Abstract
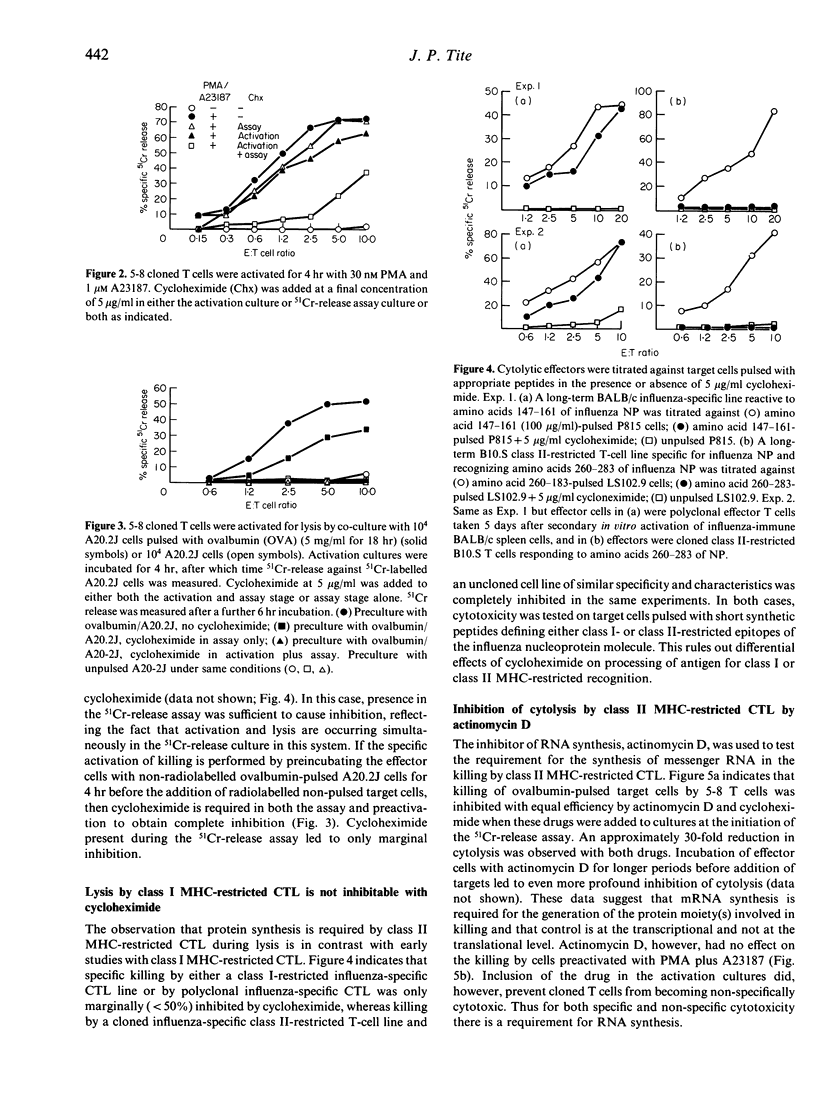
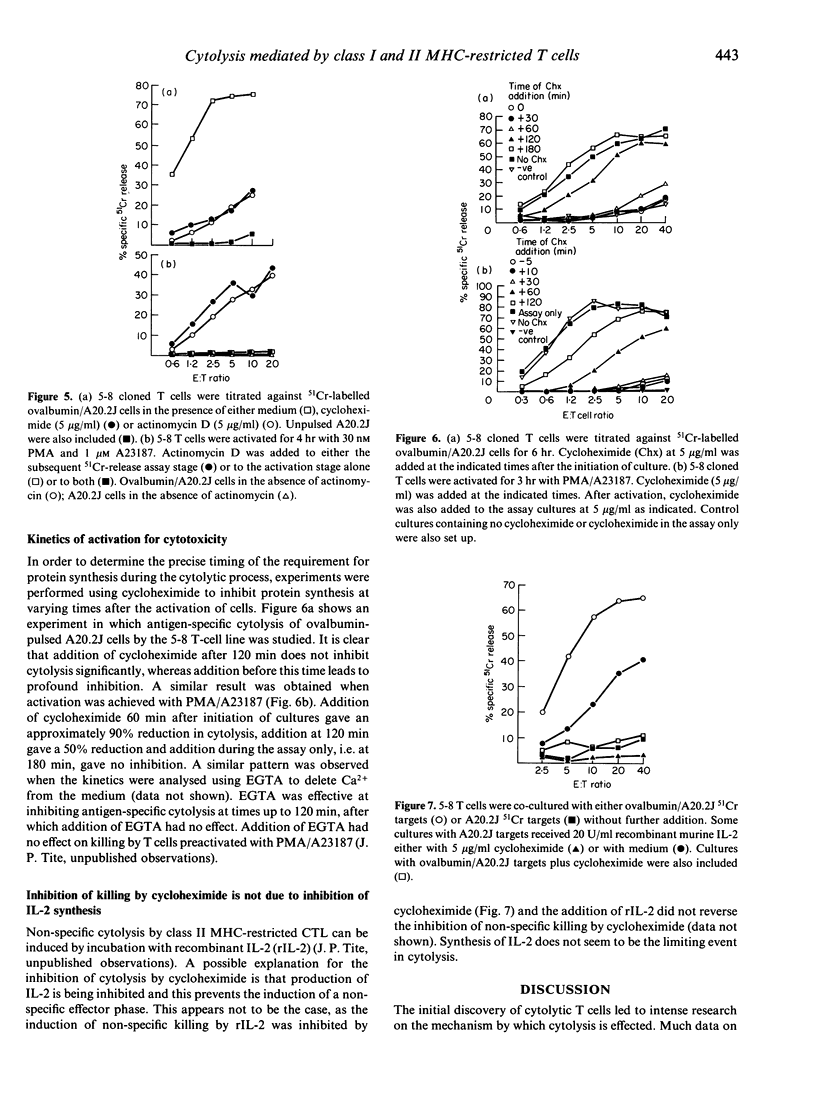
Antigen-specific cytolysis by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II-restricted cloned T-cell lines was found to be dependent on protein synthesis. Cytolysis by both polyclonal short-term and long-term class I-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) was almost completely insensitive to inhibitors of protein synthesis. Kinetic studies with class II-restricted CTL indicated that approximately 2-3 hr after initiation of activation, resistance to inhibitors of protein synthesis was acquired. This strongly suggests that either a cytotoxic effector molecule or an intermediary important in the delivery of such a molecule is synthesized rapidly after activation in class II-restricted CTL, whilst class I-restricted CTL have no such requirement.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottomly K. A functional dichotomy in CD4+ T lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1988 Sep;9(9):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet J. F., Denizot F., Suzan M., Haas W., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Berke G., Luciani M. F., Golstein P. CTLA-1 and CTLA-3 serine esterase transcripts are detected mostly in cytotoxic T cells, but not only and not always. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4102–4105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayberger C., DeKruyff R. H., Fay R., Cantor H. Identification of a unique B-cell-stimulating factor produced by a cloned dendritic cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):183–187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Anderson C. G., Prochazka G. High activity of N-alpha-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine thiobenzyl ester serine esterase and cytolytic perforin in cloned cell lines is not demonstrable in in-vivo-induced cytotoxic effector cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5004–5008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao X. M., Liew F. Y., Tite J. P. Identification and characterization of T helper epitopes in the nucleoprotein of influenza A virus. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):3007–3014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju S. T., Strack P., Stromquist D., Dekruyff R. H. Cytolytic activity of Ia-restricted T cell clones and hybridomas: evidence for a cytolytic mechanism independent of interferon-gamma, lymphotoxin, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Cell Immunol. 1988 Dec;117(2):399–413. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Steffen M., King F., Young J. D. Identification, isolation, and characterization of a novel cytotoxin in murine cytolytic lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacher A. E., Morrison L. A., Braciale V. L., Malissen B., Braciale T. J. Expression of specific cytolytic activity by H-2I region-restricted, influenza virus-specific T lymphocyte clones. