Abstract
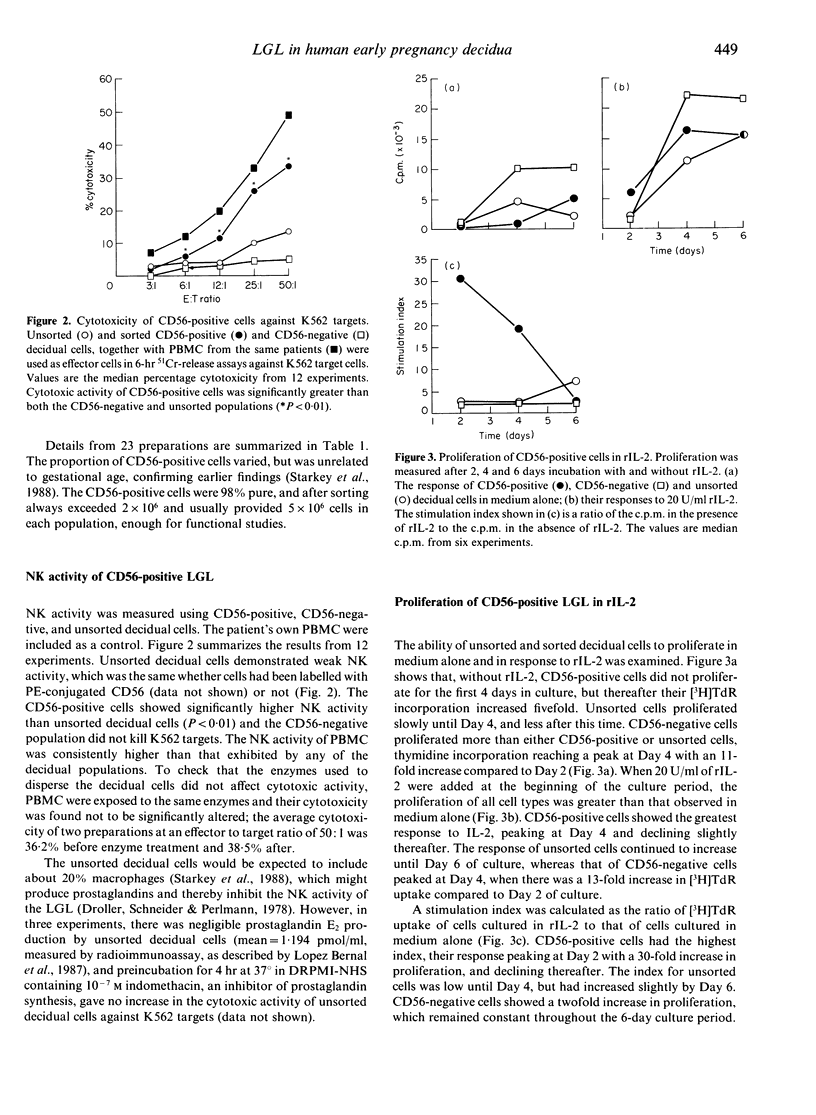
Large granular lymphocytes (LGL) have been shown previously to be the most abundant cell type in the first trimester human decidua. Purified populations of decidual LGL were prepared by flow cytometry of cell dispersions labelled with NKH1 (CD56), an antibody specific for peripheral blood LGL, and the functional properties of CD56-positive cells, CD56-negative and unsorted decidual cells compared. Both CD56-positive cells and unsorted decidual cells have cytotoxic activity against the natural killer (NK) cell target K562 which was weak compared with that of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). The CD56-negative cells had no cytotoxic activity against K562. All three decidual cell populations proliferated in response to recombinant human interleukin-2 (rIL-2), but none produced detectable levels of IL-2 in culture. When unsorted decidual cells were cultured for 7 days in rIL-2 the proportion of CD56-positive cells increased and NK activity against K562 was augmented. The NK activity of purified CD56-positive decidual cells was also augmented by culturing in rIL-2. The potential role of decidual LGL in regulating the development of the semi-allogeneic placenta is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abruzzo L. V., Rowley D. A. Homeostasis of the antibody response: immunoregulation by NK cells. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):581–585. doi: 10.1126/science.6685343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai S., Yamamoto H., Itoh K., Kumagai K. Suppressive effect of human natural killer cells on pokeweed mitogen-induced B cell differentiation. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):651–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer J. N., Sunderland C. A. Immunohistological characterization of lymphoid cell populations in the early human placental bed. Immunology. 1984 Jun;52(2):349–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croy B. A., Gambel P., Rossant J., Wegmann T. G. Characterization of murine decidual natural killer (NK) cells and their relevance to the success of pregnancy. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jul;93(2):315–326. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daya S., Clark D. A., Devlin C., Jarrell J., Chaput A. Suppressor cells in human decidua. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Jan 15;151(2):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(85)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daya S., Clark D. A., Devlin C., Jarrell J. Preliminary characterization of two types of suppressor cells in the human uterus. Fertil Steril. 1985 Dec;44(6):778–785. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)49037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Stocks N., Zoon K., Stanton G. J., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Positive self regulation of cytotoxicity in human natural killer cells by production of interferon upon exposure to influenza and herpes viruses. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1222–1234. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domzig W., Stadler B. M., Herberman R. B. Interleukin 2 dependence of human natural killer (NK) cell activity. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1970–1973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droller M. J., Schneider M. U., Perlmann P. A possible role of prostaglandins in the inhibition of natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor cells. Cell Immunol. 1978 Aug;39(1):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Hercend T., Beveridge R., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of an antigen expressed by human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2947–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearns M., Lala P. K. Characterization of hematogenous cellular constituents of the murine decidua: a surface marker study. J Reprod Immunol. 1985 Nov;8(2-3):213–234. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(85)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Birkby C., Loke Y. W. Early human decidual cells exhibit NK activity against the K562 cell line but not against first trimester trophoblast. Cell Immunol. 1989 Feb;118(2):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Wellings V., Gardner L., Loke Y. W. Immunocytochemical characterization of the unusual large granular lymphocytes in human endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle. Hum Immunol. 