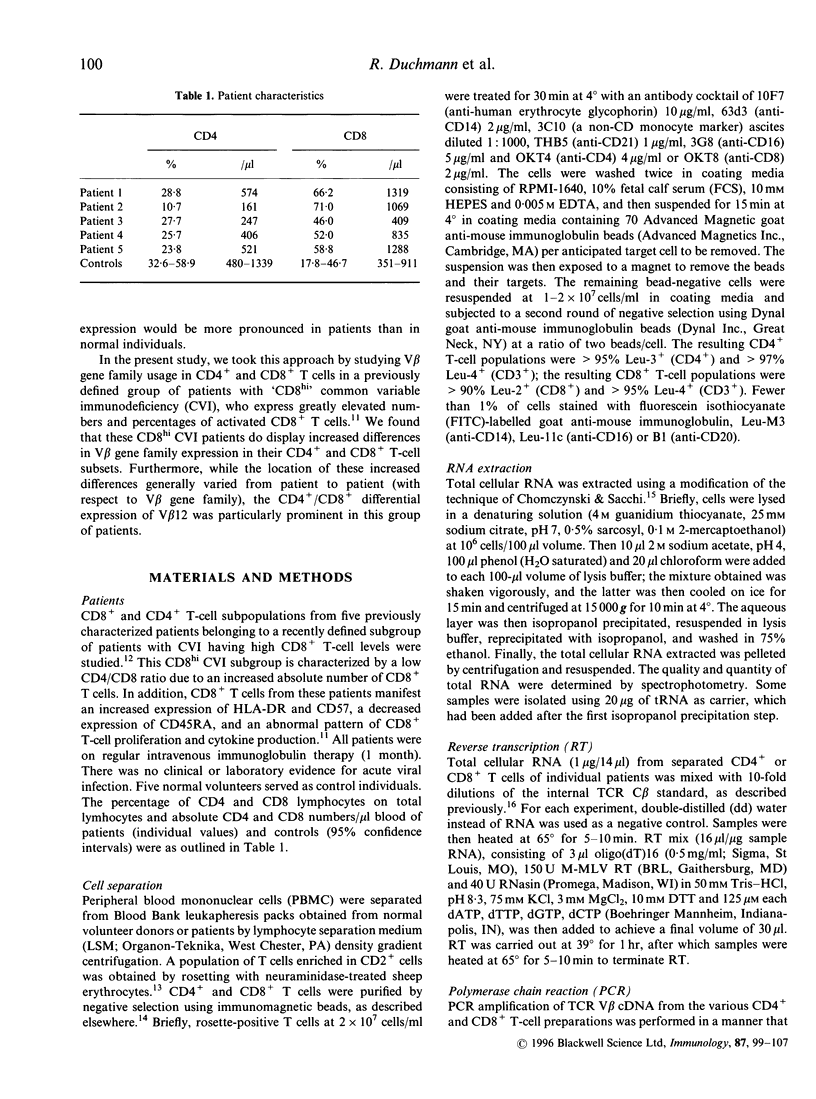
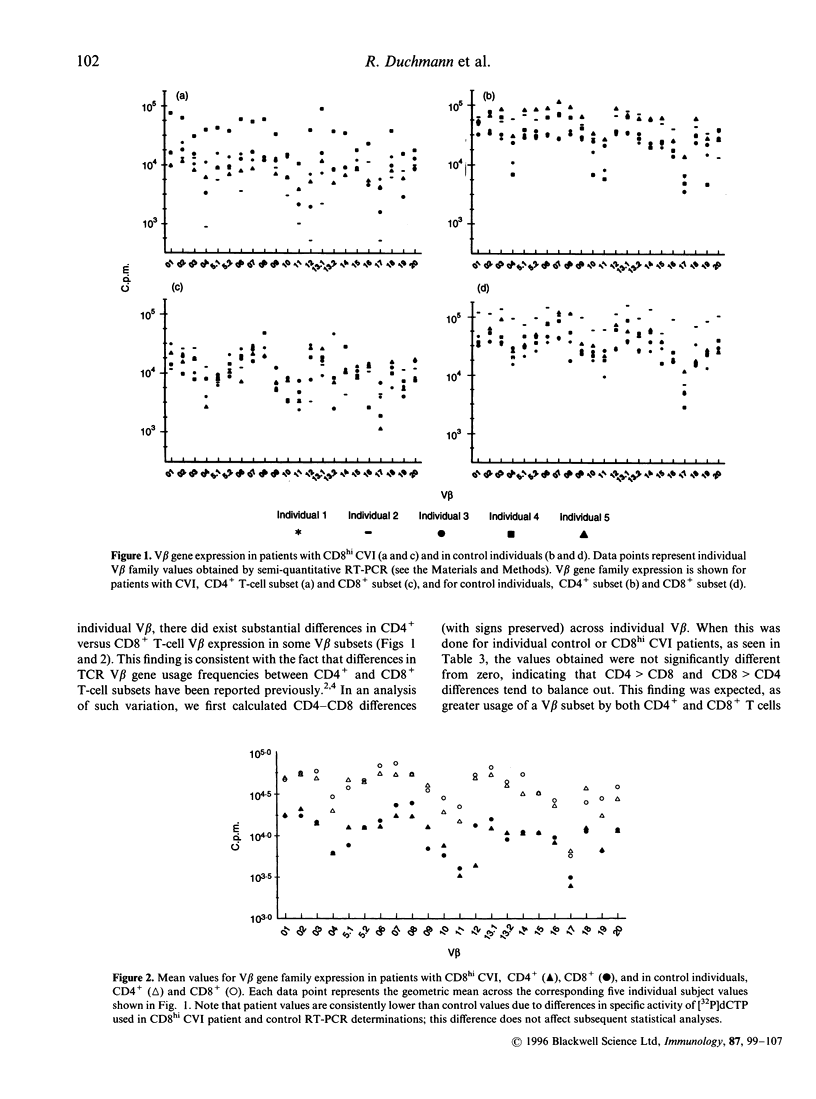
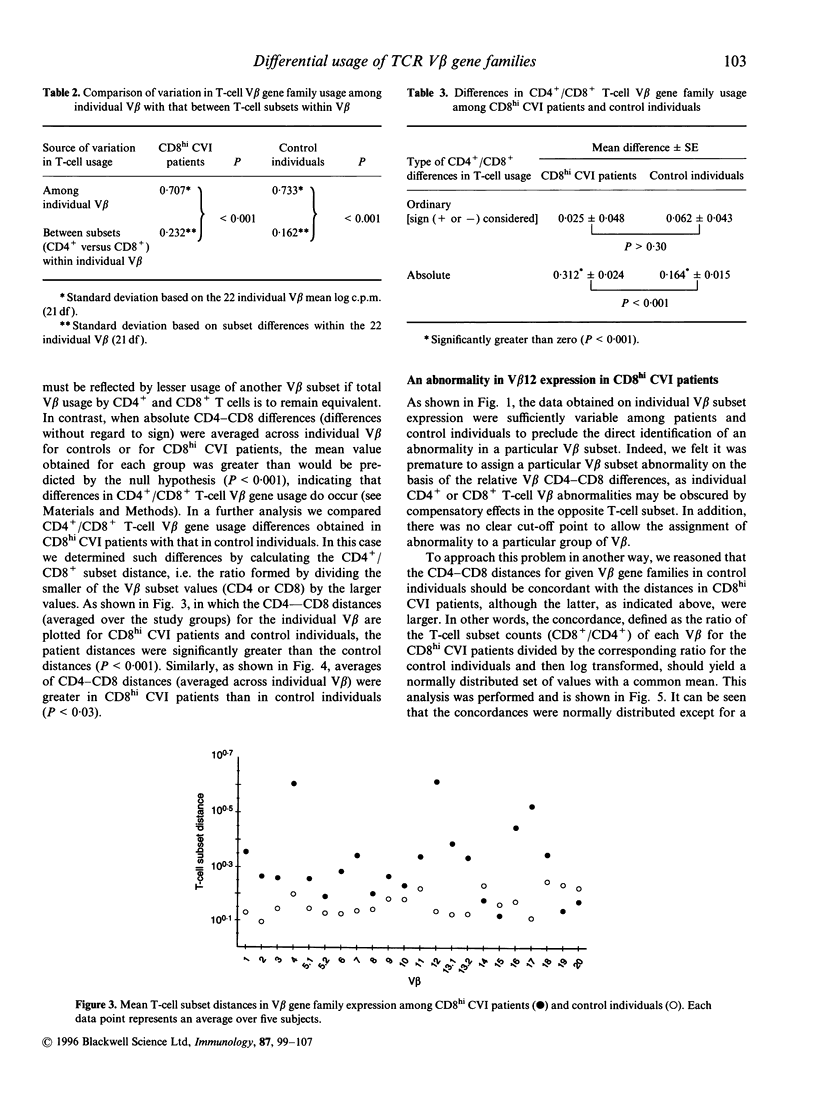
In this study, we report that differences between T-cell receptor (TCR) V beta gene family usage in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are significantly greater in a subgroup of patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVI) and high levels of activated CD8+ T cells (CD8hi CVI) than in controls (P < 0.001). In CD8hi CVI patients, such differences were also significantly greater for V beta 12 than for other V beta families. As the causes of the differential usage of V beta gene families by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are under investigation, it was interesting that the combined differences between V beta gene family usage in the CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subpopulations as a whole were significantly lower than the combined differences between individual V beta gene family usage in either CD4+ or CD8+ T-cell subpopulations (P < 0.001 in both control and CD8hi CVI patients). Further, the pattern of V beta gene family usage in CD4+ T cells was remarkably similar to that in CD8+ T cells in both groups. These data strongly suggest that differences in V beta gene family usage arising from coselection by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I versus MHC class II restriction elements do not fundamentally distort 'basic' V beta gene family usage patterns. They also support the concept that differences in CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell V beta gene family usage, which were increased in CD8hi CVI, can arise from high-affinity interactions between disease-associated antigens or superantigens and T cells in the post-thymic T-cell compartment.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baccala R., Kono D. H., Walker S., Balderas R. S., Theofilopoulos A. N. Genomically imposed and somatically modified human thymocyte V beta gene repertoires. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2908–2912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. W., Kotzin B., Herron L., Callahan J., Marrack P., Kappler J. Interaction of Staphylococcus aureus toxin "superantigens" with human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8941–8945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. P., Meyer M. M., Bakke A. C. T cell receptor V beta gene expression in monozygotic twins. Discordance in CD8 subset and in disease states. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 1;152(1):315–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. P., Meyer M. M., Munkirs D. D., Babcock D., Braun M. P., Hayden J. B., Bakke A. C. T-cell receptor variable beta genes show differential expression in CD4 and CD8 T cells. Hum Immunol. 