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):171–187. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E., Benacerraf B. An effector-cell independent step in target cell lysis by sensitized mouse lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Nov;111(5):1538–1545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E. Mechanism of specific tumor-cell lysis by alloimmune T lymphocytes: resolution and characterization of discrete steps in the cellular interaction. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1977;7:301–361. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3054-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. A family of serine esterases in lytic granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):679–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90544-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. A novel serine esterase expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):743–745. doi: 10.1038/314743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Konigsberg P. J. Cytolytic T cell granules. Isolation, structural, biochemical, and functional characterization. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):695–710. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Schild G. C. The polypeptide composition of influenza A viruses. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):396–408. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90270-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dennert G., Wormsley S., Dutton R. W. The Lyt phenotype of a long-term allospecific T cell line. Both helper and killer activities to IA are mediated by Ly-1 cells. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorn R. M., Henney C. S. Studies on the mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis. VI. A reappraisal of the requirement for protein synthesis during T cell-mediated lysis. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):146–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Janeway C. A., Jr Cloned helper T cells can kill B lymphoma cells in the presence of specific antigen: Ia restriction and cognate vs. noncognate interactions in cytolysis. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):878–886. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Powell M. B., Ruddle N. H. Protein-antigen specific Ia-restricted cytolytic T cells: analysis of frequency, target cell susceptibility, and mechanism of cytolysis. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):25–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Skehel J. J. The influenza A virus nucleoprotein gene controls the induction of both subtype specific and cross-reactive cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):552–563. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):701–702. doi: 10.1038/248701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


