Abstract
w10 and KN104 are distinct class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) serological specificities present in Boran (Bos indicus) cattle. Although these specificities are commonly expressed together, they may also be expressed independently. To establish whether w10 and KN104, when expressed together, are on the same or different molecules, and whether a second class I MHC locus exists in cattle, genomic DNA from an animal homozygous for a haplotype encoding the w10 and KN104 specificities was transfected into thymidine kinase-deficient mouse L cells (Ltk- cells), and the transfected cells were screened with monoclonal antibodies (mAb) specific for the w10 or KN104 allospecificities. Two different populations of transfectants were identified: the cells of one population reacted only with w10-specific mAb, whereas those of the other population were recognized only by the KN104-specific mAb. Alloreactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) also distinguished between the two populations. Two CTL clones, shown to be restricted by the KN104 specificity, killed only those L cells expressing molecules recognized by the KN104-reactive mAb. Of eight CTL clones which recognized class I molecules associated with the w10 specificity, four killed the L cells expressing the w10 specificity. The remaining four clones did not kill either population of transfectants. Finally, immunoprecipitation studies revealed that both populations express full-length bovine class I MHC molecules. These results demonstrate that the w10 and KN104 specificities are on distinct class I molecules. As the genes encoding these molecules were derived from a MHC-homozygous animal, the findings also provide strong evidence that there are at least two classical class I loci in cattle.
Full text
PDF

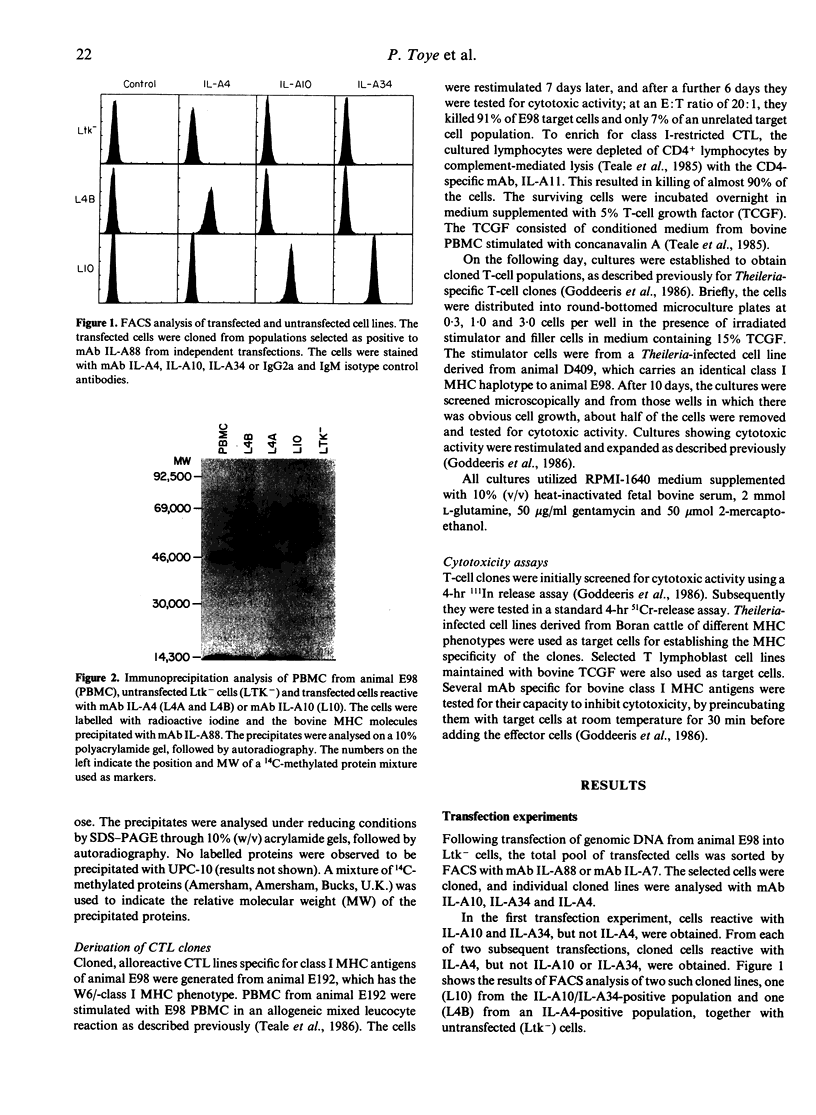
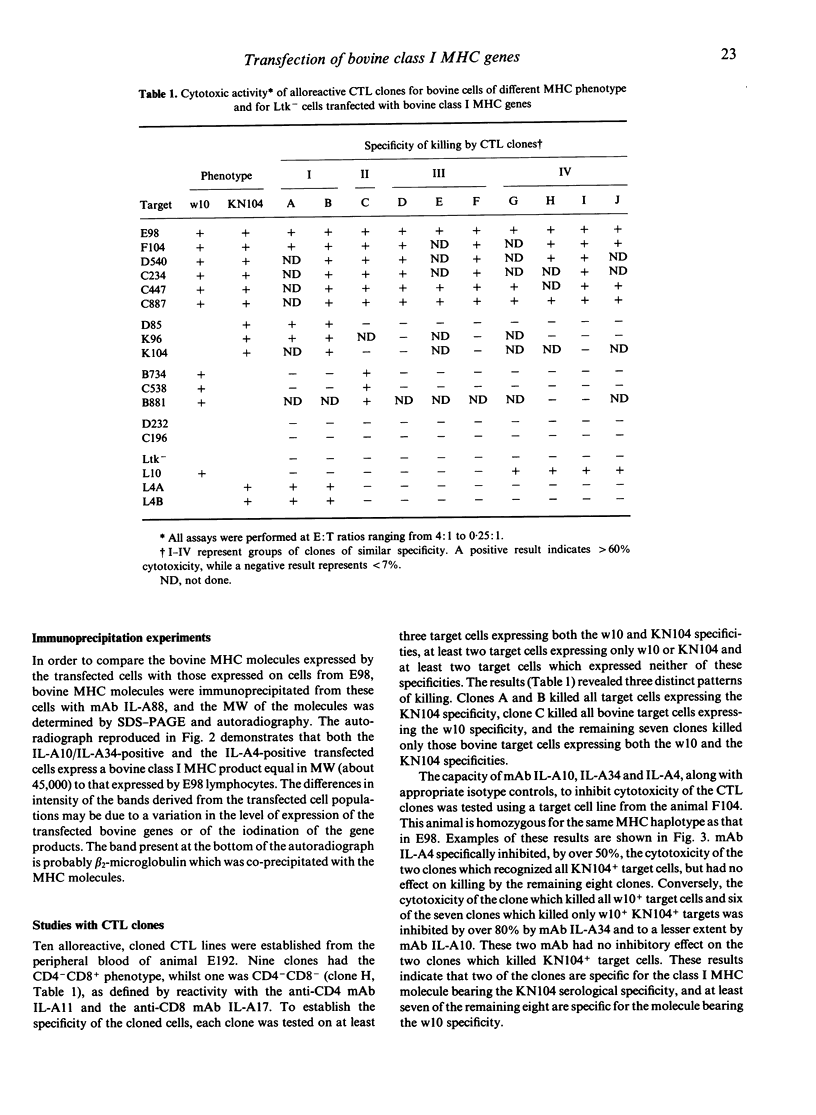



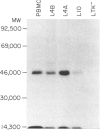
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti S., Herzenberg L. A. DNA methylation prevents transfection of genes for specific surface antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8391–8394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. L., Teale A. J., Naessens J. G., Goddeeris B. M., MacHugh N. D., Morrison W. I. Characterization of a subset of bovine T lymphocytes that express BoT4 by monoclonal antibodies and function: similarity to lymphocytes defined by human T4 and murine L3T4. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4385–4391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensaid A., Naessens J., Kemp S. J., Black S. J., Shapiro S. Z., Teale A. J. An immunochemical analysis of class I (BoLA) molecules on the surface of bovine cells. Immunogenetics. 