1989 Mar;24(3):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(89)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung P., Goldstein G., Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Monoclonal antibodies defining distinctive human T cell surface antigens. Science. 1979 Oct 19;206(4416):347–349. doi: 10.1126/science.314668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Civin C. I., Loken M. R., Phillips J. H. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4480–4486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Phillips J. H., Warner N. L., Babcock G. F. Subpopulations of human natural killer cells defined by expression of the Leu-7 (HNK-1) and Leu-11 (NK-15) antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1789–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Testi R., Bindl J., Phillips J. H. Identity of Leu-19 (CD56) leukocyte differentiation antigen and neural cell adhesion molecule. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2233–2238. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Cytotoxicity of a factor isolated from human spleen. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Feb;50(2):535–538. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.2.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López Bernal A., Hansell D. J., Alexander S., Turnbull A. C. Steroid conversion and prostaglandin production by chorionic and decidual cells in relation to term and preterm labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1987 Nov;94(11):1052–1058. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1987.tb02289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manaseki S., Searle R. F. Natural killer (NK) cell activity of first trimester human decidua. Cell Immunol. 1989 Jun;121(1):166–173. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler A., Lanier L. L., Phillips J. H. The effects of IL-4 on human natural killer cells. A potent regulator of IL-2 activation and proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2349–2351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama E., Asano S., Kodo H., Miwa S. Suppression of mixed lymphocyte reaction by cells of human first trimester pregnancy endometrium. J Reprod Immunol. 1985 Aug;8(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(85)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemlander A., Saksela E., Häyry P. Are "natural killer" cells involved in allograft rejection? Eur J Immunol. 1983 Apr;13(4):348–350. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace D., Morrison L., Bulmer J. N. Proliferative activity in endometrial stromal granulocytes throughout menstrual cycle and early pregnancy. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Jan;42(1):35–39. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson W. G., Grant K. A. Advanced intraligamentous pregnancy. Report of a case, review of the literature and a discussion of the biological implications. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1975 Nov;30(11):715–726. doi: 10.1097/00006254-197511000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Starr S., Abraham S., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte subset reactive with B73.1. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritson A., Bulmer J. N. Isolation and functional studies of granulated lymphocytes in first trimester human decidua. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Aug;77(2):263–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slapsys R. M., Clark D. A. Active suppression of host-vs-graft reaction in pregnant mice. IV. Local suppressor cells in decidua and uterine blood. J Reprod Immunol. 1982 Dec;4(6):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(82)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkey P. M., Sargent I. L., Redman C. W. Cell populations in human early pregnancy decidua: characterization and isolation of large granular lymphocytes by flow cytometry. Immunology. 1988 Sep;65(1):129–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Stadler B. M., Bonnard G. D., Sharrow S. O., Herberman R. B. Cultures of purified human natural killer cells: growth in the presence of interleukin 2. Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 1;72(1):178–185. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90295-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


