Abstract
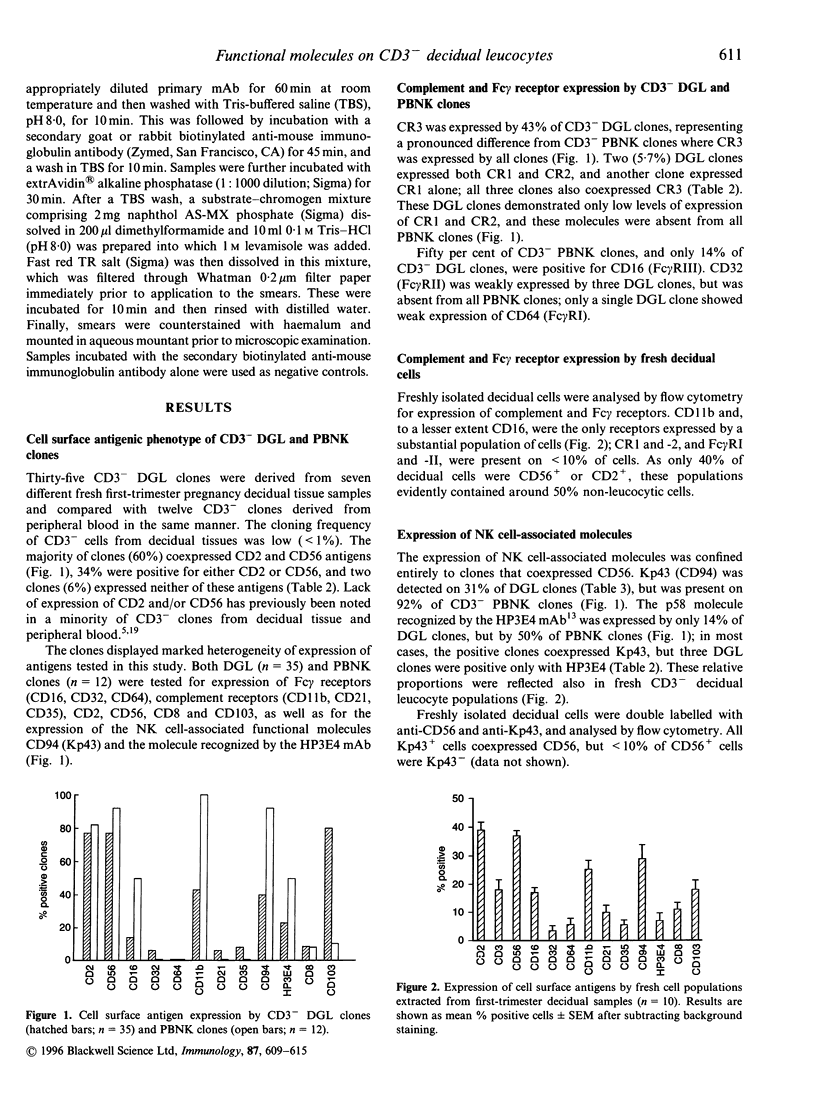
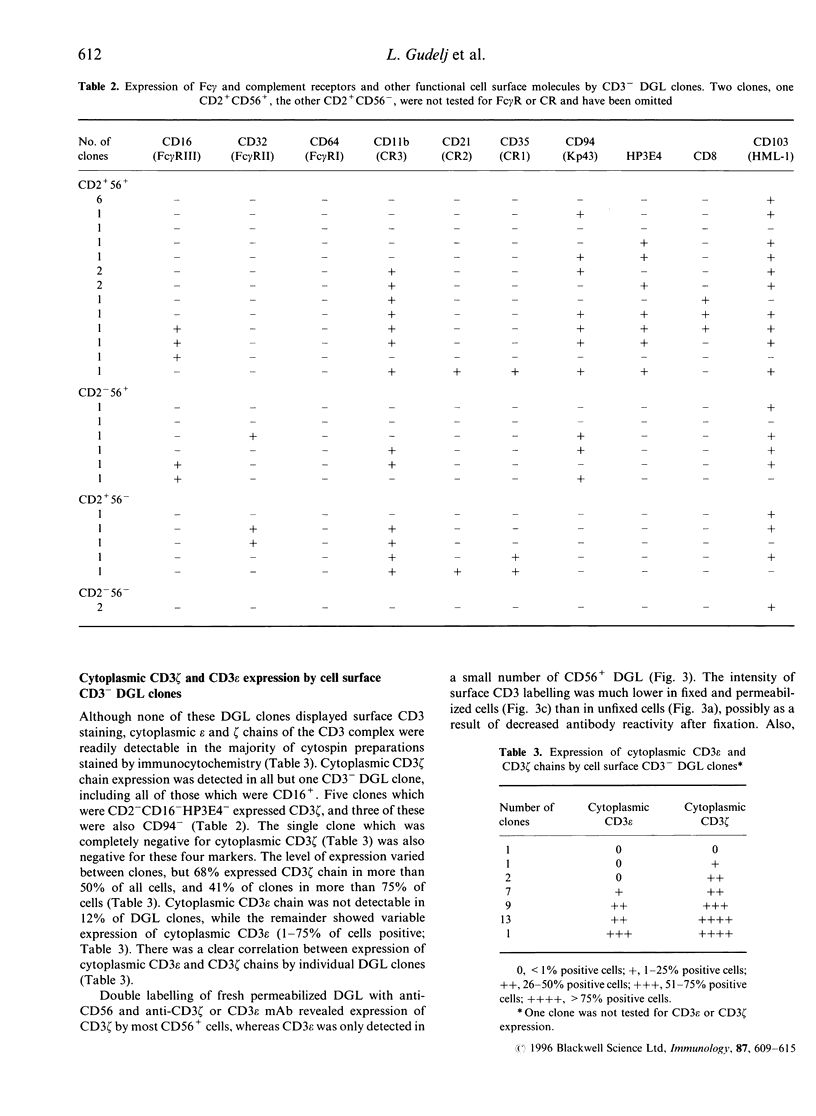
Cell surface and cytoplasmic antigen expression by 35 CD3- decidual granular leucocyte (DGL) clones, derived from human endometrial tissue in the first trimester of pregnancy, has been compared with both that of fresh CD3- decidual leucocytes and that of CD3- peripheral blood natural killer (PBNK) cell clones (n = 12). The majority of DGL clones retained the antigenic phenotype of fresh cells, although CD103 (HML-1) was expressed on 50% of DGL clones but only 17% of fresh DGL. Both cytoplasmic CD3 zeta and CD3 epsilon chains were detected in > 90% of DGL clones in the absence of cell surface CD3. Cytoplasmic CD3 zeta was present in almost all fresh CD3- DGL, whereas CD3 epsilon was not. Most DGL clones did not express surface Fc gamma receptors I-III (CD64, -32 and -16, respectively) and complement receptors (CR) types 1 and 2 (CD35 and 21, respectively), but 43% expressed CR3 (CD11b/18); in contrast, all PBNK clones were CR3+. The NK cell-associated molecules Kp43 (CD94) and the p58 molecule recognized by the HP3E4 monoclonal antibody were both present on a higher proportion of CD3- PBNK (91% and 50%, respectively) than DGL clones (31% and 14%, respectively), despite expression of CD94 by > 90% of fresh CD56+ decidual leucocytes. Five of 35 CD3- DGL clones expressed cytoplasmic CD3 zeta in the absence of expression of CD2, CD16 or the p58 molecule recognized by HP3E4. These variations between CD3- DGL and PBNK cell clones in expression of functional molecules may be related to previously reported differences in major histocompatibility complex-non-restricted cytotoxic activities between these two cell types.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Fearon D. T. Structure and function of the complement receptors, CR1 (CD35) and CR2 (CD21). Adv Immunol. 1989;46:183–219. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altin J. G., Pagler E. B., Kinnear B. F., Warren H. S. Molecular associations involving CD16, CD45 and zeta and gamma chains on human natural killer cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;72(1):87–96. doi: 10.1038/icb.1994.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramburu J., Balboa M. A., Izquierdo M., López-Botet M. A novel functional cell surface dimer (Kp43) expressed by natural killer cells and gamma/delta TCR+ T lymphocytes. II. Modulation of natural killer cytotoxicity by anti-Kp43 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):714–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottino C., Vitale M., Olcese L., Sivori S., Morelli L., Augugliaro R., Ciccone E., Moretta L., Moretta A. The human natural killer cell receptor for major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Surface modulation of p58 molecules and their linkage to CD3 zeta chain, Fc epsilon RI gamma chain and the p56lck kinase. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Oct;24(10):2527–2534. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew R., West D. C., Burthem J., Christmas S. E. Expression of the human mucosal lymphocyte antigen, HML-1, by T cells activated with mitogen or specific antigen in vitro. Scand J Immunol. 1995 Jun;41(6):553–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1995.tb03607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer J. N., Morrison L., Longfellow M., Ritson A., Pace D. Granulated lymphocytes in human endometrium: histochemical and immunohistochemical studies. Hum Reprod. 1991 Jul;6(6):791–798. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a137430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows T. D., King A., Loke Y. W. Expression of adhesion molecules by human decidual large granular lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1993 Mar;147(1):81–94. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepek K. L., Shaw S. K., Parker C. M., Russell G. J., Morrow J. S., Rimm D. L., Brenner M. B. Adhesion between epithelial cells and T lymphocytes mediated by E-cadherin and the alpha E beta 7 integrin. Nature. 1994 Nov 10;372(6502):190–193. doi: 10.1038/372190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Rodríguez A., Carretero M., López-Botet M., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Molecular characterization of human CD94: a type II membrane glycoprotein related to the C-type lectin superfamily. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Sep;25(9):2433–2437. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christmas S. E., Bulmer J. N., Meager A., Johnson P. M. Phenotypic and functional analysis of human CD3- decidual leucocyte clones. Immunology. 1990 Oct;71(2):182–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumbley G., King A., Robertson K., Holmes N., Loke Y. W. Resistance of HLA-G and HLA-A2 transfectants to lysis by decidual NK cells. Cell Immunol. 1994 May;155(2):312–322. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deniz G., Christmas S. E., Brew R., Johnson P. M. Phenotypic and functional cellular differences between human CD3- decidual and peripheral blood leukocytes. J Immunol. 1994 May 1;152(9):4255–4261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. A., Palmer M. S., McMichael A. J. Human trophoblast and the choriocarcinoma cell line BeWo express a truncated HLA Class I molecule. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):731–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassmann M., Amrein K. E., Flint N. A., Schraven B., Burn P. Identification of a signaling complex involving CD2, zeta chain and p59fyn in T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jan;24(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Ogawa H., Miyata M., Shiozaki H., Tanizawa O. Expression of E-cadherin in normal, benign, and malignant tissues of female genital organs. Am J Clin Pathol. 