1991 Nov;32(3):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(91)90056-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Waele M., Thielemans C., Van Camp B. K. Characterization of immunoregulatory T cells in EBV-induced infectious mononucleosis by monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 19;304(8):460–462. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102193040804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DerSimonian H., Band H., Brenner M. B. Increased frequency of T cell receptor V alpha 12.1 expression on CD8+ T cells: evidence that V alpha participates in shaping the peripheral T cell repertoire. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):639–648. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchmann R., Strober W., James S. P. Quantitative measurement of human T-cell receptor V beta subfamilies by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction using synthetic internal mRNA standards. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;12(3):217–225. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuy d'Angeac A., Monier S., Jorgensen C., Gao Q., Travaglio-Encinoza A., Bologna C., Combe B., Sany J., Rème T. Increased percentage of CD3+, CD57+ lymphocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation with duration of disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 May;36(5):608–612. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorochov G., Debré P., Leblond V., Sadat-Sowti B., Sigaux F., Autran B. Oligoclonal expansion of CD8+ CD57+ T cells with restricted T-cell receptor beta chain variability after bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1994 Jan 15;83(2):587–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunewald J., Janson C. H., Wigzell H. Biased expression of individual T cell receptor V gene segments in CD4+ and CD8+ human peripheral blood T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):819–822. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulwani-Akolkar B., Posnett D. N., Janson C. H., Grunewald J., Wigzell H., Akolkar P., Gregersen P. K., Silver J. T cell receptor V-segment frequencies in peripheral blood T cells correlate with human leukocyte antigen type. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1139–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawes G. E., Struyk L., van den Elsen P. J. Differential usage of T cell receptor V gene segments in CD4+ and CD8+ subsets of T lymphocytes in monozygotic twins. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):2033–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe J. S., Strober W., Sneller M. C. Functional abnormalities of CD8+ T cells define a unique subset of patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Blood. 