1988;27(2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00351089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard E. J., Le A. X., Barbosa J. A., Lacy E., Engelhard V. H. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes from HLA-A2 transgenic mice specific for HLA-A2 expressed on human cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1157–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddison W. E., Ward F. E., Shearer G. M., Shaw S. The self determinants recognized by human virus-immune T cells can be distinguished from the serologically defined HLA antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):548–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull R. W., Lewin H. A., Wu M. C., Peterbaugh K., Antczak D., Bernoco D., Cwik S., Dam L., Davies C., Dawkins R. L. Joint report of the Third International Bovine Lymphocyte Antigen (BoLA) Workshop, Helsinki, Finland, 27 July 1986. Anim Genet. 1989;20(1):109–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1989.tb00849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. A., Baldwin C. L., MacHugh N. D., Bensaid A., Teale A. J., Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I. Characterization by a monoclonal antibody and functional analysis of a subset of bovine T lymphocytes that express BoT8, a molecule analogous to human CD8. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):351–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis P. D., Jackson A. P., Parham P. Molecular cloning of bovine class I MHC cDNA. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):642–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I., Teale A. J., Bensaid A., Baldwin C. L. Bovine cytotoxic T-cell clones specific for cells infected with the protozoan parasite Theileria parva: parasite strain specificity and class I major histocompatibility complex restriction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5238–5242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S., Biddison W. E., Strominger J. L. Comparative structural analysis of HLA-A2 antigens distinguishable by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. II. Variant DK1: evidence for a discrete CTL recognition region. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1856–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krangel M. S. Secretion of HLA-A and -B antigens via an alternative RNA splicing pathway. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1173–1190. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalanne J. L., Transy C., Guerin S., Darche S., Meulien P., Kourilsky P. Expression of class I genes in the major histocompatibility complex: identification of eight distinct mRNAs in DBA/2 mouse liver. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalor P. A., Morrison W. I., Goddeeris B. M., Jack R. M., Black S. J. Monoclonal antibodies identify phenotypically and functionally distinct cell types in the bovine lymphoid system. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Sep;13(1-2):121–140. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(86)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson C. A., Williams L. C., McLaughlin-Taylor E., McMillan M. Creation of H-2 class I epitopes using synthetic peptides: recognition by alloreactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):1031–1035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Lipsich L., Wigler M. Isolation of the chicken thymidine kinase gene by plasmid rescue. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):207–210. doi: 10.1038/285207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song E. S., Linsk R., Olson C. A., McMillan M., Goodenow R. S. Allospecific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize an H-2 peptide in the context of a murine major histocompatibility complex class I molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1927–1931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stear M. J., Newman M. J., Nicholas F. W. Two closely linked loci and one apparently independent locus code for bovine lymphocyte antigens. Tissue Antigens. 1982 Oct;20(4):289–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1982.tb00359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Hood L. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex in mouse and man. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):727–733. doi: 10.1126/science.6356354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teale A. J., Baldwin C. L., Ellis J. A., Newson J., Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I. Alloreactive bovine T lymphocyte clones: an analysis of function, phenotype, and specificity. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4392–4398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teale A. J., Morrison W. I., Goddeeris B. M., Groocock C. M., Stagg D. A., Spooner R. L. Bovine alloreactive cytotoxic cells generated in vitro: target specificity in relation to BoLA phenotype. Immunology. 1985 Jun;55(2):355–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yannelli J. R., Moore L. C., Engelhard V. H. Multiple epitopes on human and murine cells expressing HLA-B7 as defined by specific murine cytotoxic T cell clones. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):900–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]