1992 Jul;98(1):76–80. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/98.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Wooding P., Gardner L., Loke Y. W. Expression of perforin, granzyme A and TIA-1 by human uterine CD56+ NK cells implies they are activated and capable of effector functions. Hum Reprod. 1993 Dec;8(12):2061–2067. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a137982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovats S., Main E. K., Librach C., Stubblebine M., Fisher S. J., DeMars R. A class I antigen, HLA-G, expressed in human trophoblasts. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):220–223. doi: 10.1126/science.2326636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Chang C., Spits H., Phillips J. H. Expression of cytoplasmic CD3 epsilon proteins in activated human adult natural killer (NK) cells and CD3 gamma, delta, epsilon complexes in fetal NK cells. Implications for the relationship of NK and T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):1876–1880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Gumperz J. E., Parham P., Melero I., López-Botet M., Phillips J. H. The NKB1 and HP-3E4 NK cells receptors are structurally distinct glycoproteins and independently recognize polymorphic HLA-B and HLA-C molecules. J Immunol. 1995 Apr 1;154(7):3320–3327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Civin C. I., Loken M. R., Phillips J. H. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4480–4486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson R. S., Springer T. A. Structure and function of leukocyte integrins. Immunol Rev. 1990 Apr;114:181–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin V., Gumperz J., Parham P., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. NKB1: a natural killer cell receptor involved in the recognition of polymorphic HLA-B molecules. J Exp Med. 1994 Aug 1;180(2):537–543. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen B., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Transmembrane signalling through the T-cell-receptor-CD3 complex. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melero I., Salmerón A., Balboa M. A., Aramburu J., López-Botet M. Tyrosine kinase-dependent activation of human NK cell functions upon stimulation through a 58-kDa surface antigen selectively expressed on discrete subsets of NK cells and T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 15;152(4):1662–1673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moingeon P., Stebbins C. C., D'Adamio L., Lucich J., Reinherz E. L. Human natural killer cells and mature T lymphocytes express identical CD3 zeta subunits as defined by cDNA cloning and sequence analysis. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Aug;20(8):1741–1745. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Vitale M., Sivori S., Bottino C., Morelli L., Augugliaro R., Barbaresi M., Pende D., Ciccone E., Lopez-Botet M. Human natural killer cell receptors for HLA-class I molecules. Evidence that the Kp43 (CD94) molecule functions as receptor for HLA-B alleles. J Exp Med. 1994 Aug 1;180(2):545–555. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagomi H., Petersson M., Magnusson I., Juhlin C., Matsuda M., Mellstedt H., Taupin J. L., Vivier E., Anderson P., Kiessling R. Decreased expression of the signal-transducing zeta chains in tumor-infiltrating T-cells and NK cells of patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1993 Dec 1;53(23):5610–5612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace D., Longfellow M., Bulmer J. N. Characterization of intraepithelial lymphocytes in human endometrium. J Reprod Fertil. 1991 Jan;91(1):165–174. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0910165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrović O., Gudelj L., Rubesa G., Haller H., Beer A. E., Rukavina D. Decidual-trophoblast interactions: decidual lymphoid cell function in normal, anembryonic, missed abortion and ectopic human pregnancy. J Reprod Immunol. 1994 May;26(3):217–231. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(94)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos O. F., Kai C., Yefenof E., Klein E. The elevated natural killer sensitivity of targets carrying surface-attached C3 fragments require the availability of the iC3b receptor (CR3) on the effectors. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1239–1243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritson A., Bulmer J. N. Isolation and functional studies of granulated lymphocytes in first trimester human decidua. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Aug;77(2):263–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmerón A., Sánchez-Madrid F., Ursa M. A., Fresno M., Alarcón B. A conformational epitope expressed upon association of CD3-epsilon with either CD3-delta or CD3-gamma is the main target for recognition by anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3047–3052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez M. J., Muench M. O., Roncarolo M. G., Lanier L. L., Phillips J. H. Identification of a common T/natural killer cell progenitor in human fetal thymus. J Exp Med. 1994 Aug 1;180(2):569–576. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivier E., Morin P. M., O'Brien C., Schlossman S. F., Anderson P. CD2 is functionally linked to the zeta-natural killer receptor complex. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):1077–1080. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivier E., da Silva A. J., Ackerly M., Levine H., Rudd C. E., Anderson P. Association of a 70-kDa tyrosine phosphoprotein with the CD16: zeta: gamma complex expressed in human natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Aug;23(8):1872–1876. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