1993 Jul 1;82(1):192–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Neckers L. M., Graeff A. S., Cossman J., Balch C. M., Strober W. Suppression of immunoglobulin synthesis by lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jun;86(6):1510–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence J., Hodtsev A. S., Posnett D. N. Superantigen implicated in dependence of HIV-1 replication in T cells on TCR V beta expression. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):255–259. doi: 10.1038/358255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao N. S., Maltzman J., Raulet D. H. Expression of the V beta 5.1 gene by murine peripheral T cells is controlled by MHC genes and skewed to the CD8+ subset. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):844–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh H. S., Garvin A. M., Forbush K. A., Carlow D. A., Davis C. B., Littman D. R., Perlmutter R. M. Participation of CD4 coreceptor molecules in T-cell repertoire selection. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):241–243. doi: 10.1038/349241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh H. S., Kisielow P., Scott B., Kishi H., Uematsu Y., Blüthmann H., von Boehmer H. Thymic major histocompatibility complex antigens and the alpha beta T-cell receptor determine the CD4/CD8 phenotype of T cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):229–233. doi: 10.1038/335229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Zhu Z. B., Schaffer F. M., Macon K. J., Palermos J., Barger B. O., Go R., Campbell R. D., Schroeder H. W., Jr, Cooper M. D. Major histocompatibility complex class III genes and susceptibility to immunoglobulin A deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1914–1922. doi: 10.1172/JCI115797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. C., Taylor-Wiedeman J., Perera P., Fisher J., Borysiewicz L. K. Subsets of CD8+, CD57+ cells in normal, healthy individuals: correlations with human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) carrier status, phenotypic and functional analyses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Nov;94(2):297–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb03447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. J., Wagner D. K., Blaese R. M., Hagengruber C., Waldmann T. A., Fleisher T. A. Characterization of common variable immunodeficiency: identification of a subset of patients with distinctive immunophenotypic and clinical features. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):2046–2051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]